11
8126F–AVR–05/12
ATtiny13A
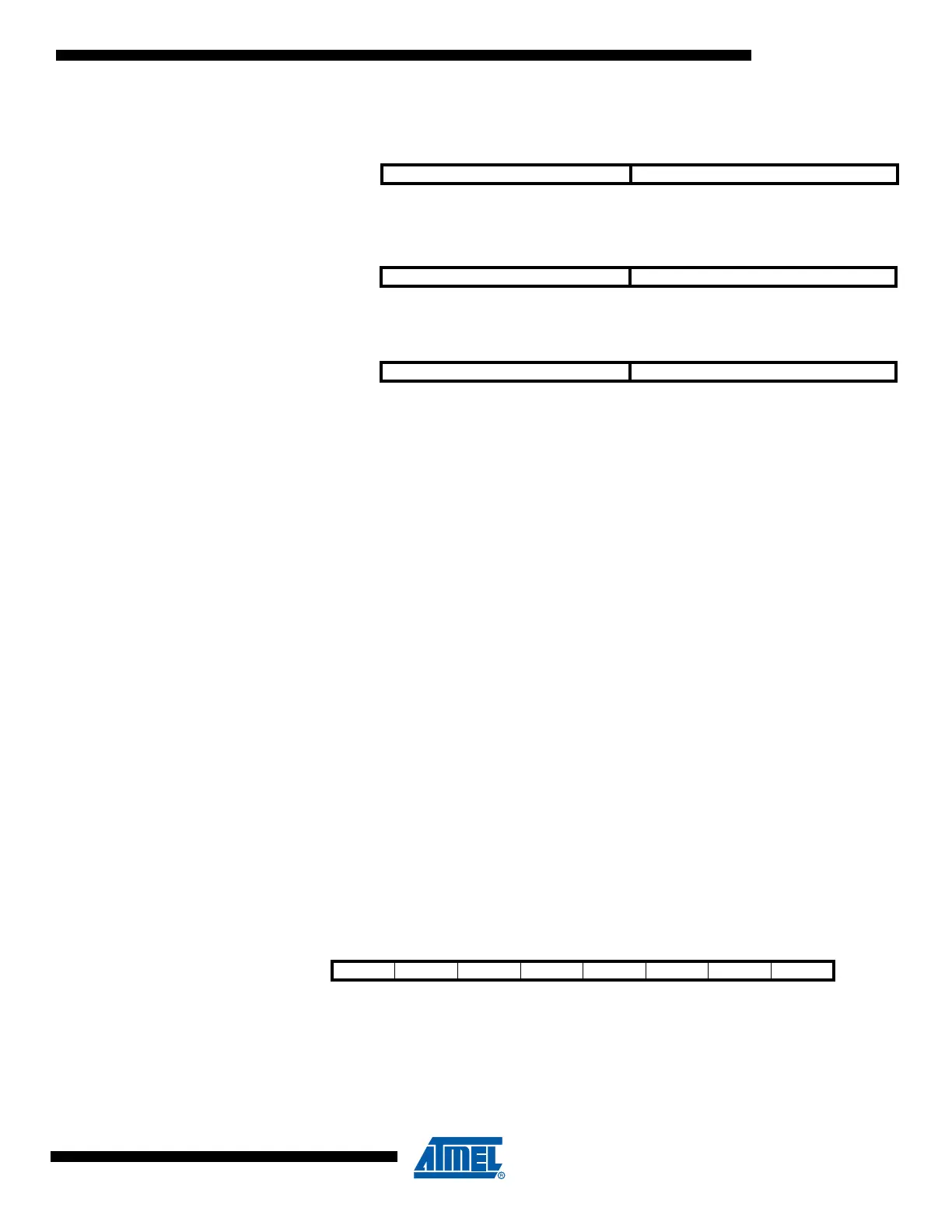
Figure 4-3. The X-, Y-, and Z-registers
In the different addressing modes these address registers have functions as fixed displacement,
automatic increment, and automatic decrement (see the instruction set reference for details).
4.5 Stack Pointer
The Stack is mainly used for storing temporary data, for storing local variables and for storing
return addresses after interrupts and subroutine calls. The Stack Pointer Register always points
to the top of the Stack. Note that the Stack is implemented as growing from higher memory loca-
tions to lower memory locations. This implies that a Stack PUSH command decreases the Stack
Pointer.
The Stack Pointer points to the data SRAM Stack area where the Subroutine and Interrupt
Stacks are located. This Stack space in the data SRAM is automaticall defined to the last
address in SRAM during power on reset. The Stack Pointer must be set to point above 0x60.
The Stack Pointer is decremented by one when data is pushed onto the Stack with the PUSH
instruction, and it is decremented by two when the return address is pushed onto the Stack with
subroutine call or interrupt. The Stack Pointer is incremented by one when data is popped from
the Stack with the POP instruction, and it is incremented by two when data is popped from the
Stack with return from subroutine RET or return from interrupt RETI.
The AVR Stack Pointer is implemented as two 8-bit registers in the I/O space. The number of
bits actually used is implementation dependent. Note that the data space in some implementa-
tions of the AVR architecture is so small that only SPL is needed. In this case, the SPH Register
will not be present.
4.5.1 SPL – Stack Pointer Low
15 XH XL 0
X-register 707 0
R27 (0x1B) R26 (0x1A)
15 YH YL 0
Y-register 707 0
R29 (0x1D) R28 (0x1C)
15 ZH ZL 0
Z-register 7070
R31 (0x1F) R30 (0x1E)
Bit 76543210
0x3D SP7 SP6 SP5 SP4 SP3 SP2 SP1 SP0 SPL
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial Value10011111

 Loading...
Loading...