1-13
4. Using the Math Input/Output Mode
Selecting “Math” for the “Input/Output” mode setting on the Setup screen (page 1-32) turns on
the Math input/output mode, which allows natural input and display of certain functions, just as
they appear in your textbook.
• The operations in this section all are performed in the Math input/output mode. The initial
default setting for this calculator is the Math input/output mode. If you have changed to the
Linear input/output mode, switch back to the Math input/output mode before performing the
operations in this section. See “Using the Setup Screen” (page 1-32) for information about
how to switch modes.
• In the Math input/output mode, all input is insert mode (not overwrite mode) input. Note that
the !D(INS) operation (page 1-7) you use in the Linear input/output mode to switch to
insert mode input performs a completely different function in the Math input/output mode. For
more information, see “Using Values and Expressions as Arguments” (page 1-17).
• Unless specifically stated otherwise, all operations in this section are performed in the
Run-Matrix mode.
k Input Operations in the Math Input/Output Mode
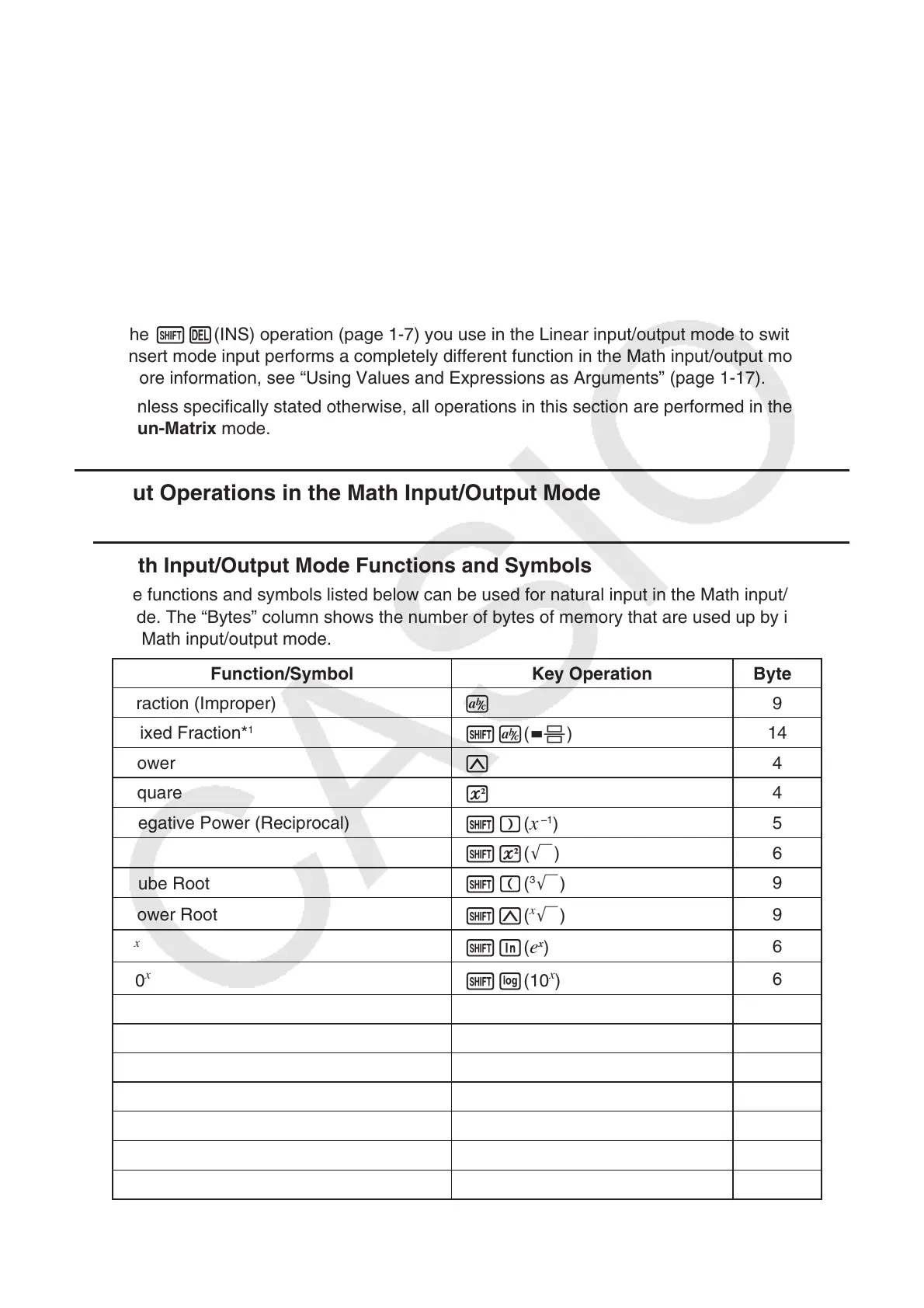
u Math Input/Output Mode Functions and Symbols
The functions and symbols listed below can be used for natural input in the Math input/output
mode. The “Bytes” column shows the number of bytes of memory that are used up by input in
the Math input/output mode.
Function/Symbol Key Operation Bytes
Fraction (Improper)
v
9
Mixed Fraction*
1
!v( & )
14
Power
M
4
Square
x
4
Negative Power (Reciprocal)
!)(
x
–1
)
5
'
!x( ')
6
Cube Root
!((
3
')
9
Power Root
!M(
x
')
9
e
x
!I( e
x
)
6
10
x
!l(10
x
)
6
log(a,b) (Input from MATH menu*
2
) 7
Abs (Absolute Value) (Input from MATH menu*
2
) 6
First Derivative (Input from MATH menu*
2
) 7
Second Derivative (Input from MATH menu*
2
) 7
Integral*
3
(Input from MATH menu*
2
) 8
Σ Calculation*
4
(Input from MATH menu*
2
) 11
Matrix (Input from MATH menu*
2
) 14*
5
 Loading...
Loading...











