Chapter 1 Get Started
About Standard Curve Experiments
Applied Biosystems 7500/7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System Getting Started Guide for Standard Curve
Experiments
8
Notes
PCR Options
When performing real-time PCR, select between:
• Singleplex and multiplex PCR (below)
and
• 1-step and 2-step RT-PCR (page 8)
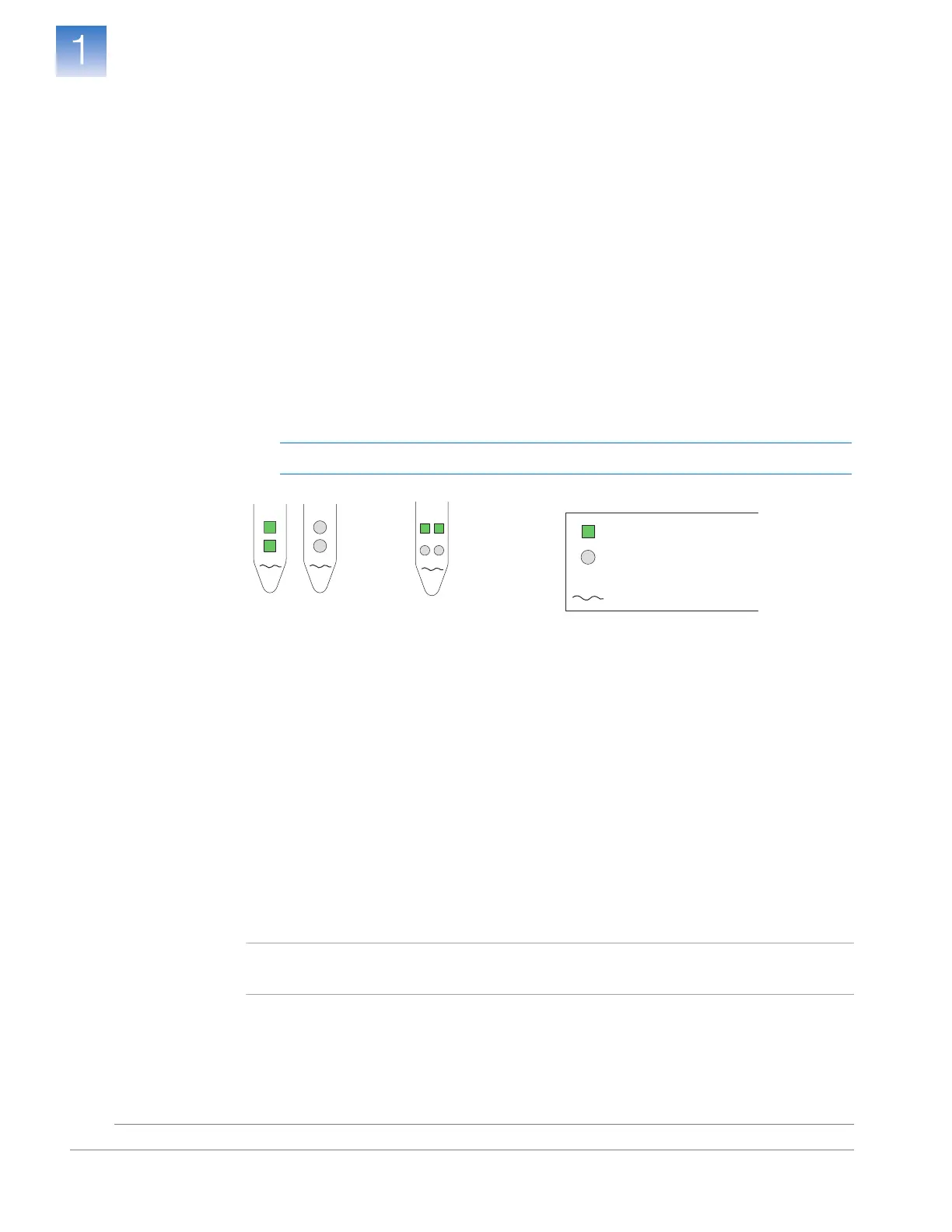
Singleplex vs. Multiplex PCR
You can perform a PCR reaction using either:
• Singleplex PCR – In singleplex PCR a single primer set is present in the reaction
tube or well. Only one target or endogenous control can be amplified per reaction.
or
• Multiplex PCR – In multiplex PCR, two or more primer sets are present in the
reaction tube or well. Each set amplifies a specific target or endogenous control.
Typically, a probe labeled with FAM
™
dye detects the target and a probe labeled
with VIC
®
dye detects the endogenous control.
IMPORTANT! SYBR
®
Green reagents cannot be used for multiplex PCR.
1- vs. 2-Step RT-PCR
You can perform reverse transcription (RT) and PCR in a single reaction (1-step) or in
separate reactions (2-step). The reagent configuration you use depends on whether you
are performing 1- or 2-step RT-PCR:
• In 1-step RT-PCR, RT and PCR take place in one buffer system, which provides the
convenience of a single-tube preparation for RT and PCR amplification. However,
you cannot use Fast PCR master mix or the carryover prevention enzyme,
AmpErase
®
UNG (uracil-N-glycosylase), to perform 1-step RT-PCR.
• 2-step RT-PCR is performed in two separate reactions: First, total RNA is reverse-
transcribed into cDNA, then the cDNA is amplified by PCR. This method is useful
for detecting multiple transcripts from a single cDNA template or for storing cDNA
aliquots for later use. The AmpErase
®
UNG enzyme can be used to prevent
carryover contamination.
Note: For more information on AmpErase
®
UNG, refer to the Applied Biosystems Real-
Time PCR Systems Reagent Guide.
GR2331
Target Primer Set
Endogenous Control
Primer Set
cDNA
Singleplex PCR
Multiplex PCR

 Loading...
Loading...