Wiring 3-37
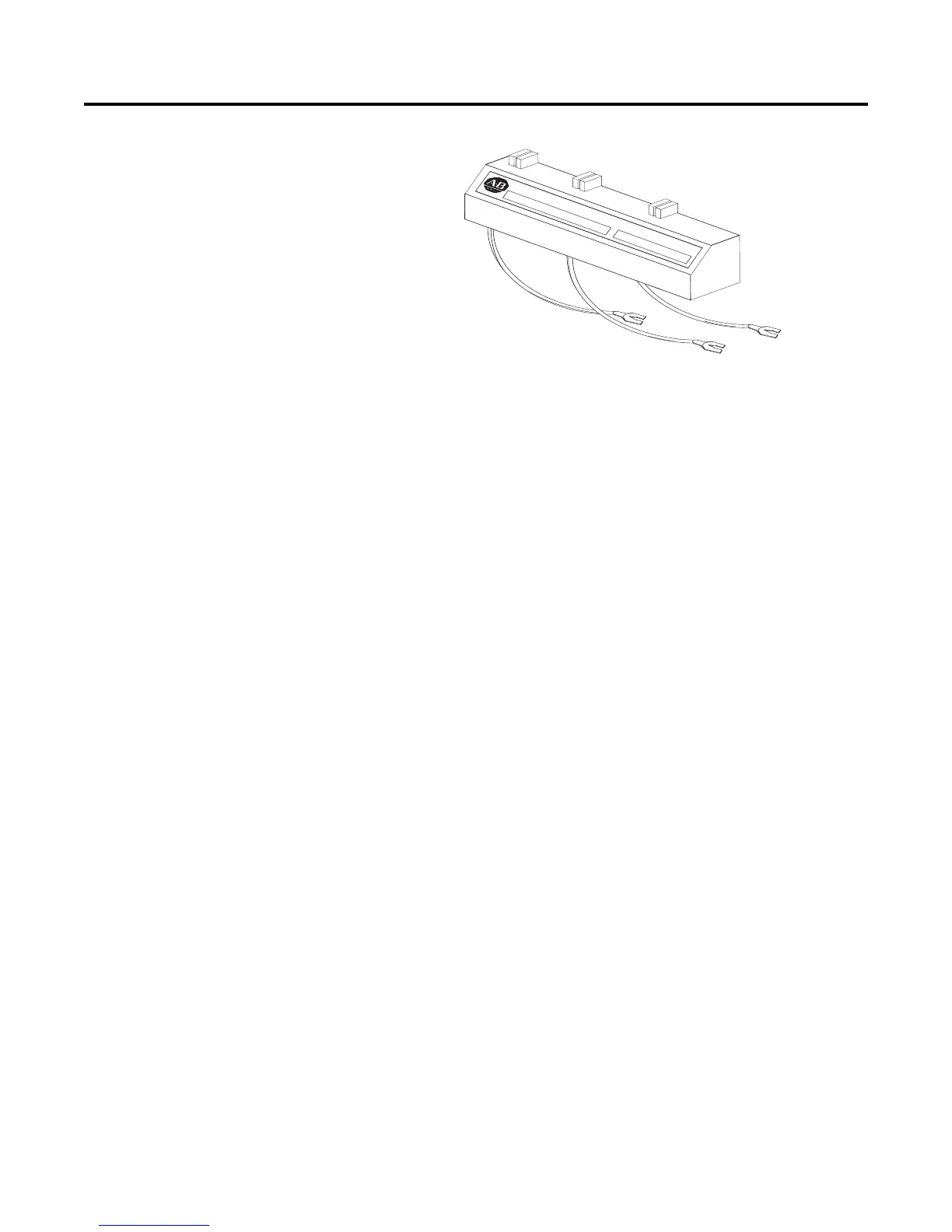
Figure 3.35 Protective Module
There are two general situations that may occur which would indicate
the need for using the protective modules.
1. Transient spikes may occur on the lines feeding the SMC-Flex
controller (or feeding the load from the SMC-Flex controller).
Spikes are created on the line when devices are attached with
current-carrying inductances that are open-circuited. The energy
stored in the magnetic field is released when the contacts open the
circuit. Examples of these are lightly loaded motors,
transformers, solenoids, and electromechanical brakes. Lightning
can also cause spikes.
2. The second situation arises when the SMC-Flex controller is
installed on a system that has fast-rising wavefronts present,
although not necessarily high peak voltages. Lightning strikes can
cause this type of response. Additionally, if the SMC-Flex con-
troller is on the same bus as other SCR devices, (AC/DC drives,
induction heating equipment, or welding equipment) the firing of
the SCRs in those devices can cause noise.
Note: protective modules may be placed on the line, load, or both
sides of the SMC. However, protective modules must NOT be
placed on the load side of the SMC when using inside-the-
delta motor connections or with pump, linear speed, or
braking control.
MADE IN U.S.A
PROTECTIVE MODULE
MAX. LINE VOLTAGE
 Loading...
Loading...











