G-6
V/f control
The rotating speed N (r/min) of a motor can be stated
in an expression as
)s1(
p
f120
N u
u
where,
f: Output frequency
p: Number of poles
s: Slippage
On the basis of this expression, varying the output
frequency varies the speed of the motor. However,
simply varying the output frequency f (Hz) would
result in an overheated motor or would not allow the
motor to demonstrate its optimum utility if the output
voltage V (V) remains constant. For this reason, the
output voltage V must be varied with the output
frequency f by using an inverter. This scheme of
control is called V/f control.
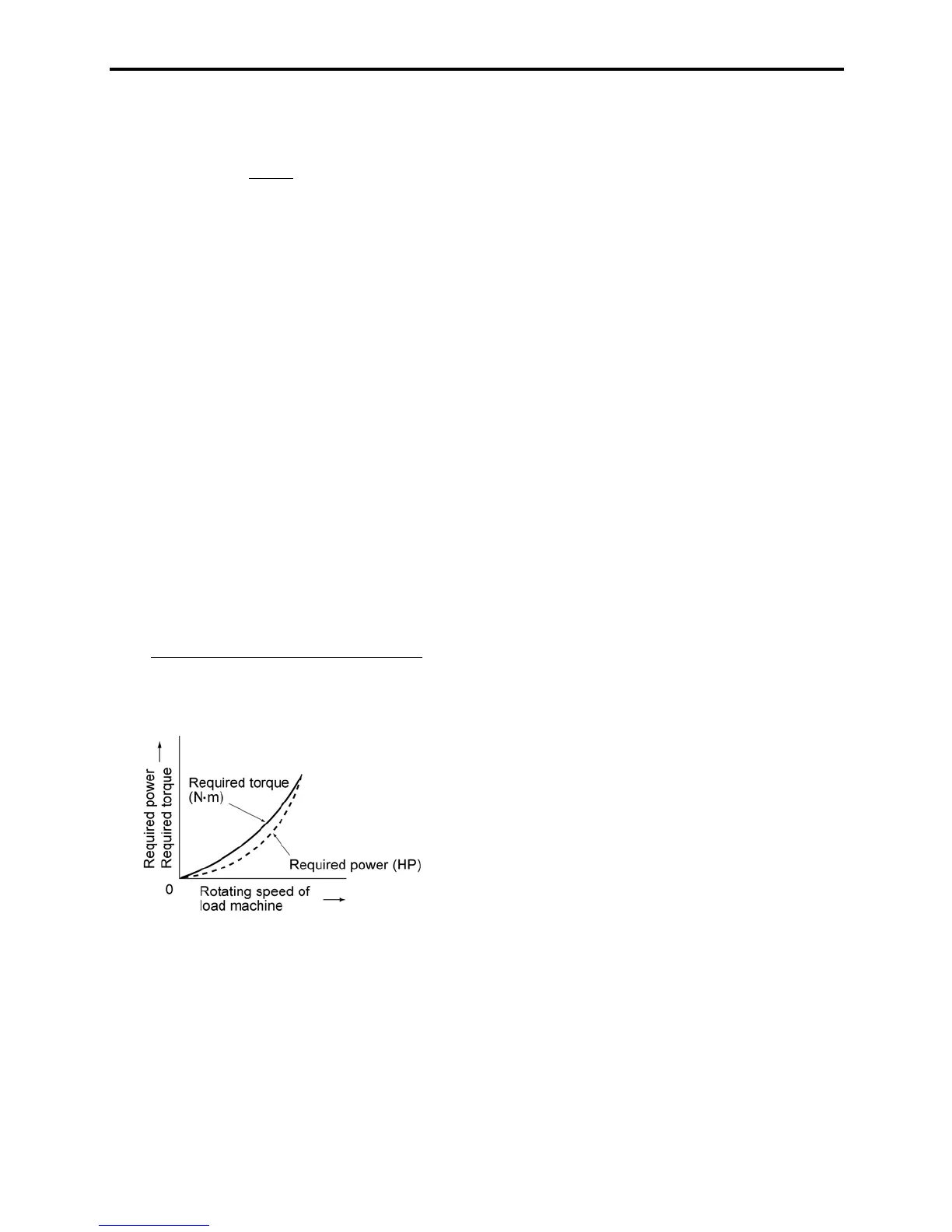
Variable torque load
A squared torque load is characterized by:
1) A change in the required torque in proportion to
the square of the number of revolutions per minute.
2) A power requirement that decreases in proportion
to the cube of the decrease in the number of
revolutions per minute.
55.9
)mN(Torquemin)/r(speedRotating
)HP(powerquiredRe
xu
Related function code: F37
Applications: Fans and pumps
Voltage and frequency variations
Variations in the input voltage or frequency within
permissible limits. Variations outside these limits
might cause an inverter or motor to fail.

 Loading...
Loading...











