40
Configuring Smart Link
Smart Link overview
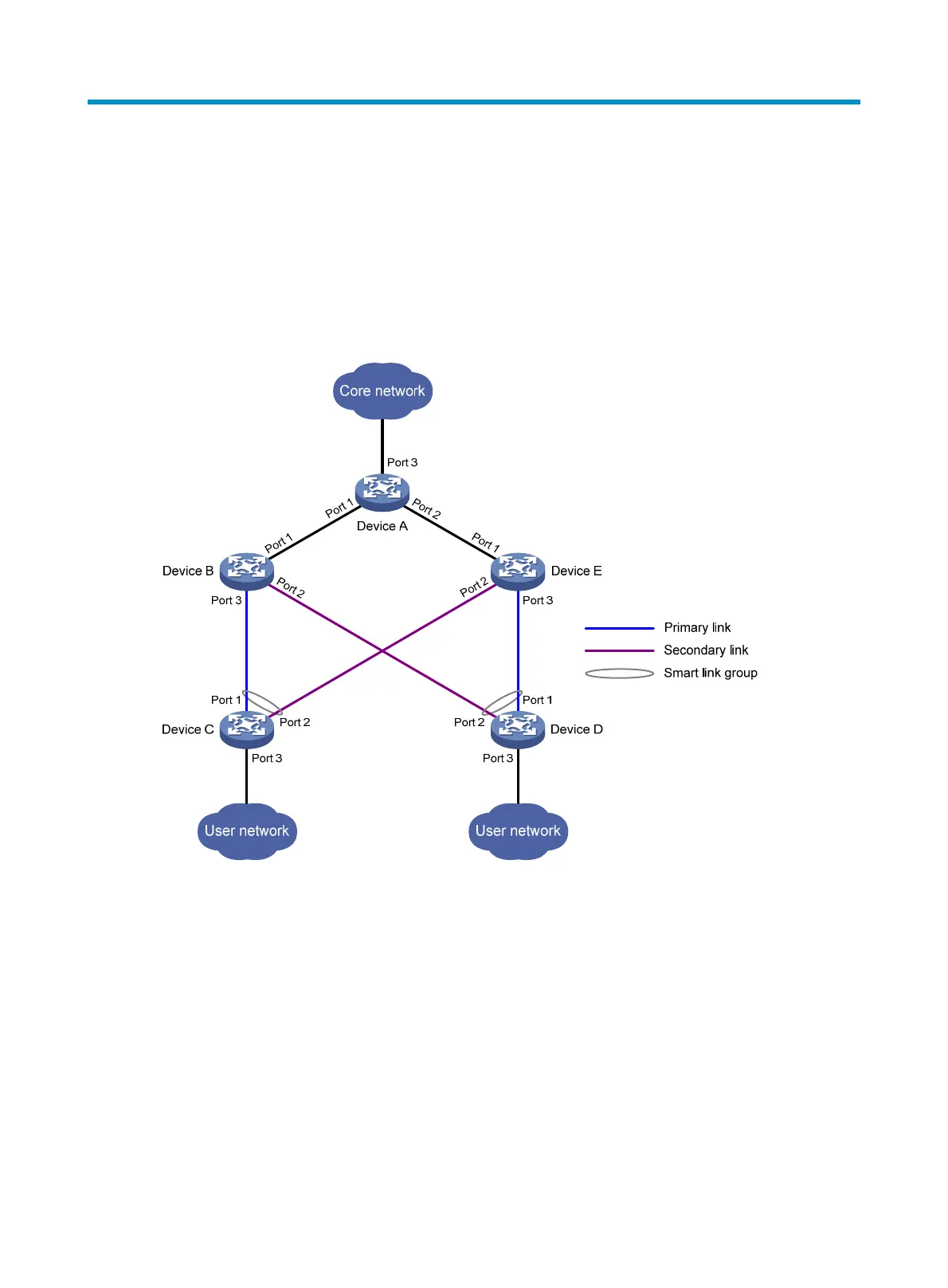
To avoid single-point failures and guarantee network reliability, downstream devices are usually
dual-homed to upstream devices, as shown in Figure 12.
Figure 12 Dual uplink network diagra
m
To remove network loops on a dual-homed network, you can use a spanning tree protocol. However,
convergence time is long with spanning tree protocols, which makes it unsuitable for users who have
high demand on convergence speed.
For more information about spanning tree protocols, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Smart Link is a feature developed to address the slow convergence issue with STP. It provides link
redundancy as well as fast convergence in a dual uplink network, allowing the backup link to take over
quickly when the primary link fails. Smart Link features subsecond convergence time.
A Smart Link device is configured with a smart link group and a transmit control VLAN to transmit flush
messages. For example, Device C and Device D in Figure 12 ar
e Smar
t Link devices.
An associated device supports Smart Link, and receives flush messages sent from the specified control
VLAN. For example, Device A, Device B, and Device E in Figure 12 ar
e a
ssociated devices.

 Loading...
Loading...