Issue 01/05 Data transfer using CANopen
CANopen Option Module Operating Instructions
6SE6400-5BC00-0BP0
47
PDO data transfer types
CANopen makes a differentiation between various data transfer types (trigger
events for the PDOs).
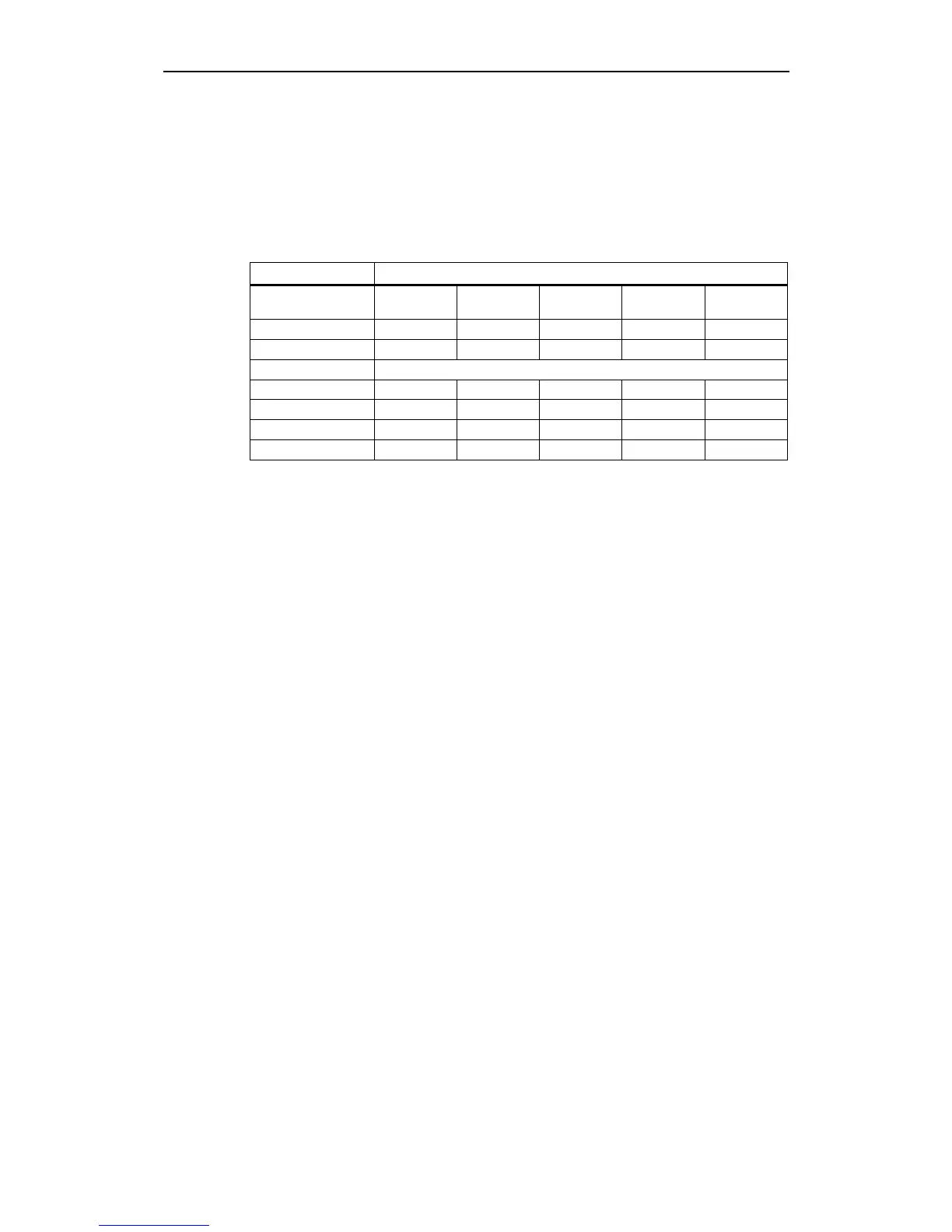
The various data transfer types for PDOs is shown in the following table:
Table 3-11 PDO data transfer types
Data transfer type PDO data transfer
Cyclic Non-cyclic Synchronous Non-
synchronous
RTR
0 X X
1 - 240 X X
241 - 251 Reserved
252 X X
253 X X
254 X
255 X
Significance of the various data transfer types:
Non-cyclic synchronous transfer
⇒
If a value has changed, it is sent after
each SYNC telegram
Cyclic synchronous data transfer
⇒
A value is sent (n = 1 - 240) after each
n
th
SYNC telegram
RTR, synchronous data transfer
⇒
After an RTR query has been received,
after the next received SYNC message,
the value is sent.
RTR, non-synchronous data transfer
⇒
The value is immediately sent after an
RTR query has been received.
Non-synchronous
⇒
Non-synchronous PDOs are always sent
if an event has occurred (the value has
changed). Data transfer types 254 and
255 differ as follows: For 254, the trigger
has a manufacturer-specific origin. For
255, the trigger is received from an event
defined in the profile. In order to receive
the PDO in a specific cycle, in spite of
the non-synchronous data transfer, even
if the value did not change, in the
communication objects event timers can
be set which means that PDOs are sent
after the selected time.
Synchronous PDOs are transferred using the standardized SYNC object. The
SYNC Producer sends these periodically.
 Loading...
Loading...











