Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-UM003K-EN-P - January 2019 259
Homing Chapter 12
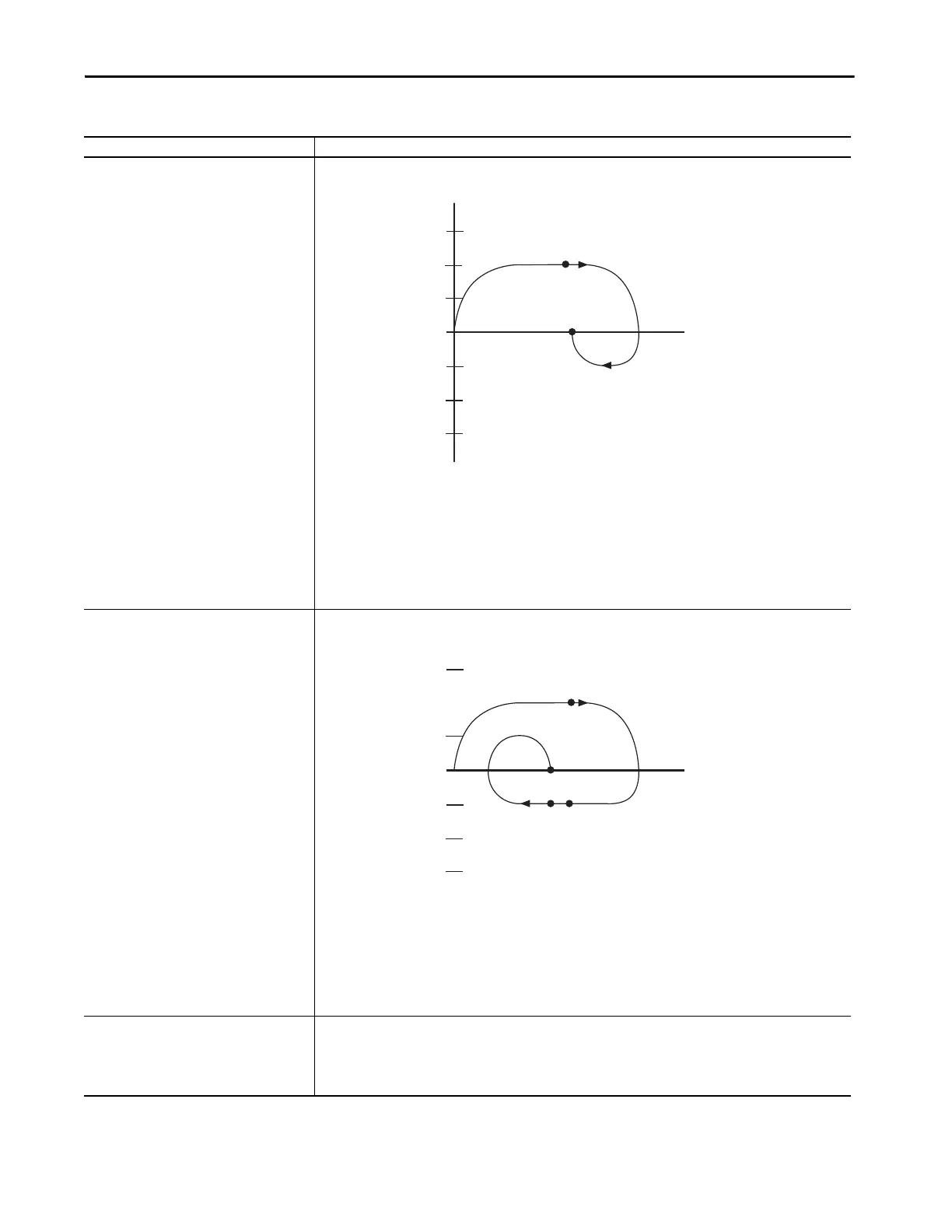
Active home to marker in forward bidirectional The marker homing sequence is useful for single-turn rotary and linear encoder applications because these applications
have one encoder marker only for full axis travel.
These steps occur during the sequence.
1. The axis moves in the Home Direction at the Home Speed to the marker and stops.
2. The axis moves back to the marker or it moves to the Offset position. The axis moves at the Home Return Speed. If the
axis is a Rotary Axis, the move back to the Home Position takes the shortest path (that is, no more than a half
revolution).
The accuracy of this homing sequence depends on the homing speed and the delay to detect the marker transition.
Uncertainty = Home Speed x delay to detect the marker.
Example: Suppose that your Home Speed is 1 in/s and it takes 1 <Symbol>m<Symbol>s to detect the marker.
Uncertainty = 1 In./s x 0.000001 s = 0.000001 in.
Active home to switch and marker in forward
bidirectional
This sequence is the most precise active homing sequence available.
These steps occur during the sequence.
1. The axis moves in the Home Direction at the Home Speed to the home limit switch and stops.
2. The axis reverses direction and moves at the Home Return Speed until it clears the home limit switch.
3. The axis continues to move at the Home Return Speed until it gets to the marker.
4. The axis moves back to the marker or it moves to the Offset position. The axis moves at the Home Return Speed. If the
axis is a Rotary Axis, the move back to the Home Position takes the shortest path (that is, no more than ½ revolution).
If the axis is past the home limit switch at the start of the homing sequence, the axis reverses direction and starts the return
leg of the homing sequence.
Active home to switch in forward unidirectional This active homing sequence is useful for when an encoder marker is not available and either unidirectional motion is
required or proximity switch is being used.
These steps occur during the sequence.
1. The axis moves in the Home Direction at the Home Speed to the home limit switch.
2. If it’s in the same direction as the Home Direction, the axis moves to the Home Offset position.
Table 56 - Active Homing Examples (continued)
Sequence Description
Homing Vel
Return Vel
Axis Position
Axis Velocity
1
2
1: Encoder Marker Detected
2: Home Position
Active Bidirectional Home with Marker
Homing Vel
Return Vel
Axis Position
Axis Velocity
1
2
4
3
1: Home Limit Switch Detected
2: Home Limit Switch Cleared
3: Encoder Marker Detected
4: Home Position
Active Bidirectional Home with Switch then Marker

 Loading...
Loading...











