Principles of Measurement and Parameters
Operator´s Manual PiCCO
2
Page
Version 3.1 B-3
2.3 Transpulmonary volume determination
Specific volumes can be calculated by multiplying cardiac output with characteristic time variables of the
thermodilution curve.
The parameters can alternatively be displayed as absolute parameters or indexed to the patient´s body
characteristics.
The PiCCO
2
uses predicted body weight (PBW) to index intrathoracic volumetric parameters.
Absolute Parameters Indexed Parameters
Parameter Abbr. Unit Abbr. Unit
Global End-Diastolic Volume GEDV ml GEDI ml/m
2
Extravascular Lung Water EVLW ml ELWI ml/kg
Global Ejection Fraction GEF %
Pulmonary Vascular Permeability Index PVPI -
Cardiac Function Index CFI 1/min
Intrathoracic Blood Volume ITBV ml ITBI ml/m
2
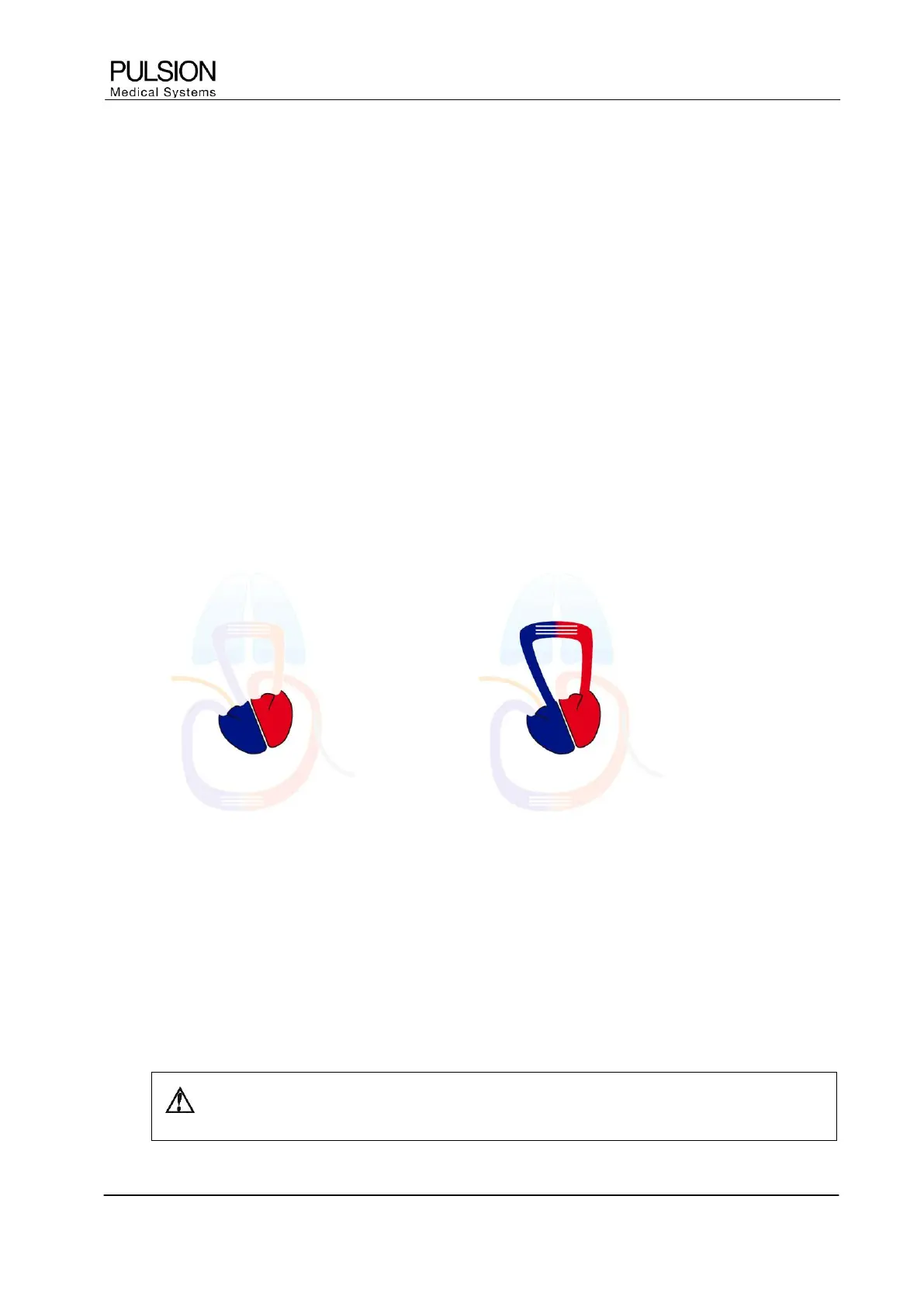
2.3.1 GEDV / ITBV
GEDV ITBV
Figure 2: GEDV / ITBV
Global End-Diastolic Volume (GEDV) is the total amount of blood left in all four heart chambers, i.e. atria and
ventricles, at the end of diastole.
Intrathoracic Blood Volume (ITBV) represents the total amount of blood in the thorax.
GEDV and ITBV reflect the circulatory volume status and are excellent indicators of cardiac preload. GEDV
and ITBV are used for managing the patient´s vascular filling status and guiding volume therapy.
CAUTION: Aortic aneurysms may cause the displayed blood volume (GEDV/ITBV) derived by
thermodilution measurement to be erroneously high.

 Loading...
Loading...