Calibrator
Theory of Operation
13
PF Adder Watts Adder for PF = 0.5 (Φ=60) at 50 Hz is 0.76 % (see “Phase Specifications”).
Total Watts Output Specification =
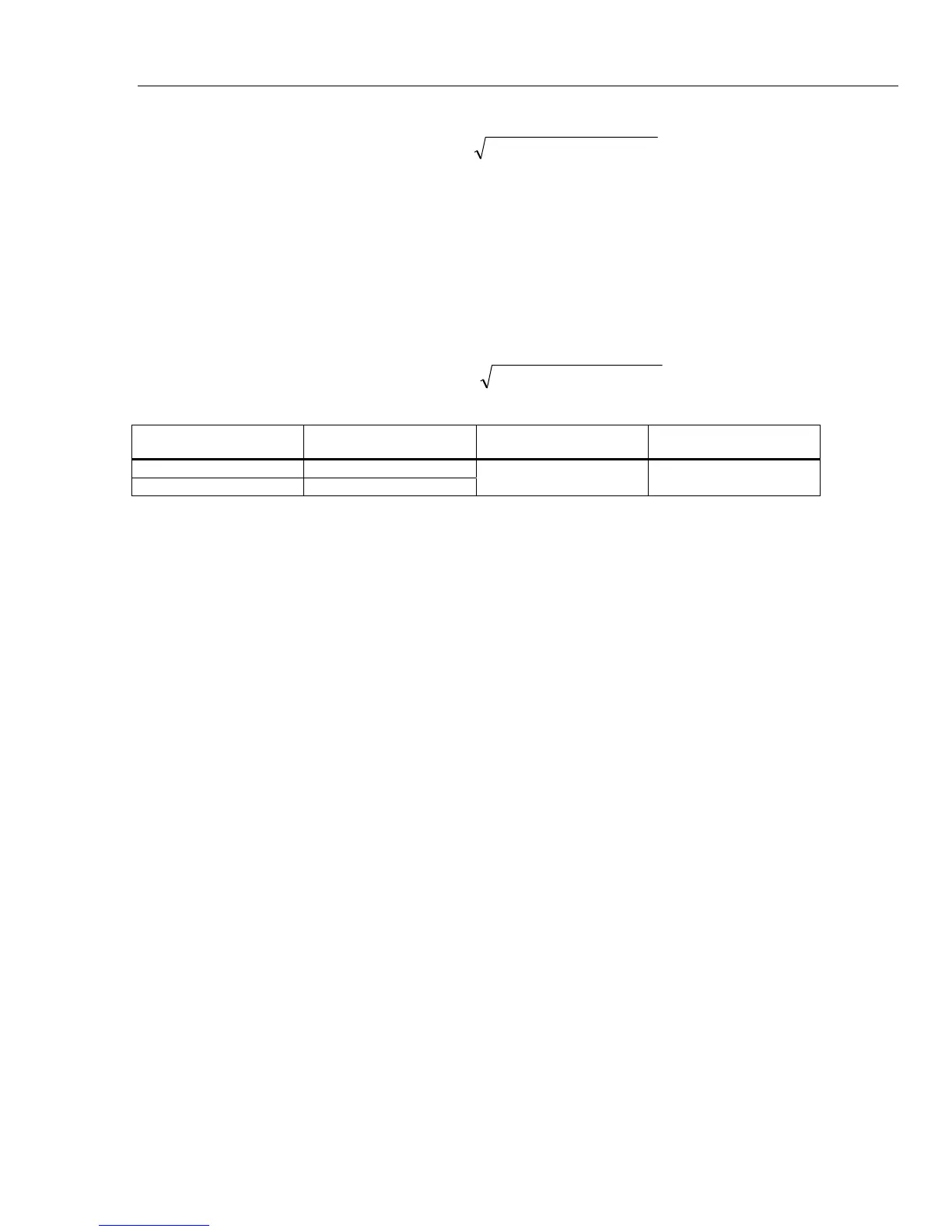
%81.076.022.0158.0
22
power
=++=
2
Spec
VARs When the Power Factor approaches 0.0, the watts output specification becomes unrealistic because the dominant
characteristic is the VARs (volts-amps-reactive) output. In these cases, calculate the Total VARs Output Specification, as
shown in example 3:
Example 3 Output: 100 V, 1 A, 400 Hz, Power Factor = 0.174 (Φ=80), 1-year specifications
Voltage Specification Specification for 100 V at 400 Hz is, 0.15 % + 18 mV, totaling:
100 V x 0.0015 = 150 mV added to 18 mV = 168 mV. Expressed in percent:
168 mV/100 V x 100 = 0.168 % (see “AC Voltage Specifications”).
Current Specification Specification for 1 A at 400 Hz is 0.24 % + 1200 μA, totaling:
1 A x 0.0024 = 2400 μA added to 1200 μA = 3.6 mA. Expressed in percent:
3.6 mA/1 A x 100 = 0.36 % (see “AC Current Specifications”).
VARs Adder VARs Adder for Φ = 80 at 400 Hz is 0.50 % (see “Phase Specifications”).
Total VARS Output Specification =
%64.05.036.0168.0=
22
VARs
=++
2
Spec
Frequency
Frequency Range Resolution
Specification,
1 year, tcal ±5 °C
Jitter
45.00 to 119.99 Hz 0.01 Hz
0.0050 % ±2 mHz 4 μs
120.0 to 1000.0 Hz 0.1 Hz
Theory of Operation
This section gives a description of the analog and digital sections of the Product
at a block diagram level. Figure 1 shows the assemblies loaded into the Product.
The Product outputs:
• DC voltage from 0 V to ±1020 V.
• AC voltage from 1 mV to 1020 V, with output from 45 Hz to 1 kHz.
• AC current from 29 μA to 20.5 A, with variable frequency limits.
• DC current from 0 to ±20.5 A.
• Discrete resistance values from a short circuit to 190 MΩ.
• Simultaneous voltage and current, up to an equivalent of 20.9 kVA.
• Two simultaneous voltages
• Variable phase signal
 Loading...
Loading...