EPSON Stylus CX4100/CX4200/CX4700/CX4800/DX4200/DX4800/DX4850 Revision A
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Printer Mechanism 63
Ink Cavity
The ink absorbed from the Ink Cartridge goes through the filter and then is stored
temporarily in this tank called “ink cavity” until PZT is driven.
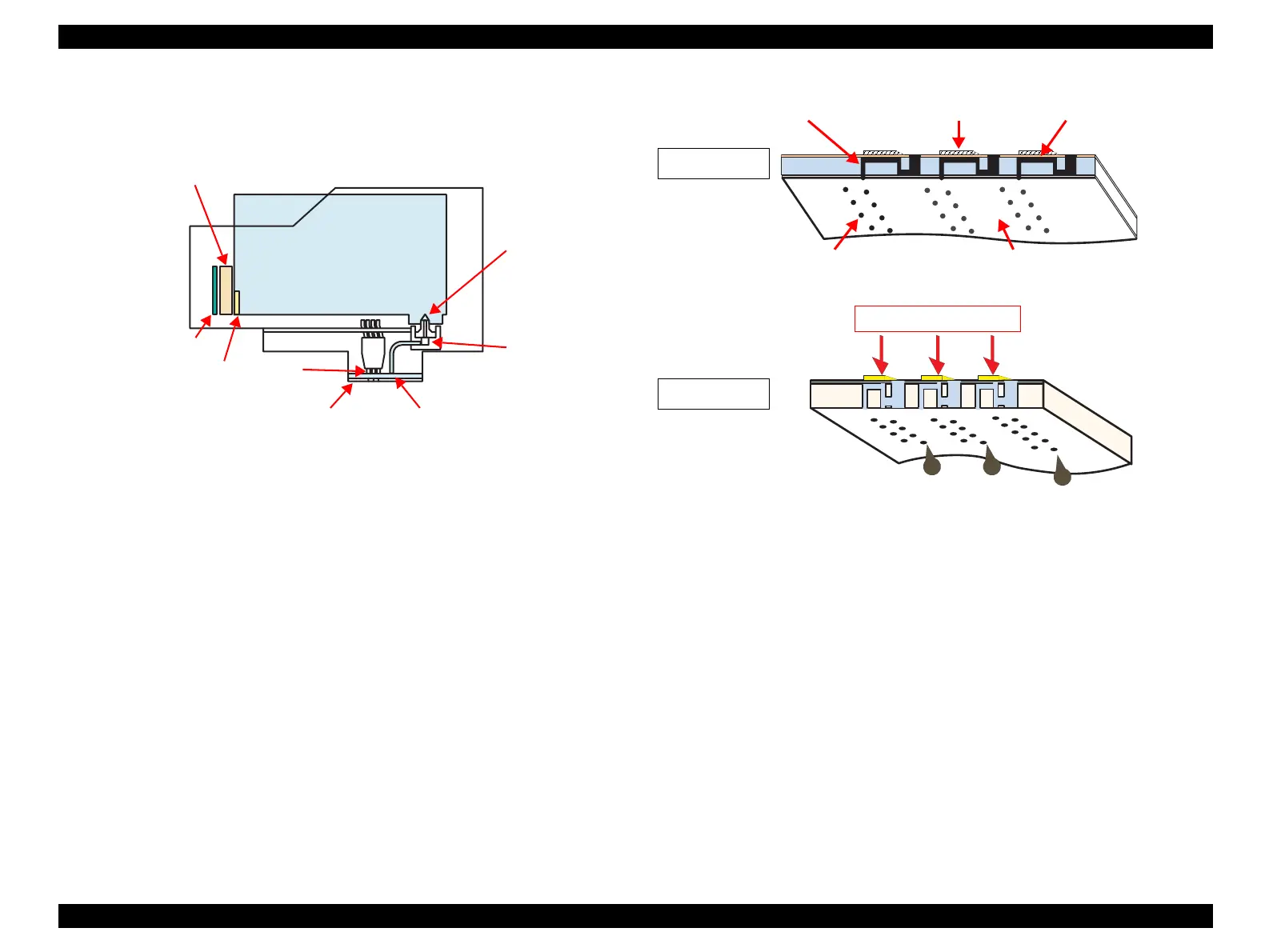
Figure 2-3. Printhead sectional drawing
2.2.2.1 Printing Process
This section explains the process which the Printheads of On-Demand inkjet printers
eject ink from each nozzle.
1. Normal state:
When the printing signal is not output from the Main Board (C610 Main), or the
PZT drive voltage is not applied, the PZT does not change the shape. Therefore,
the PZT does not push the ink cavity. The ink pressure inside the ink cavity is kept
normal. (refer to Figure 2-4 (p.63): Normal state)
2. Ejecting state:
When the print signal is output from Main Board (C610 Main), the nozzle selector
IC located on the Print Head latches the data once by 1-byte unit. Based on the
drive waveform (common voltage) generated on the Main Board, the PZT selected
by the nozzle selector IC pushes the top of the ink cavity. By this operation, the ink
stored in the ink cavity is ejected from nozzles. (refer to Figure 2-4 (p.63):
Ejecting state)
Figure 2-4. Print Head printing process
2.2.2.2 Printing Method
The dot printing systems of Stylus CX4100/CX4200/CX4700/CX4800/DX4200/
DX4800/DX4850 are variable dot printing systems.
Variable dot printing
This printing mode is developed to improve the print quality on exclusive paper.
This mode is basically the same as variable dot printing mode used on other
products; micro dot, middle dot and large dot compose this mode. The printing dot
size varies according to the print data and this mode enables to output even sharper
image on exclusive paper.
Nozzle selector board
Needle
Ink cartridge
Cavity
PZT
Nozzle plate
CSIC Memory chip
Electric poles for CSIC
*Head ID for the Print Head is
stored to the EEPROM.
Filter
Ink path PZT Ink cavity
Nozzle Nozzle plate
PZT drive voltage
Normal state
Ejecting state

 Loading...
Loading...