Overview
2.2 Introduction
Product User Manual
20 Operating Instructions, Version AE 12/2009, A5E01454341C
2.2.1 Clean Power
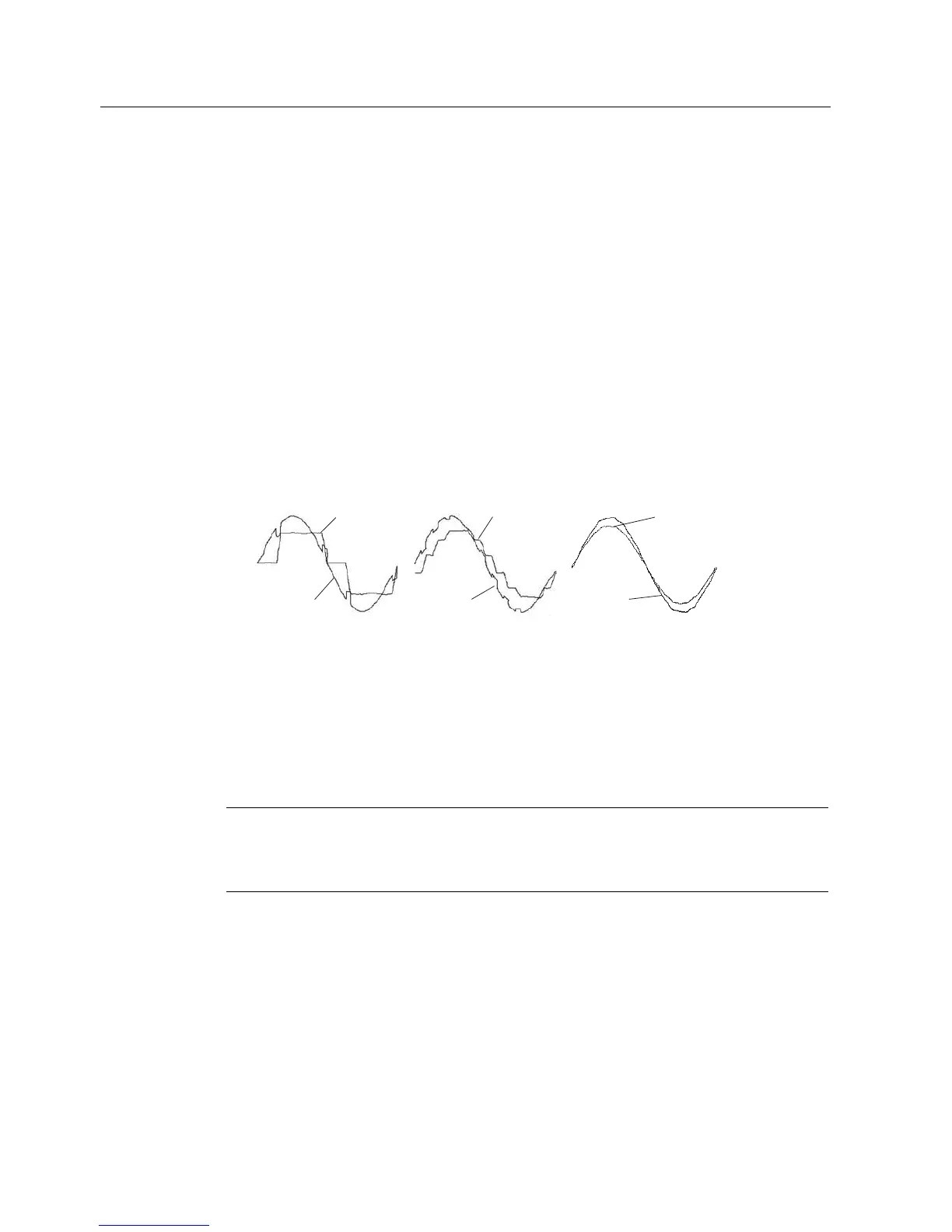
Prior to the introduction of the Perfect Harmony Drive, other solutions with variable frequency
output power conversion created unwanted line disturbance (refer to Figure "Harmonic
Distortion Waveform Comparisons", six-pulse and twelve-pulse input waveforms).
The Perfect Harmony drive system mitigates power quality issues by:
● Providing clean power input (low values of flicker, TIF, harmonic current distortion)
● Providing a high power factor
● Providing a nearly perfect sinusoidal output
The Perfect Harmony drive series meets the most stringent IEEE 519-1992 requirements for
voltage and current harmonic distortion, even if the source capacity is no larger than the
drive rating. This series protects other on-line equipment (such as computers, telephones,
and lighting ballasts) from harmonic disturbances. Perfect Harmony also prevents "cross
talk" with other variable speed drives. Clean power input eliminates the need for time-
consuming harmonic/resonance analyses and costly harmonic filters. Figure "Harmonic
Distortion Waveform Comparisons" illustrates harmonic distortion waveforms for a typical 6-
pulse, a typical 12-pulse, and the Perfect Harmony series drive.
7\SLFDOSXOVH
,QSXW:DYHIRUP
3HUIHFW+DUPRQ\6HULHV
,QSXW:DYHIRUP
7\SLFDOSXOVH
,QSXW:DYHIRUP
6RXUFH9ROWDJH
6RXUFH&XUUHQW
6RXUFH&XUUHQW
6RXUFH&XUUHQW
6RXUFH9ROWDJH
6RXUFH9ROWDJH
Figure 2-2 Harmonic Distortion Wave Form Comparisons (6-pulse, 12-pulse, and Perfect Harmony)
Total harmonic distortion of the source current is 25% for the 6 pulse, 8.8% for the 12-pulse
and 0.8% for the Perfect Harmony. The corresponding voltage distortions with a typical
source impedance are 10%, 5.9% and 1.2%, respectively.
Note
The above comparisons were done using a typical 1,000 Hp current source drive (6-pulse
and 12-pulse modes), and a Perfect Harmony series drive operating from an 1100 kVA,
5.75% impedance source.
2.2.2 High Power Factor
Power factor is a measure of the fraction of current that produces real power to the load.
Typically, power factor is given as a percentage. A high power factor VFD (e.g., 94%) makes
much better use of its input line current demand in producing real power to the motor than a
VFD operating at a low power factor (e.g., 30%). VFDs having a low operating power factor

 Loading...
Loading...











