264
MLD SSM mapping
The MLD SSM mapping feature enables you to configure static MLD SSM mappings on the last hop router
to provide SSM support for receiver hosts that are running MLDv1. The SSM model assumes that the last
hop router has identified the desired IPv6 multicast sources when receivers join IPv6 multicast groups.
• When an MLDv2 enabled host joins a multicast group, it can explicitly specify one or more multicast
sources in its MLDv2 report.
• An MLDv1-enabled host, however, cannot specify multicast source addresses in its MLDv1 report.
You must configure the MLD SSM mapping feature to translate the (*, G) information in the MLDv1
report into (G, INCLUDE, (S1, S2...)) information.
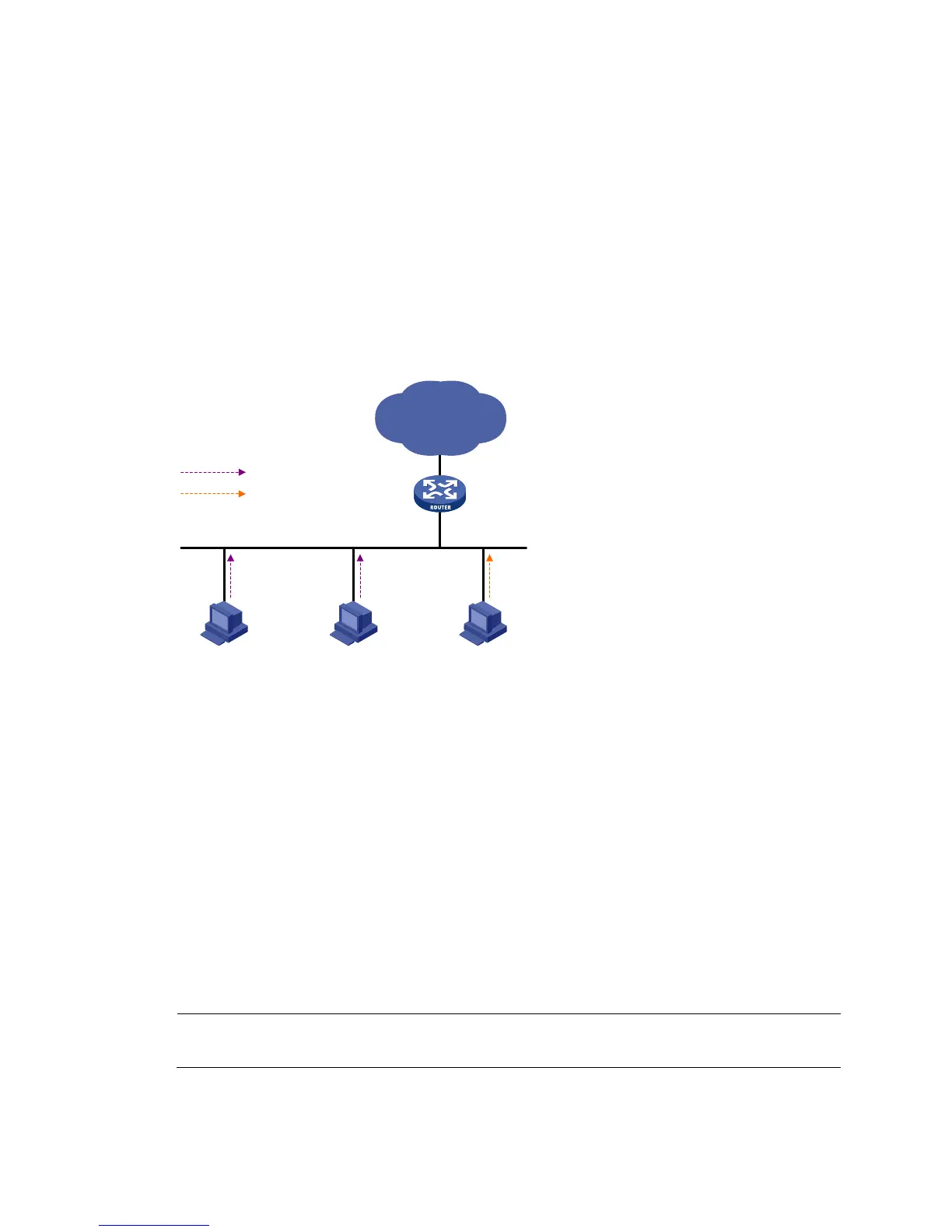
Figure 76 Network diagram
On the IPv6 SSM network in Figure 76, Host A and Host B are running MLDv1 and Host C is running
MLDv2. To provide SSM service for Host A and Host B, you must configure the MLD SSM mapping
feature on Router A.
With the MLD SSM mapping feature configured, when Router A receives an MLDv1 report, it checks the
IPv6 multicast group address G carried in the message.
• If G is not in the IPv6 SSM group range, Router A cannot provide the SSM service but can provide
the ASM service.
• If G is in the IPv6 SSM group range but no MLD SSM mappings have been configured for the IPv6
multicast group G on Router A, Router A cannot provide SSM service and drops the packet.
• If G is in the IPv6 SSM group range, and the MLD SSM mappings have been configured on Router
A for multicast group G, Router A translates the (*, G) information in the MLD report into (G,
INCLUDE, (S1, S2...)) information based on the configured MLD SSM mappings and provides SSM
service accordingly.
NOTE:
The MLD SSM mapping feature does not process MLDv2 reports.
For more information about the IPv6 SSM group range, see "Configuring IPv6 PIM."
MLDv1 report
MLDv2 report
Router A
Querier
Host A (MLDv1)
IPv6 SSM
Receiver
Host B (MLDv1)
Receiver
Host C (MLDv2)
Receiver

 Loading...
Loading...











