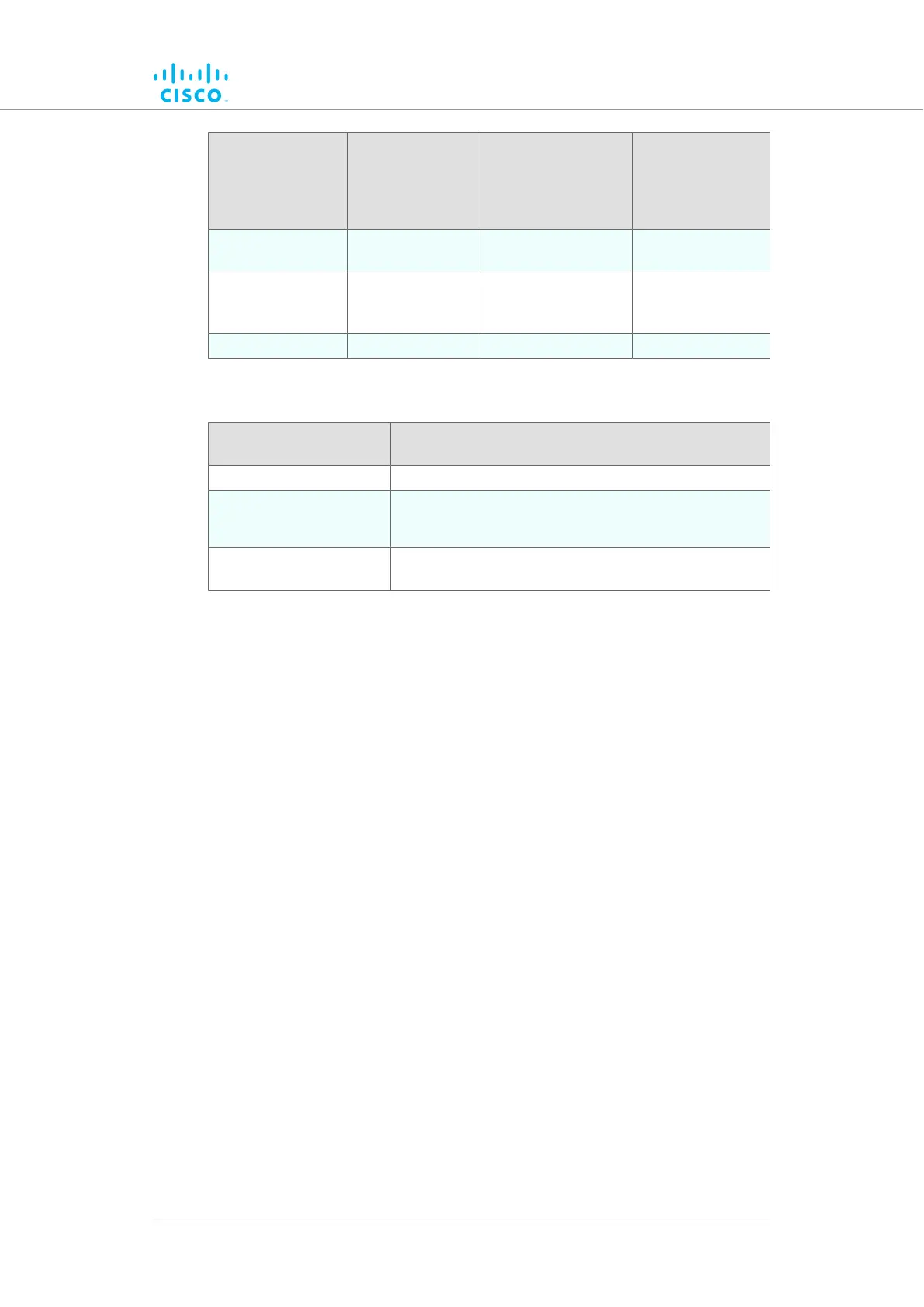
Unit series Minimum power
consumption
Nominal power
consumption
(typical conditions)
Maximum power
consumption
(realistic system-
design
assumption)
FM3500 Endo
(Model FM3500)
8 Watts 10 to 12 Watts 15 Watts
FM4500-series
(Models FM4500F
and FM4500)
8 Watts 10 to 12 Watts 15 Watts
FM 4800 Fiber 13 Watts 15 to 17 Watts 20 Watts
Table 2. Power consumption figures (gateway units)
Unit Maximum power consumption (realistic system-
design assumption)
FM1000 Gateway 60 Watts
FM10000 Gateway
(Gen. 1)
275 Watts (redundant AC power supply)
250 Watts (non-redundant AC power supply)
FM10000 Gateway
(Gen. 2)
300 Watts (redundant AC power supply)
3.2. Cisco architecture
3.2.1. Overview
Wireless network architectures
Depending on the network design and the type of components used, the
Cisco FM4200 Fiber can be used to create wireless network architectures,
including:
• Point-to-point (P2P) links.
• Point-to-multipoint (PTMP) sectors.
• Mesh networks.
• Mobility networks.
• Mixed networks that are capable of using any combination of types
listed above.
The FluidMAX TDMA protocol
Individual radio transceivers can easily be assigned different roles within
the same network, using Cisco's patented FluidMAX™ technology. A
typical example of a general network architecture that uses a combination
of Cisco components is shown below:
Getting Started
© 2021 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Page 16 of 189

 Loading...
Loading...