9-34
6. Spreadsheet
Mode Memory
You can use the calculator’s different types of memory (variables, list memory, file memory,
matrix memory) to store data, and recall data from a memory into the spreadsheet.
k Saving Spreadsheet Data to a Memory
The following table shows an overview of the store operations for each type of memory. For
details about each operation, see the example operations following the table.
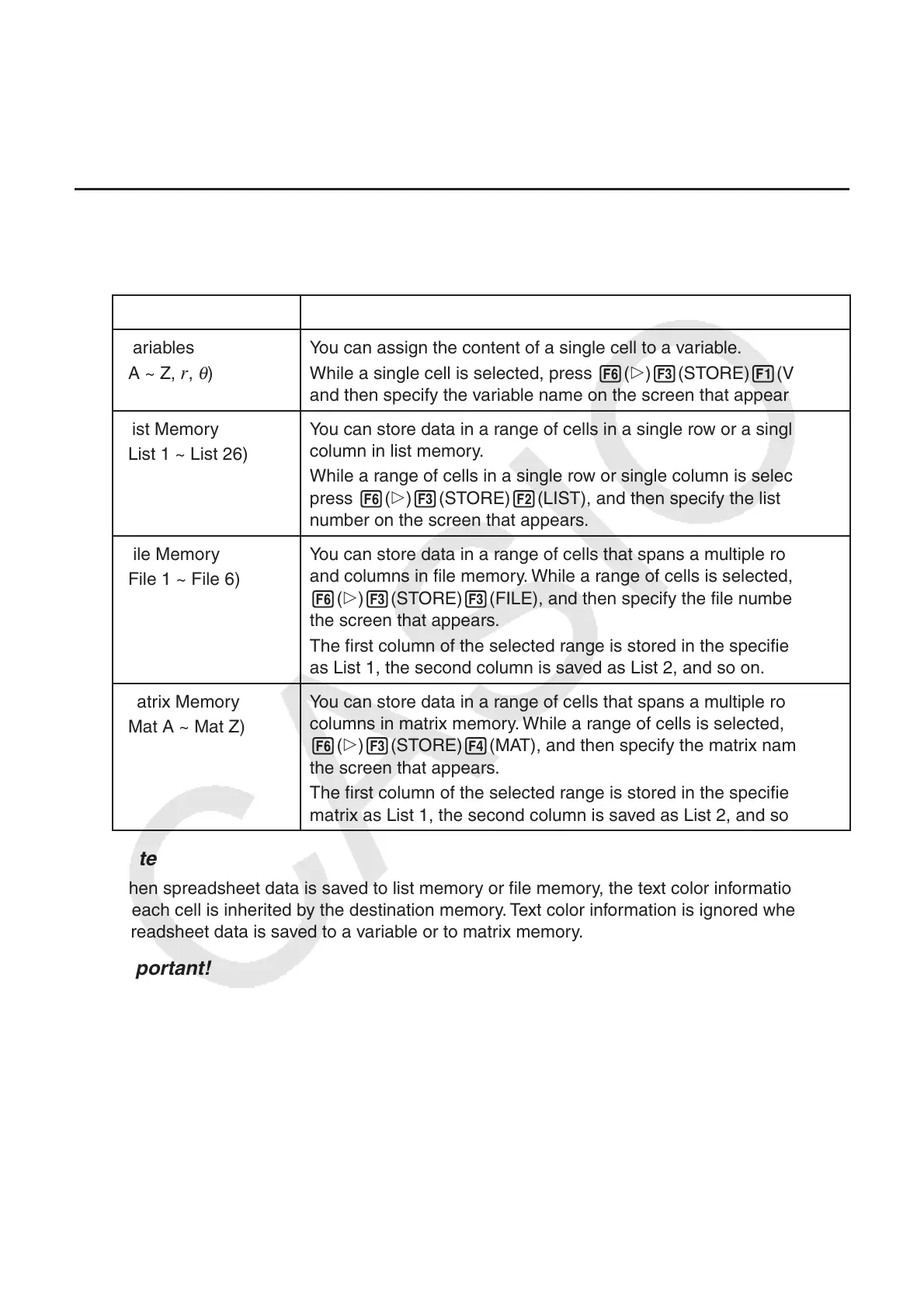
Memory Type Store Operation
Variables
(A ~ Z,
r ,
θ
)
You can assign the content of a single cell to a variable.
While a single cell is selected, press 6( g) 3(STORE) 1(VAR),
and then specify the variable name on the screen that appears.
List Memory
(List 1 ~ List 26)
You can store data in a range of cells in a single row or a single
column in list memory.
While a range of cells in a single row or single column is selected,
press 6( g) 3(STORE) 2(LIST), and then specify the list
number on the screen that appears.
File Memory
(File 1 ~ File 6)
You can store data in a range of cells that spans a multiple rows
and columns in file memory. While a range of cells is selected, press
6( g) 3(STORE) 3(FILE), and then specify the file number on
the screen that appears.
The first column of the selected range is stored in the specified file
as List 1, the second column is saved as List 2, and so on.
Matrix Memory
(Mat A ~ Mat Z)
You can store data in a range of cells that spans a multiple rows and
columns in matrix memory. While a range of cells is selected, press
6( g) 3(STORE) 4(MAT), and then specify the matrix name on
the screen that appears.
The first column of the selected range is stored in the specified
matrix as List 1, the second column is saved as List 2, and so on.
Note
When spreadsheet data is saved to list memory or file memory, the text color information
of each cell is inherited by the destination memory. Text color information is ignored when
spreadsheet data is saved to a variable or to matrix memory.
Important!
The following describes what happens if you try to store data in memory when a cell does not
contain any data, when a cell contains text, or when ERROR is displayed for a cell.
• If you are assigning data to a variable, an error occurs.
• If you are storing data in list memory, file memory, or matrix memory, 0 is written into the
applicable cell(s).
 Loading...
Loading...











