Data transfer using CANopen Issue 01/05
CANopen Option Module Operating Instructions
34 6SE6400-5BC00-0BP0
3.2.2 Communication monitoring services
There are three communication monitoring services in CANopen:
• Node Guarding / Life Guarding
• Heartbeat
• Sync loss detection
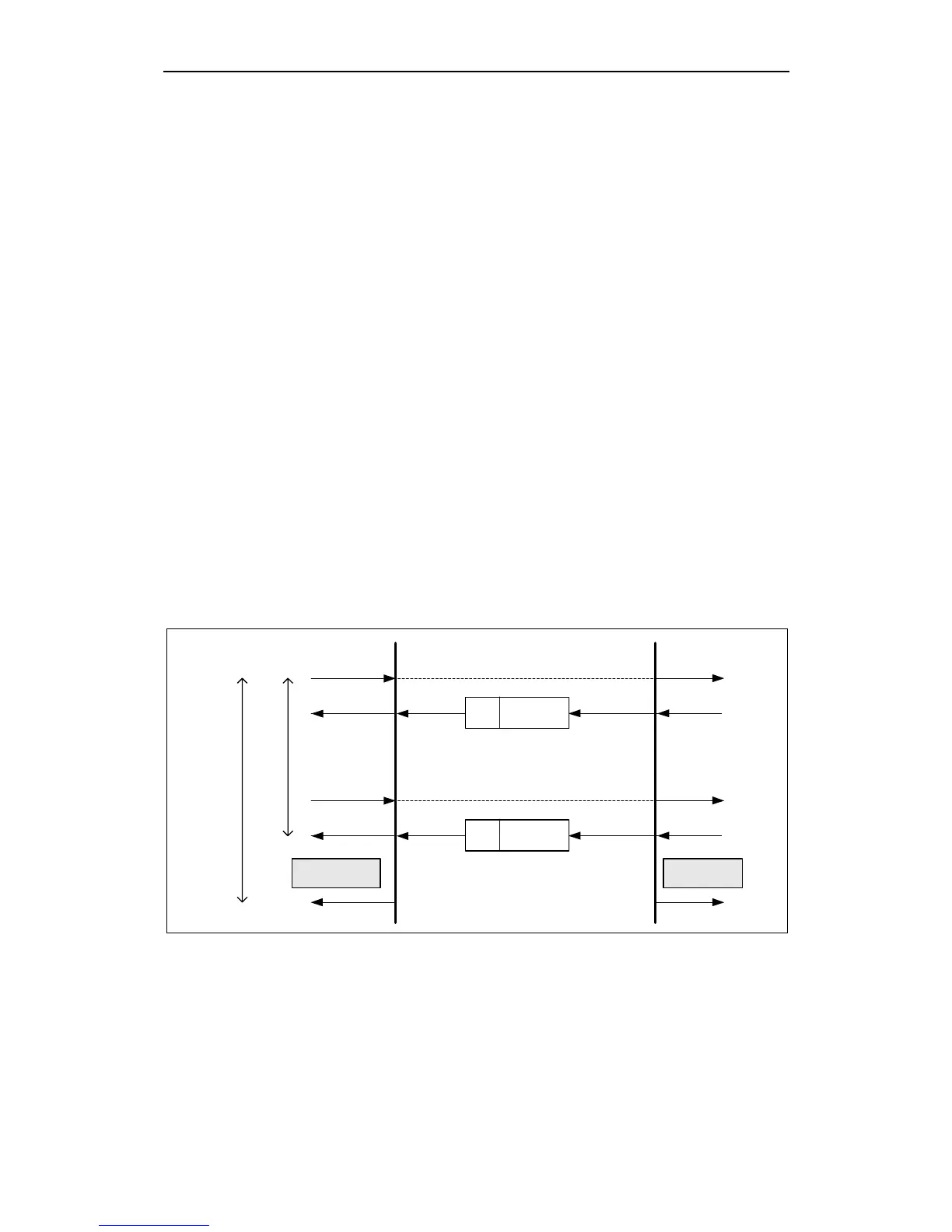
Node Guarding:
MICROMASTER 420/430/440 supports Node Guarding and Life Guarding. With
Node Guarding, the CANopen master sends, to each slave, an RTR telegram with
the COB-ID 700H + node-ID. The slave responds, with the same COB-ID, with its
communications state. This means either Pre-Operational, Operational or Stopped.
Further, the message that is sent contains a toggle bit - using the Object Guard
Time, the time between two RTR messages, received at the slave, is set.
Life Guarding:
The CANopen slave monitors the incoming RTR messages from the master. The
number of RTR telegrams which can fail as a maximum before the slave initiates a
Life Guarding event is defined using the Life Time Factor object. The lifetime of the
master is calculated from the product of the Guard Time (refer to Node Guarding)
and Life Time Factor. This is the maximum time that the slave waits for an RTR
telegram (message) before it initiates a Life Guarding Event.
COB-ID = 700H + Node-ID
Request
Indication
Node
Guard
time
Life Guarding
Event
Remote transmit request
Response
Confirmation
7
t
6 ... 0
s
COB-ID = 700H + Node-ID
Request
Indication
Remote transmit request
Response
Confirmation
7
t
6 ... 0
s
Indication
Indication
Node Guarding
Event
Node
Life
time
Fig. 3-3 Node Guarding/ Life Guarding protocols
 Loading...
Loading...











