253
Assume that IPv6 unicast routes are available in the network, IPv6 MBGP is not configured, and IPv6
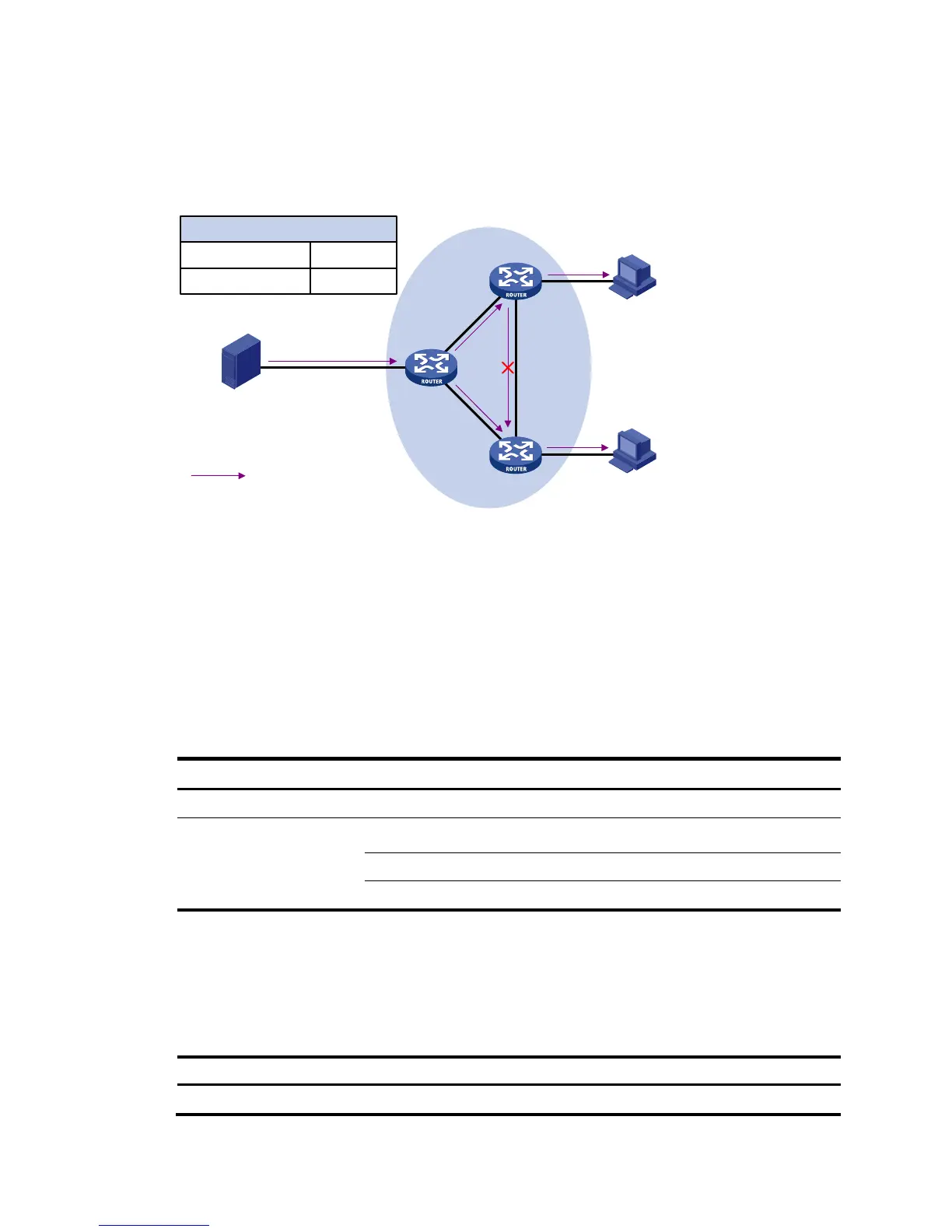
multicast packets travel along the SPT from the multicast source to the receivers, as shown in Figure 71.
T
he IPv6 multicast forwarding table on Router C contains the (S, G) entry, with VLAN-interface 20 as the
RPF interface.
Figure 71 RPF check process
• When an IPv6 multicast packet arrives on VLAN-interface 20 of Router C, because the interface is
the incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router forwards the packet to all outgoing interfaces.
• When an IPv6 multicast packet arrives on VLAN-interface 10 of Router C, because the interface is
not the incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router performs an RPF check on the packet. The
router searches its IPv6 unicast routing table and finds that the outgoing interface to Source (the RPF
interface) is VLAN-interface 20. This means that the (S, G) entry is correct and the packet arrived
along a wrong path. The RPF check fails and the packet is discarded.
Configuration task list
Task Remarks
Enabling IPv6 multicast routing Required
Configuring IPv6 multicast
routing and forwarding
Configuring an IPv6 multicast routing policy Optional
Configuring an IPv6 multicast forwarding range Optional
Configuring the IPv6 multicast forwarding table size Optional
Enabling IPv6 multicast routing
Before you configure any Layer 3 IPv6 multicast functionality, you must enable IPv6 multicast routing.
To enable IPv6 multicast routing:
Ste

 Loading...
Loading...











