Synthesis Engine
Synthesis Engine
104 105
Gap Filter, Filter Response
0 dB 0 dB
Balance = 0, Mix = 1, Reson = var. Balance = 0, Mix = –1, Reson = var.
0 dB
Balance = 0, Reson = 0.5, Mix = –1 ... 0
0 dB
Mix = –1, Balance = 0 ... –1
0 dB
Mix = –1, Balance = 0 ... 1
Parallel/Band Reject (Mix > 0) Serial/Band Pass (Mix < 0)
0 dB
Balance = 0, Reson = 0.5, Mix = 0 ... 1
0 dB
Mix = 1, Balance = 0 ... –1
0 dB
Mix = 1, Balance = 0 ... 1
1.001.00
–1 –1 11
1.41
A_lo A_hi
A_lo A_hi
Gain Gain
Balance Balance
Gain
Frequency Frequency
Gain
Gain
Frequency Frequency
Gain
Gain
Frequency Frequency
Gain
Gain
Frequency Frequency
Gain
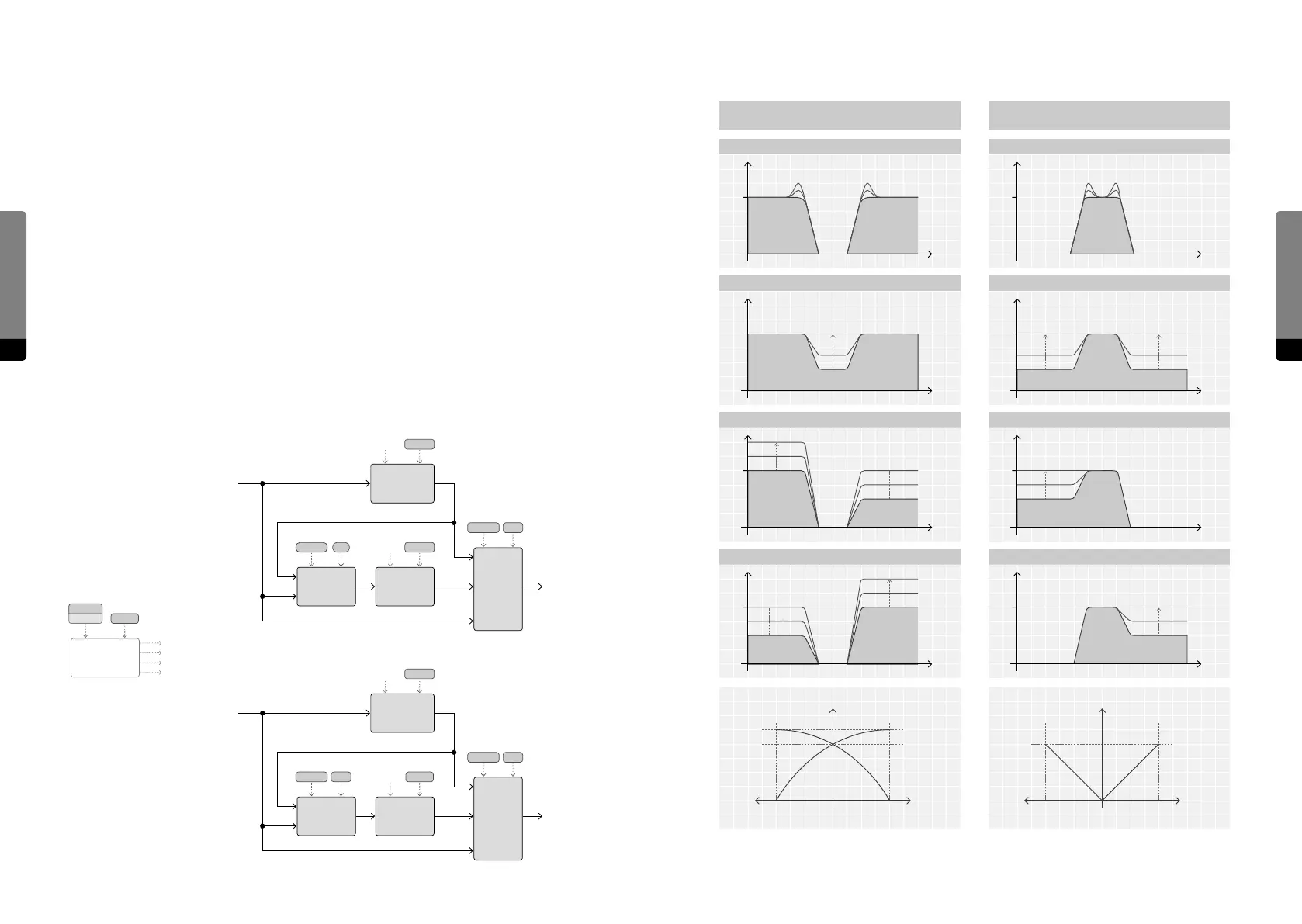
Gap Filter
The Gap Filter marks the third eect and provides further filtering of the signal. It consists
of two four-pole filters (with a damping slope of 24 dB per octave) which can run in
parallel or in series. The filter types are static, as the first filter is a highpass, followed by
the second (lowpass) filter.
The filter frequencies can be determined by a „Center“ frequency, which can be spread in
the stereo field and shied by the „Gap“ parameter, creating an oset between the high-
and lowpass filters. The filter resonance can be adjusted as well, creating two resonance
peaks in the signal spectrum.
Both filter outputs can be blended by a Balance parameter, defining a crossfade mix of
the two components.
The bipolar Mix parameter determines the amount of filtering in the resulting signal,
crossfading the input signal with the filtered signal. Positive mix values mean that the
filter components run in parallel, resulting in a band-reject behavior. Negative values
produce a bandpass eect, as the filter components are running in series.
Gap
Center
Reson
Reson
Balance Mix
Balance Mix
Balance Mix
Reson
ResonBalance Mix
Lo Cut L
Lo Cut R
Hi Cut L
Hi Cut R
Lo Cut L
Hi Cut L
Lo Cut R
Hi Cut R
Stereo
Cuto
Control
X-Fade
4-Pole
Lowpass
X-Fade
4-Pole
Highpass
Out L
In L
X-Fade
4-Pole
Lowpass
X-Fade
4-Pole
Highpass
Out R
In R
 Loading...
Loading...