- 36 -
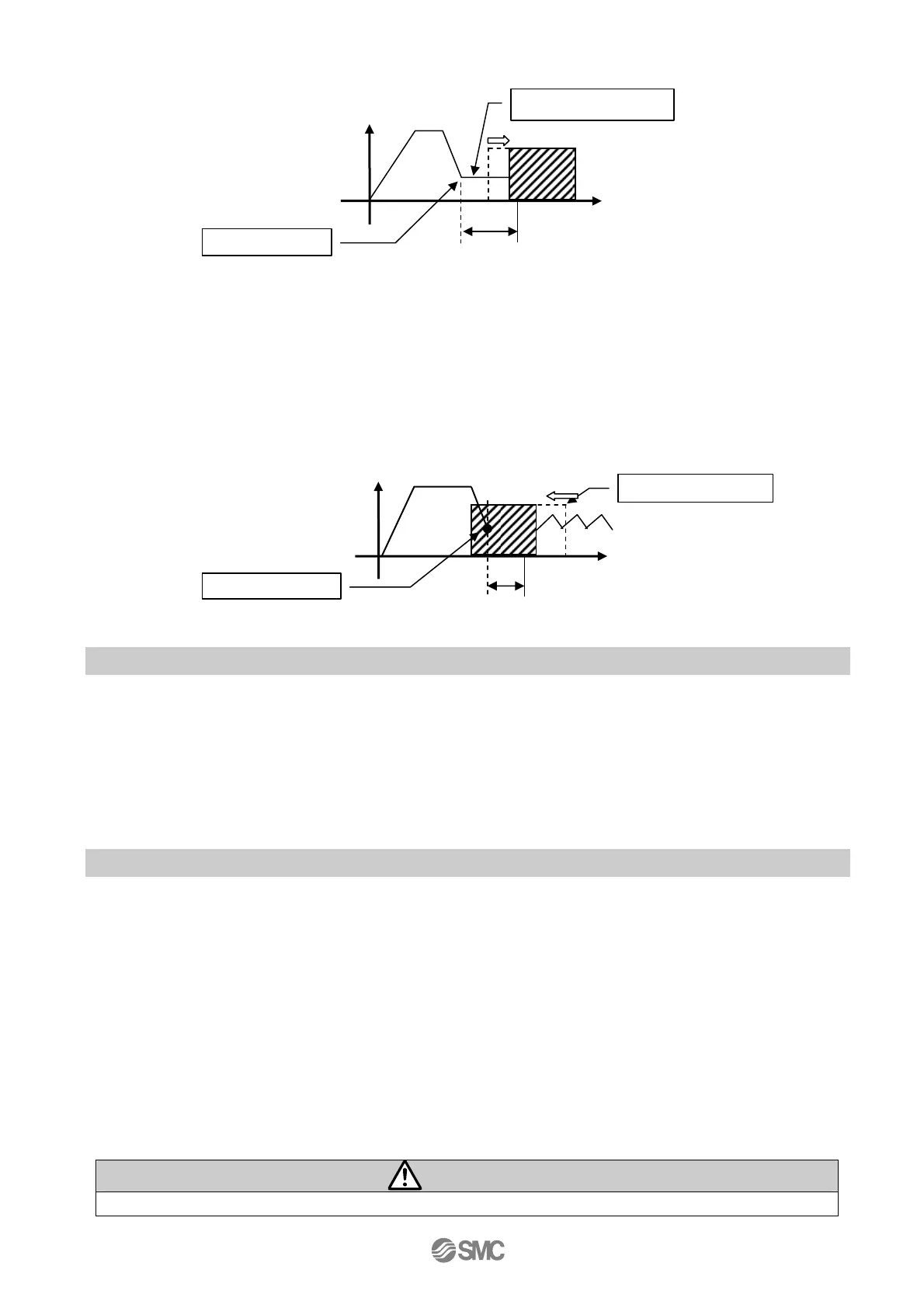
(2) Movement of the workpiece in the direction opposite to the pushing direction
(The actuator is pushed back since the reaction force from the workpiece is too large.)
After completion of the pushing operation, if the reaction force from the workpiece becomes larger, the
actuator may be pushed back. In such case, while the INP output is kept be ON, the actuator will be
pushed back to the point where the reaction force and the actuator pushing force are balanced (pushed
back toward the target position). If the actuator is pushed back over the target position, the alarm
(
ORIG ALM) will be activated.
8.4 Controller input signal response time
The factors that may cause the controller to delay’s in responding to the input signal are as follows:
(1) The controller delayed in scanning the input signal.
(2) The analysis and computing of the input signal is delayed.
(3) The analysis and processing of the command is delayed.
Leave an interval of 15 ms (30 ms if possible) or more between input signals and maintain the state of the
signal for 30ms or more, as PLC processing delays and controller scaning delays can occur.
8.5 Methods of interrupting operation
There are two methods of interrupting operation and stopping the actuator during positioning operation
and pushing operation, as shown below. The state after stopping is different, so use the method
appropriate to the application.
[Stopping by EMG signal]
If the EMG signal is turned OFF during operation, after the actuator decelerates and stops, the servo will
turn OFF so the stopped position is not held. (For an actuator with lock, it is held by the lock function.)
[Stopping by RESET signal]
If the RESET signal is turned ON during operation, after the actuator decelerates and stops, the stopped
position is held. (The servo does not turn OFF.)
[Stopped by HOLD signal]
The actuator decelerates to stop when HOLD signal is ON during operation.
Caution
If instructed to stop by EMG signal and RESET signal, all OUT signals will turn OFF.
Positioning range
(In position)
Speed
Tar
et position
Pushing process
Position
Positioning range
(In position)
Counterforce
Speed
Position
Tar
et
osition

 Loading...
Loading...