With good GPS antenna visibility, it takes up to 15 minutes for the GPS system to find the satellites
(connection to a minimum of four satellites required), and start synchronizing the IED's internal clock
with global time from the GPS system.
IEC10000203 V1 EN-US
Figure 10: Setting the GPS clock
At synchronization start, the internal clock is adjusted to have the correct global time in seconds with
only integers set. The remaining fractional parts, milliseconds (ms) and microseconds (μs), to reach
global time, are used to slowly synchronize the internal clock to global time.
Synchronizing the internal clock to global time is done at a rate of 1 ms/s. When the internal clock is
within 16 μs from global time, the protection function is enabled. If time deviation between the
internal clock time and global time is more than 16 μs, GPS timing is deactivated and the differential
protection is either blocked or changed to Echo mode depending on the setting for LDCM (GPSerr).
After the protection function is enabled, soft calibration is performed to have the internal clock remain
within 1 μs from global time for < 1 hour. This reduces the restart time after a short GPS interruption.
If time deviation after the interruption is less than the set MaxtDiffLevel, the protection function can
be enabled directly.
In the case of GPS interruption, the protection function is disabled or echo timing is enabled as a
back-up synchronization method. Enabling echo timing has a delay which depends on how long the
GPS system has been in service after start. Inaccuracy of the internal clock starts at 16 μs and goes
down to ±1μs after some minutes.
In telecommunication networks with unspecified route switching, echo timing can only be used with
unchanged time delay in both directions. As soon as the time delay is outside the set limits, the
protection function gets blocked. Some additional features are available to increase the performance
of echo timing:
• If redundant or alternative routes are available, they are also supervised for changes in time
delay. If no time delay difference is observed in these routes, echo timing continues to use the
reserve channel.
• In telecommunication networks with unspecified route switching, time deviations below the set
limits are accumulated to handle multiple route switching, and these accumulated deviations can
reach the set time deviation limit.
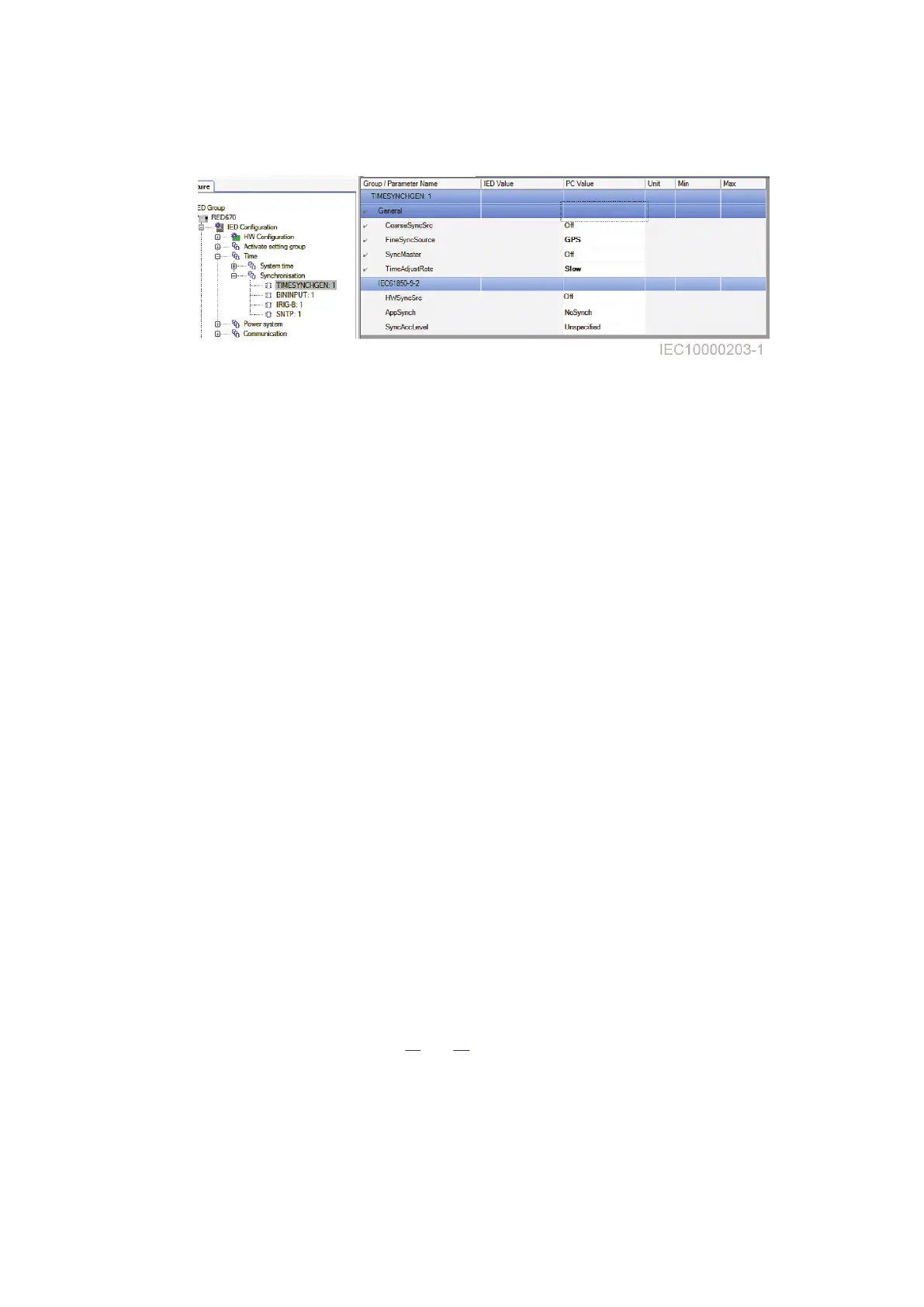
3.3 Time synchronization using IRIG-B
GUID-16212191-F952-4155-80C3-3B2245998311 v1
Time synchronization can be provided via IRIG-B 00X with IEEE1344 support. This setting can be
done via PCM600 (see Figures
11 and 12).
Procedure:
1MRK505382-UEN Rev. K Section 3
Common time synchronization
Communication set-up, 670/650 series 19
Application Guide
© 2017 - 2023 Hitachi Energy. All rights reserved

 Loading...
Loading...