FC 300 Design Guide
How to Install
" Use of EMC-Correct Cables
Danfoss recommends braided shielded/armored cables to optimize EMC immunity of the
control cables a nd the EMC emission from the motor cables.
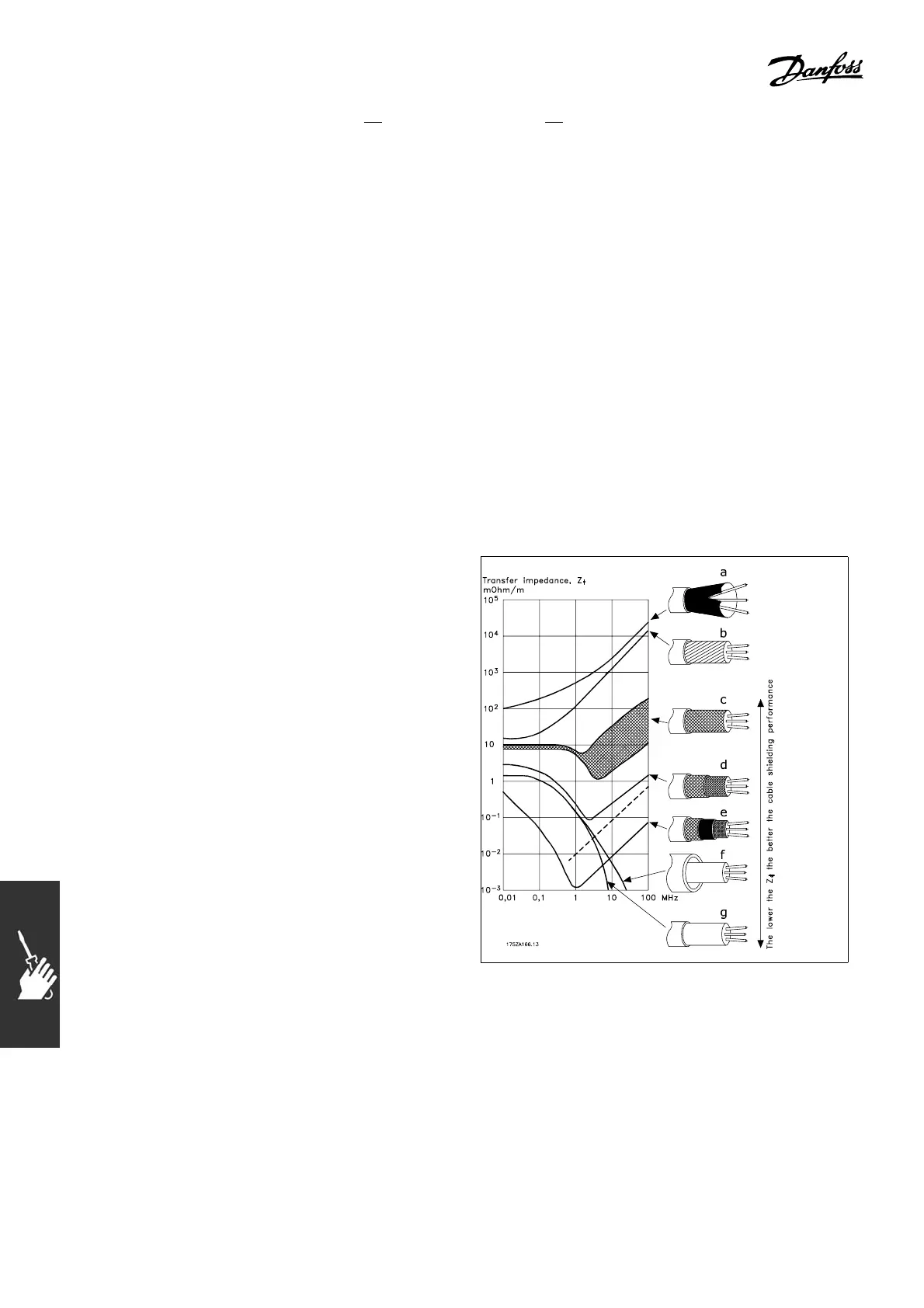
The ability of a cable to reduce the incoming and outgoing radiation of electric noise depends
on the transfer impedance (Z
T
). The shield of a cable is normally designed to reduce the
transfer of electric noise; however, a shield with a lower transfer impedance (Z
T
)valueismore
effective than a shield with a higher transfer imped ance (Z
T
).
Transfer impedance (Z
T
) is rarely stated by cable ma nufacturers but it is o ften possible to estimate
transfer impedance (Z
T
) by assessing th e physical design o f the cable.
Transfer impedance (Z
T
) ca n be assessed on the basis of the following factors:
- The conductibility of the shield material.
- The contact resistance between the individual shield conductors.
- The shield coverage, i.e. the physical a rea of the cable covered by the shield -
often stated as a percentage value.
- Shield type, i.e. b raided or twisted pattern.
a. Aluminum-clad with copper wire.
b. Twisted copper wire or armored steel wire cable.
c. Single-layer braided copp er wire with varying
percentage shield coverage.
This is the typical Danfoss reference ca ble.
d. Double-layer braided copper wire.
e. Twin layer of braided cop per wire with a
magnetic, shielded/armore d intermediate layer.
f. Cable that runs in copper tube or steel tube.
g. Lead cable with 0.043 in. (1.1 mm )
wall thickness .
108
MG.33.B3.22 - VLT is a registered Danfoss trademark

 Loading...
Loading...



















