A-7
TCP State Transitions
There are 11 types of TCP connection state.
You can check the TCP state with the TCP connection status that is output by the SktGetTCPStatus
(Read TCP Socket Status) instruction.
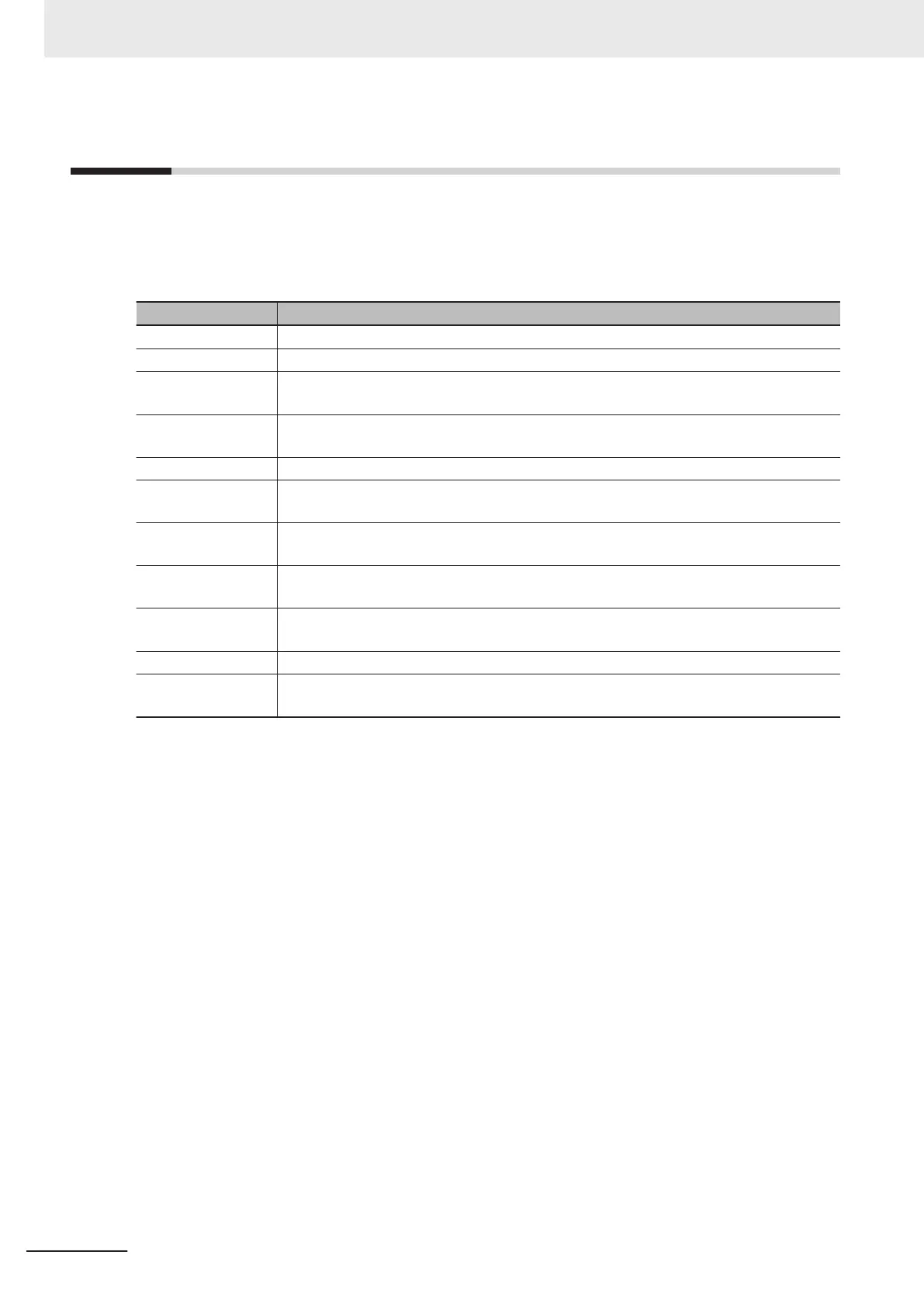
The table below shows the TCP states and what each state means.
TCP state Definition
CLOSED The connection is closed.
LISTEN The server is waiting for a connection request (SYN) with a passive open.
SYN SENT The client sent a connection request (SYN) for an active open and is waiting for acknowl-
edgment (SYN + ACK).
SYN RECEIVED The server sent an acknowledgment (SYN + ACK) to a connection request (SYN) and is
waiting for acknowledgment (ACK).
ESTABLISHED A connection is established.
CLOSE WAIT The server sent acknowledgment (ACK) to a connection close request (FIN) and is wait-
ing for the server application to be ready to close.
FIN WAIT-1 The client sent a connection close request (FIN) and is waiting for acknowledgment
(ACK).
CLOSING The client and server simultaneously received a connection close request (FIN) and are
waiting for acknowledgment (ACK).
LAST-ACK The server sent a connection close request (FIN) and is waiting for acknowledgment
(ACK).
FIN WAIT-2 The client is waiting for a connection close request (FIN).
TIME WAIT The client received acknowledgment (ACK) to a connection close request (FIN) and is
waiting for it to be received and processed by the server
.
The TCP state changes as requests and acknowledgments are received from the remote node, and
as TCP socket connection and close instructions are executed in the user program.
When the state changes, a connection request (SYN), close request (FIN), and acknowledgment
(ACK) to those requests are sent to and received from the remote node.
The following figure shows TCP state transitions.
The TCP states are given in £ in the figure. Between states, the text in the upper row indicates the
condition for the state change, and the text in the lower row indicates the action that is performed at
the state change. (If no action is performed, none is given.)
Example: When SYN and ACK are received in SYN SENT
state, ACK is sent and the state changes to
ESTABLISHED.
Appendices
A-60
NJ/NX-series CPU Unit Built-in EtherNet/IP Port User’s Manual (W506)

 Loading...
Loading...