Measurements (18-0015) AM-48 Test Set
0015-S088-2
intensity of
arbitrary zero reference for noise measurements
1 milliwatt
of power
relative zero
reference can
be established
at any point
-90 -80 -70
-60 -50
-40 -30
-20
-10 0 +10
0
+10
+20
+30 +40
+50
+60
+70
+80 +90
+100
dBrn
dBm
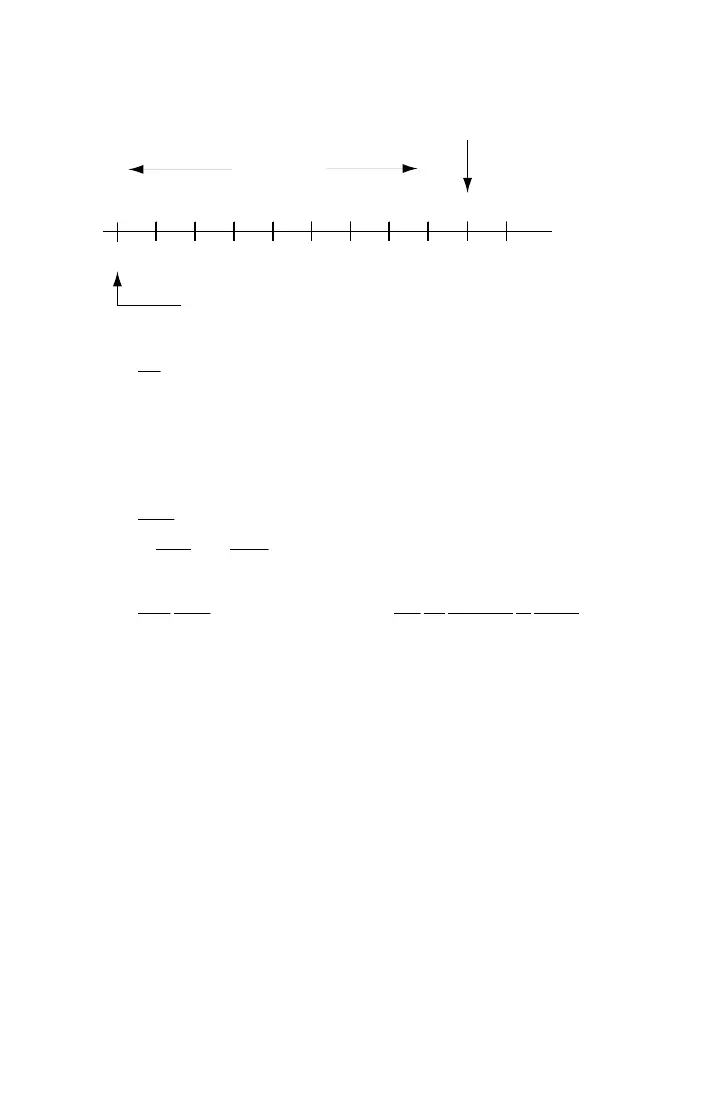
Figure 8-1. Level and Noise Units of Measurement
1.
dB . The decibel (dB) is a logarithmic (base 10) electrical unit
used to compare or indicate changes in level of intensity. The
dB unit is only a unit of intensity, and does not have meaning
unless a point of reference is established. Therefore, the systems
of dBm and dBrn were established as described below.
2.
dBm . To establish a point of reference in making comparisons
in
level (and noise for CCITT standard) measurements in
transmission testing, the system of dBm was adopted.
00.0 dBm is defined as the level of one (1) milliwatt of power ,
hence the abbreviation “m” after the dB. Levels of less intensity
than this reference point are negative (-dBm) values, and levels
of greater intensity are positive (+dBm).
It turns out that 00.0 dBm is a strong level for a telephone line,
so most level measurements in units of dBm are negative, i.e.,
less intense than 00.0 dBm reference. For example, -10.0 dBm
is a typical level at which dialing tones are sent.
 Loading...
Loading...