59
EN
the next time they are changed. This applies even if the power source is switched off
and on again in the meantime.
Start welding
HotStart function To obtain optimum welding results, it will sometimes be necessary to adjust the HotStart
function.
Benefits
- Improved ignition, even when using electrodes with poor ignition properties
- Better fusion of the base material in the start-up phase, meaning fewer cold-shut de-
fects
- Largely prevents slag inclusions
See the "Setup menu: level 2" section for details on setting the available welding parame-
ters.
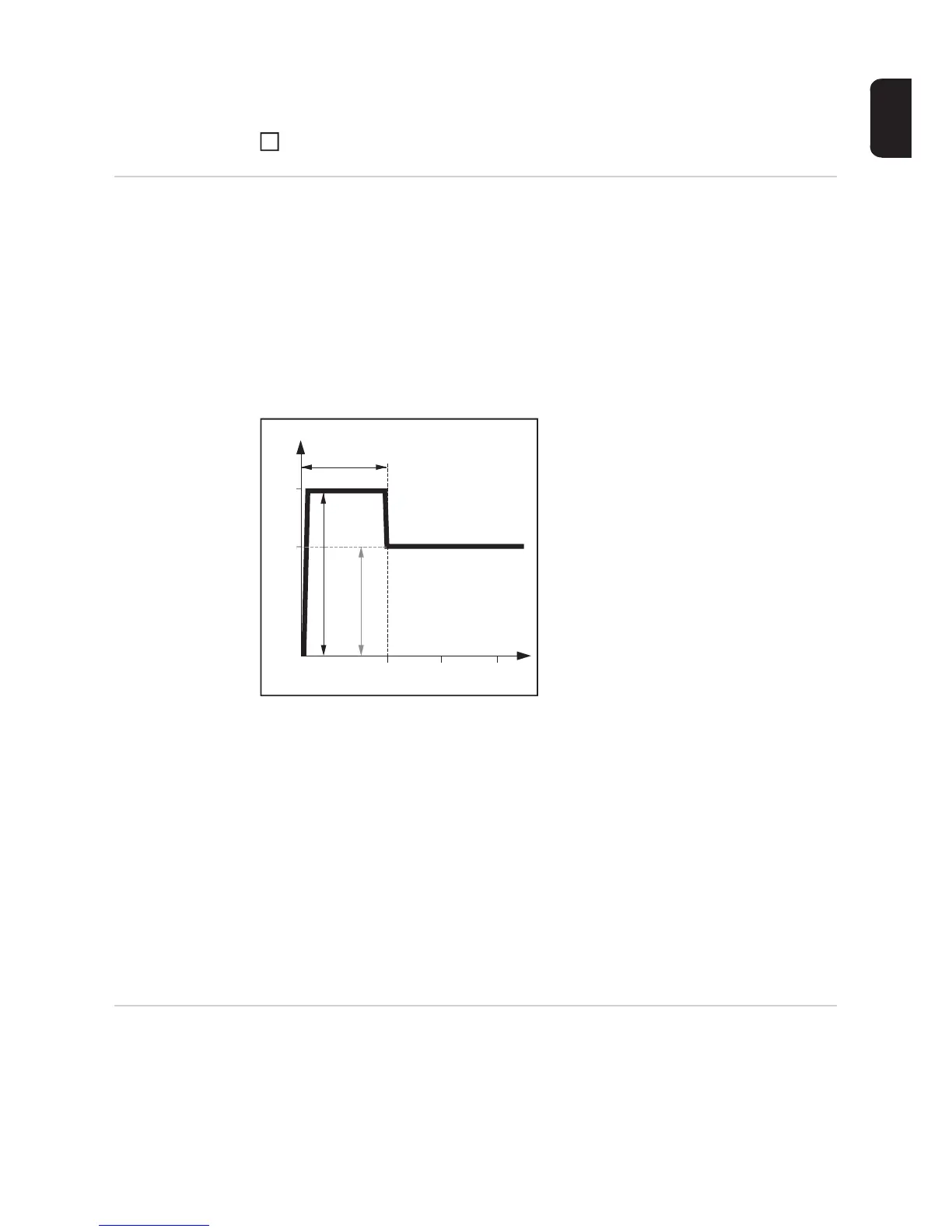
Example of HotStart function
Function:
during the specified hot-current time (Hti),
the welding current I
1
is increased to the
Hotstart current HCU.
To activate the HotStart function, the Hot-
start current HCU must be > 100.
Setting examples:
HCU = 100
The HotStart current is adequate to the actually set welding current I
1
.
The HotStart function is not activated.
HCU = 170
The HotStart current is 70 % higher then the actually set welding current I
1
.
The HotStart function is activated.
HCU = 200
The HotStart current is adequate twice the actually set welding current I
1
.
The HotStart function is activated, the HotStart current is at its maximum.
HCU = 2 x I
1
Anti-stick func-
tion
As the arc becomes shorter, the welding voltage may drop so far that the rod electrode will
tend to stick. This may also cause the rod electrode to burn out.
Electrode burn-out is prevented by activating the anti-stick function. If the rod electrode be-
gins to stick, the power source immediately switches the welding current off. After the rod
electrode has been detached from the workpiece, the welding process can be continued
without any problems.
3
I (A)
t (s)
0,5 1 1,5
Hti
I
1
HCU
100
150
Legend
Hti Hot-current time, 0-2 s,
factory setting: 0.5 s
HCU HotStart current, 0-200 %,
factory setting 150 %
I
1
Main current = set welding current

 Loading...
Loading...











