same capacity as the smallest drive in the array. The excess capacity of any larger drives is
wasted because it is unavailable for data storage.
• The probability that an array will experience a drive failure increases with the number of
physical drives in the array. If you configure a logical drive with RAID 5, keep the probability
of failure low by using no more than 14 physical drives in the array.
For conceptual information about arrays, logical drives, and fault-tolerance methods, and for
information about default array configuration settings, see the HP Array Configuration Utility User
Guide at I/O Cards and Networking Software at:
http://www.hp.com/go/integrity-iocards-docs
Comparing the Utilities
Table 18 lists the supported features and procedures for the ACU and ORCA utilities.
Table 18 ACU and ORCA Supported Features and Procedures
ORCAACU
Supported Features
NoYesUses a graphical interface
NoYesAvailable in languages other than English
NoYesAvailable on CD
NoYesUses a wizard to suggest the optimum configuration for an unconfigured controller
NoYesDescribes configuration errors
NoYesSuitable for configuration while online
YesNoSuitable for configuration while offline
Supported Procedures
YesYesCreation and deletion of arrays and logical drives
YesYesAssignment of RAID level
NoYesSharing of spare drives among several arrays
NoYesAssignment of multiple spare drives per array
NoYesSetting of stripe size
NoYesMigration of RAID level or stripe size
NoYesConfiguration of controller settings
NoYesExpansion of an array
NoYesCreation of multiple logical drives per array
ORCA Utility
To use ORCA, follow these steps:
1. Power on the server. POST runs, and any array controllers that are in the server are initialized
one at a time. During each controller initialization process, POST halts for several seconds
while an ORCA prompt message displays.
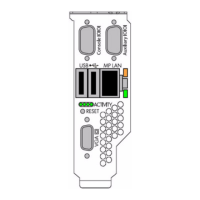
Core I/O Card Configuration 69

 Loading...
Loading...