319
Analog Input Functions and Operating Procedures Section 7-6
3. After making the DM settings from a Programming Device, it will be neces-
sary to either turn the power to the PLC OFF and ON, or turn ON the Spe-
cial I/O Unit Restart Bit in order to transfer the contents of the DM settings
to the Special I/O Unit.
Voltage/Current Range
Setting
When “1 to 5 V, 4 to 20 mA” is selected for the input signal range, either the “1
to 5 V” or “4 to 20 mA” range can then be selected by means of the D(m+35)
setting. Adjusting the factory-set voltage and current can improve the accu-
racy of current output specifications.
Reading Conversion
Values
Analog input conversion values are stored for each input number, in CIO
words n+5 to n+8.
Note For the CIO word addresses, n = CIO 2000 + (unit number x 10).
Use MOV(021) or XFER(070) to read conversion values in the user program.
Example 1 In this example, the conversion data from only one input is read. (The unit
number is 0.)
Example 2 In this example, the conversion data from multiple inputs is read. (The unit
number is 0.)
For details regarding conversion value scaling, refer to Scaling on page 366.
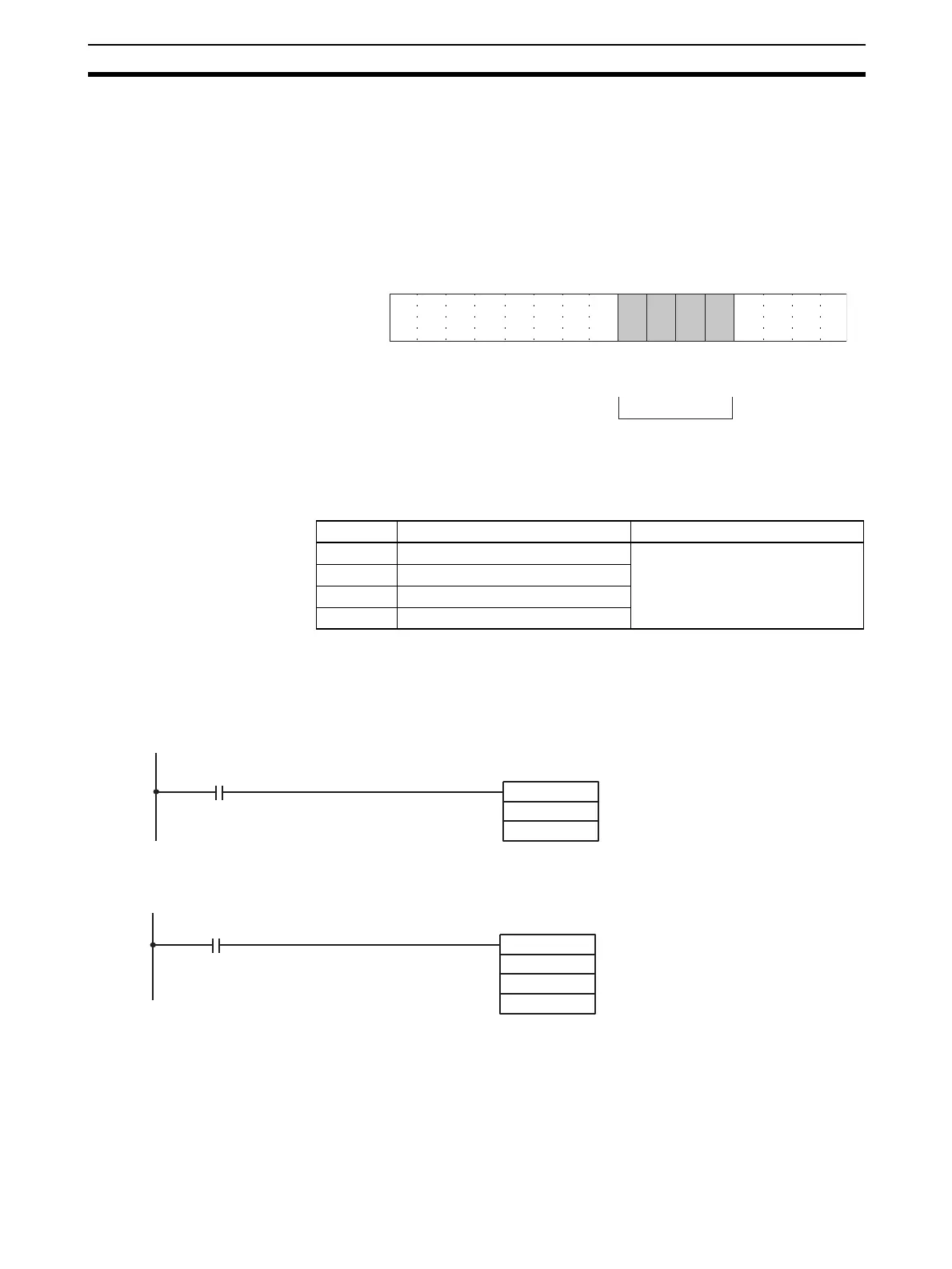
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Bit
D(m+35)
Input 2
Input 1
0: Voltage: 1 V to 5 V
1: Current 4 mA to 20 mA
Input 4
Input 3
Word Function Stored value
n+5 Input 1 conversion value 16-bit binary data
n+6 Input 2 conversion value
n+7 Input 3 conversion value
n+8 Input 4 conversion value
MOV(021)
2005
D00001
Input condition
Conversion data in CIO word
2005 (input number 1) is read
to D00001.
XFER(070)
#0004
2005
D00001
Input condition
Conversion data in CIO words
2005 and 2008 (input num-
bers 1 and 4) is read to
D00001 and D00004.
 Loading...
Loading...











