Chapter 1 RAID Introduction
1.1 What is RAID?
RAID (redundant array of independent disks or redundant array of inexpensive disks)
Whenever and wherever we are, we store our data in a hard drive. Abnormally access, slower speed
and unresponsiveness are all expected when an accident occurs or the hard disk reaches its service
life because a hard disk is widely used. By then, all data stored within may be destroyed and become
permanently irretrievable. RAID technology spares you from the threats of losing your data again!
RAID (redundant array of independent disks or redundant array of inexpensive disks) allows you to
store your data into multiple drives by dividing them up into segments. It provides data redundancy and
creates a fault-tolerant environment for data storage. With multiple drives used (at least 2) in a RAID,
it increases storage capacity as well as enhances the speed of data transfer. Be equipped with it and
you will never have to worry about the integrity of your data again because your data will be 100%
protected.
1.2 RAID Functions
‧ Expanding storage capacity
‧ Increasing data transfer speed
‧ Saving cost
‧ Inherent Fault Tolerance
‧ Hot Swap Capability
‧ Auto-Rebuild of Data
‧ Hot Spare Drive
‧ On-line Capacity Expansion
1.3 RAID 0 / RAID 1 / Linear
SL3610/SL3620-2S-LB2 provides RAID 0, RAID 1 and Linear functions described as follows:
Notice : SL3610 ONLY support RAID 0 and RAID 1
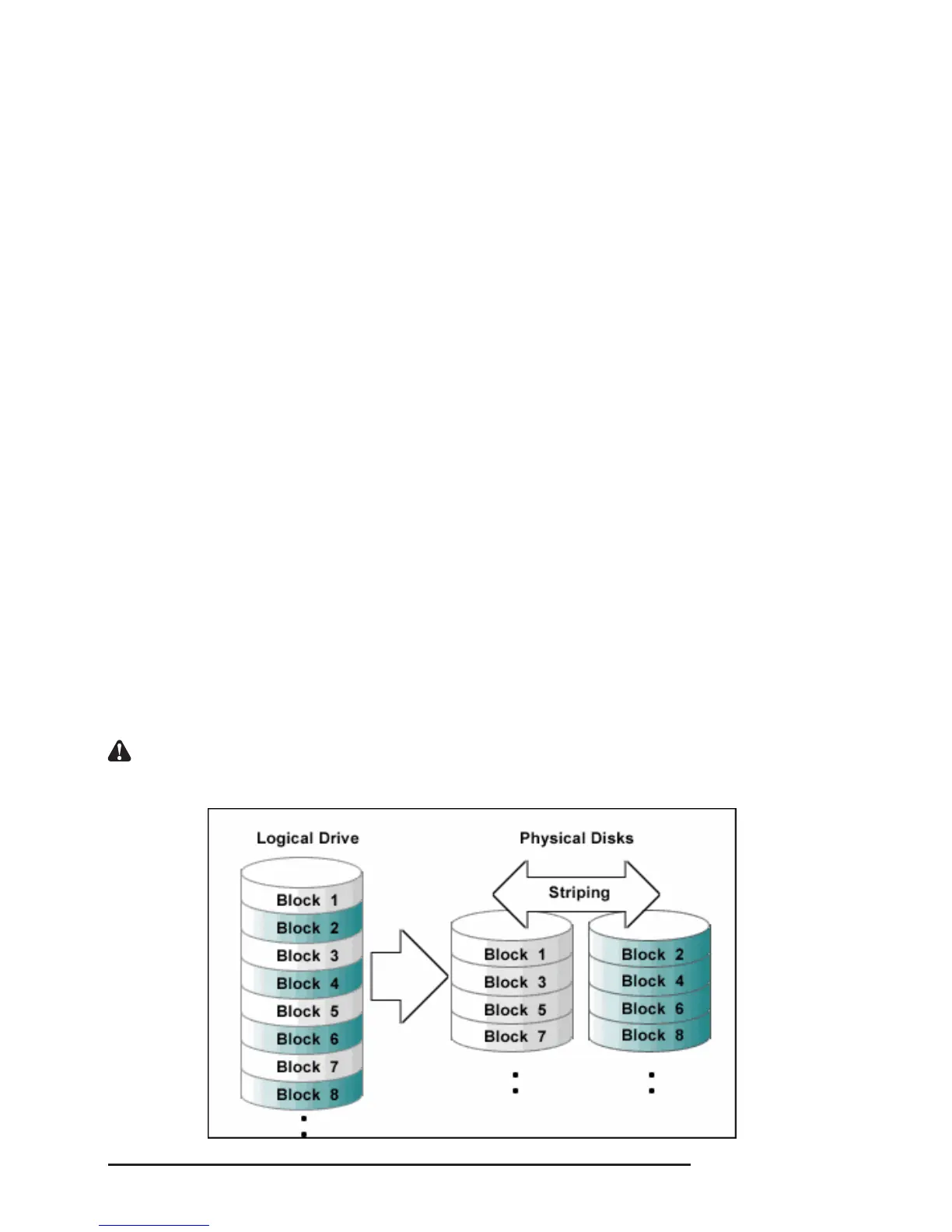
Striping (fast, has no fault tolerance; requires at least two hard disks)
RAID Introduction 5

 Loading...
Loading...