17–8 MULTILINK ML3000 ETHERNET COMMUNICATIONS SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
LACP CHAPTER 17: LACP
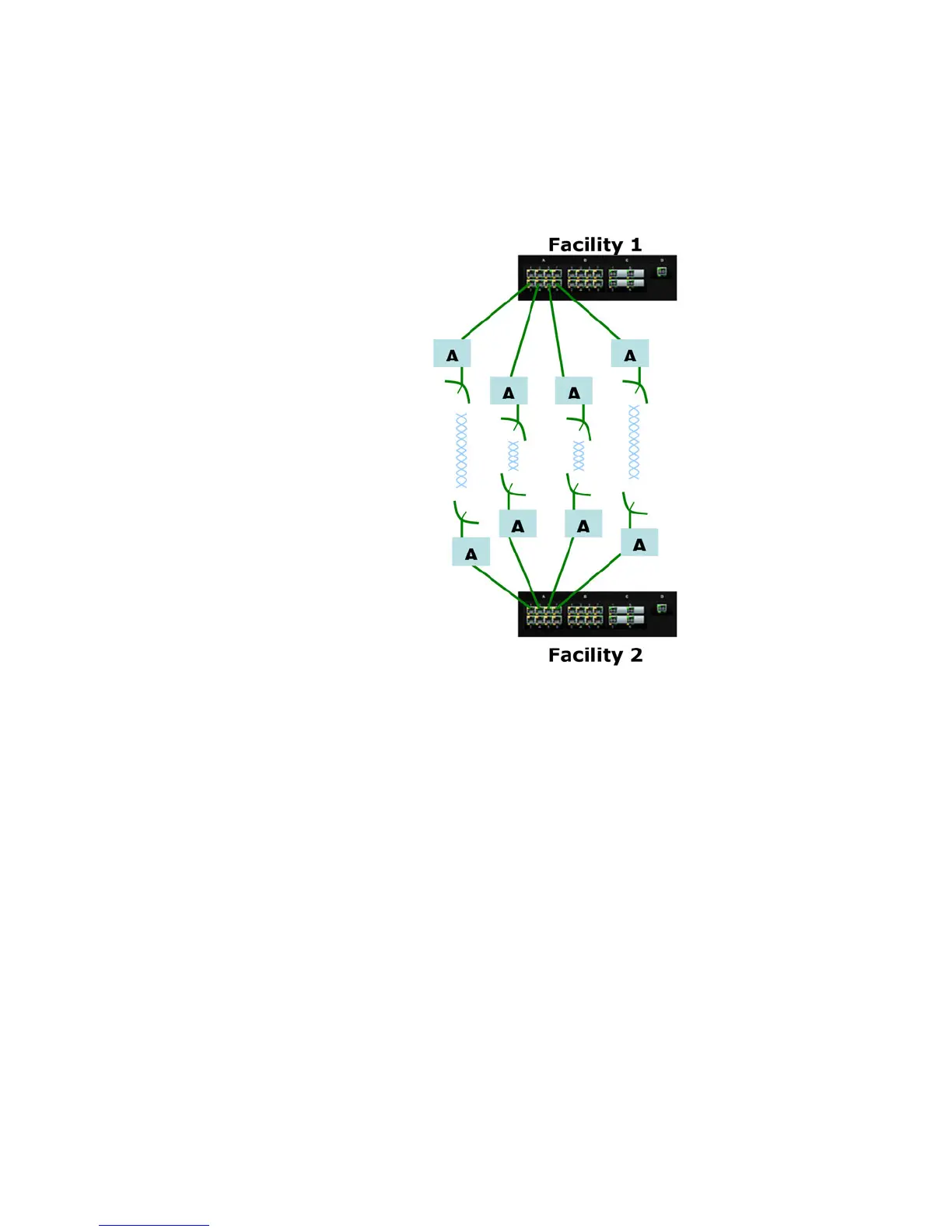
LACP can be used for creating a reliable network between two facilities connected via a
wireless bridge. As shown in the figure below, four trunk ports are connected to four
wireless bridge pairs. This increases the effective throughput of the wireless connections
and also increases the reliability. If one of the bridges were to stop functioning, the other
three continues to operate, providing a very reliable infrastructure.
Figure 17-9: Wire Bridge Connection between 2 Facilities
Creating a reliable infrastructure using wireless bridges (between two facilities) and LACP is
shown in the figure above. “A” indicates a Wi-Fi wireless Bridge or other wireless Bridges.
Another definition worth noting is primary port. Primary port is the port over which specific
traffic like Multicast (IGMP), unknown Unicast and broadcast traffic is transmitted. As
shown by the add port command, the port with the lowest priority value has the highest
priority and is designated as the primary port. If traffic analysis is required, it is
recommended to mirror the primary port (and physically disconnect the other ports if all
traffic needs to be captured).
If multiple ports have the same priority, the first port physically connected becomes the
primary port. In case the ports are already connected, the port with the lowest port count
becomes the primary port i.e. if ports 12, 13, 14 are designated as the LACP group, port 12
would become the primary port.
If the primary port fails, the next available secondary port is designated as the primary
port. So in the example above, if port 12 fails, port 13 is designated as the primary port.
To configure LACP, first define the set of ports which make up the trunk. Next define the set
of trunks. In the example below, we define ports 12, 13 as a set of ports for the trunk.

 Loading...
Loading...