SECTION 5 MAINTENANCE
Page 38
OM560C99/1E DRESSTA
ENGINE
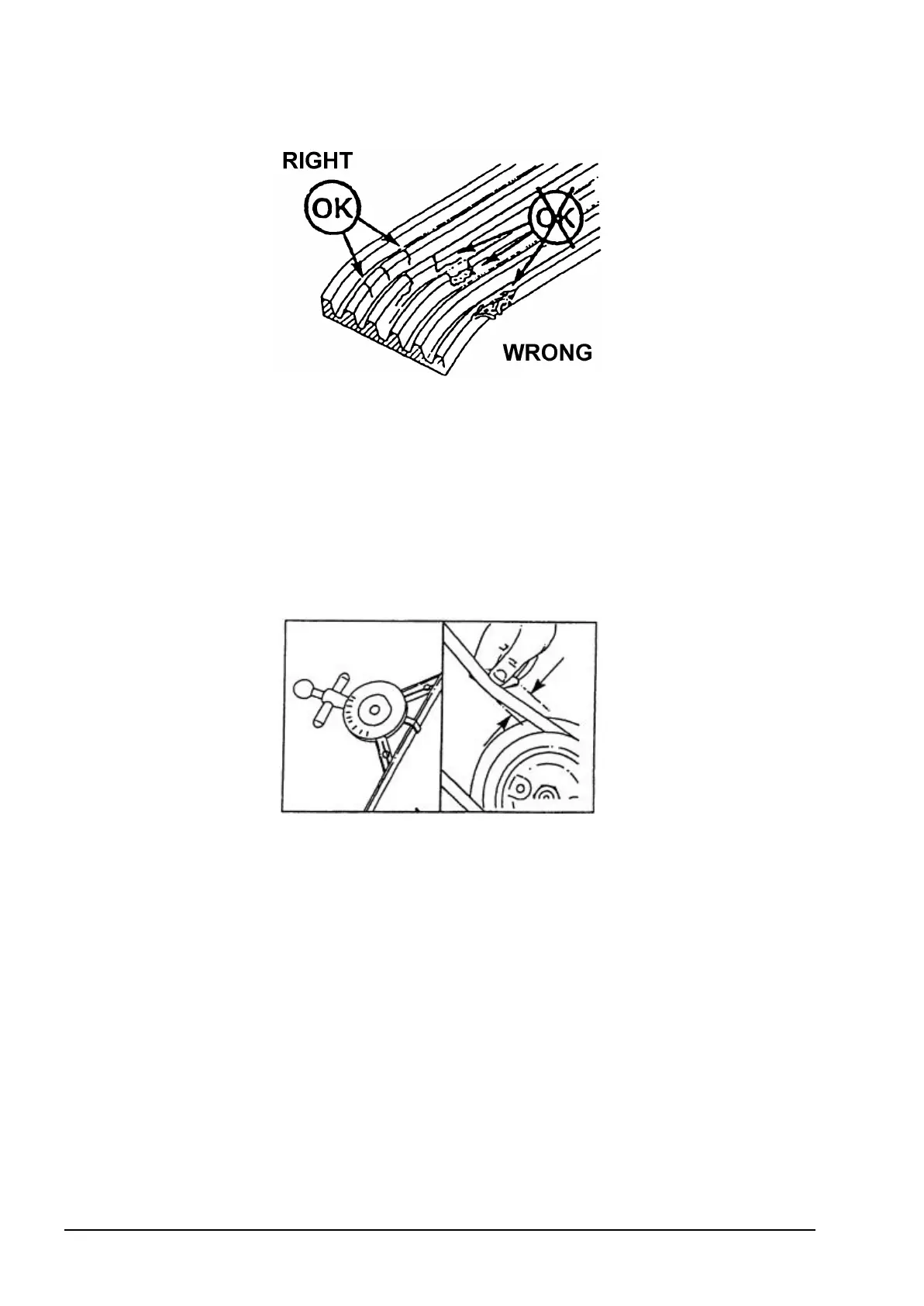
Fig. 5.36. Belt Inspection
Belt damage may occur due to:
− improper tension,
− improper installation,
− severe operating conditions,
− contamination with oil or grease.
CHECKING THE TENSION
Check the bet tension midway at the longest span between the pulleys using a tension gauge.
Fig. 5.37. Checking Belt Tension
Refer to Engine Operation Manual for the type of a tension gauge as well as the tension values for
various belt widths.
For QSK 19-C (5-groove belt) these values are as follows: a new belt tension 670 N, retension 270
to 530 N.
For KT 19-C (15-groove belt) those values are as follows: a new belt tension 1670 N, retension 670
to 1340 N.
A belt is considered used when operated at least 10 minutes.
Alternately belt tension may be checked by pressing the belt midway between pulleys as shown in
Fig. 5.37. Deflection under a force of 110 N should nor exceed belt thickness at a 30 cm distance
between the pulleys. Adjust the belt if deflection exceeds the above value. New belts loose their
tension during operation.
 Loading...
Loading...