3-10
u To find the minimum value in a list [OPTN] - [LIST] - [Min]
K1(LIST) 6( g) 1(Min) 6( g) 6( g) 1(List) <list number 1 - 26> )w
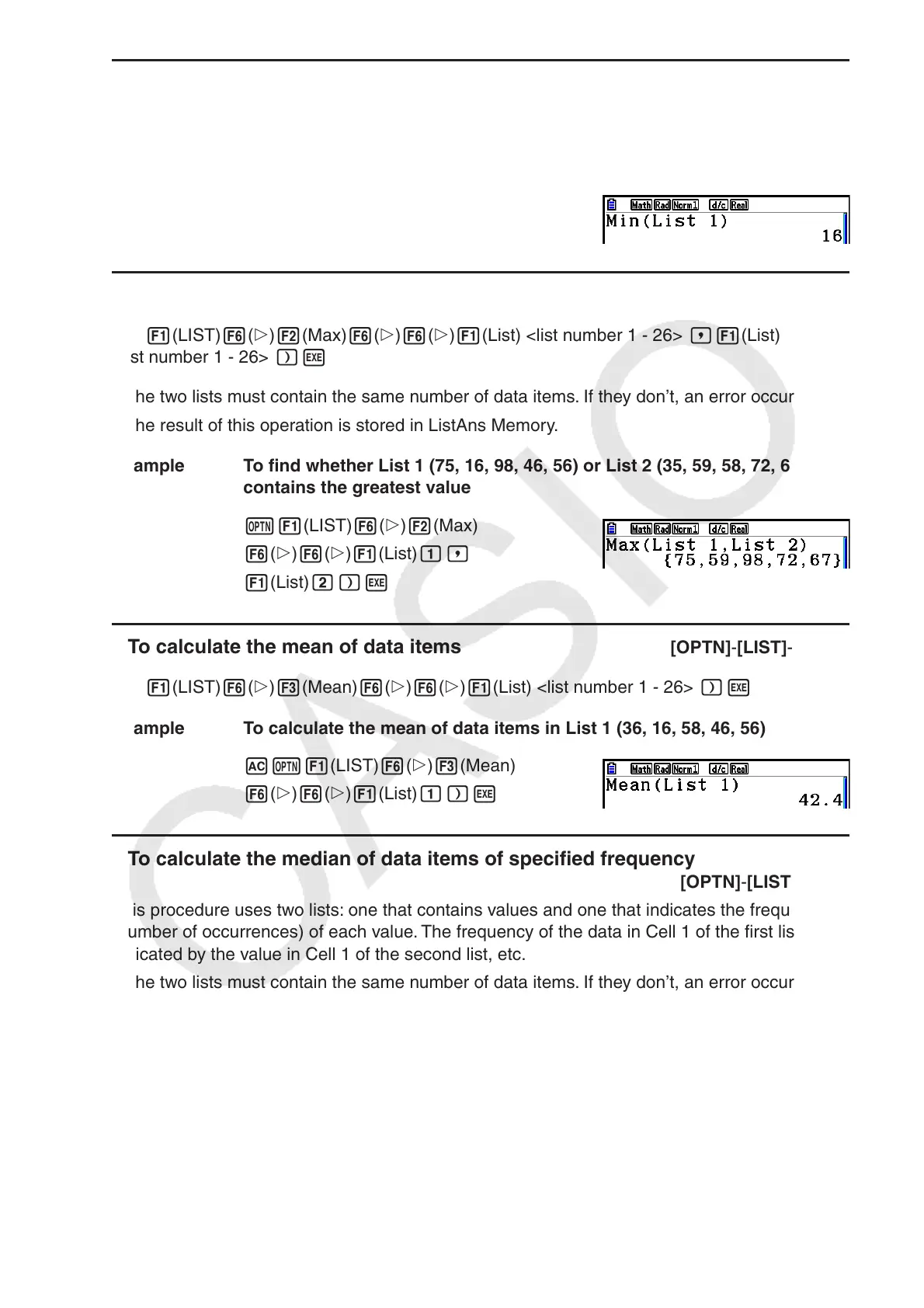
Example To find the minimum value in List 1 (36, 16, 58, 46, 56)
AK1(LIST) 6( g) 1(Min)
6( g) 6( g) 1(List) b)w
u To find which of two lists contains the greatest value [OPTN] - [LIST] - [Max]
K1(LIST) 6( g) 2(Max) 6( g) 6( g) 1(List) <list number 1 - 26> ,1(List)
<list number 1 - 26> )w
• The two lists must contain the same number of data items. If they don’t, an error occurs.
• The result of this operation is stored in ListAns Memory.
Example To find whether List 1 (75, 16, 98, 46, 56) or List 2 (35, 59, 58, 72, 67)
contains the greatest value
K1(LIST) 6( g) 2(Max)
6( g) 6( g) 1(List) b,
1(List) c)w
u To calculate the mean of data items [OPTN] - [LIST] - [Mean]
K1(LIST) 6( g) 3(Mean) 6( g) 6( g) 1(List) <list number 1 - 26> )w
Example To calculate the mean of data items in List 1 (36, 16, 58, 46, 56)
AK1(LIST) 6( g) 3(Mean)
6( g) 6( g) 1(List) b)w
u To calculate the median of data items of specified frequency
[OPTN] - [LIST] - [Med]
This procedure uses two lists: one that contains values and one that indicates the frequency
(number of occurrences) of each value. The frequency of the data in Cell 1 of the first list is
indicated by the value in Cell 1 of the second list, etc.
• The two lists must contain the same number of data items. If they don’t, an error occurs.
K1(LIST) 6( g) 4(Med) 6( g) 6( g) 1(List) <list number 1 - 26 (data)> ,1(List)
<list number 1 - 26 (frequency)> )w
 Loading...
Loading...











