19
Theory of Operation
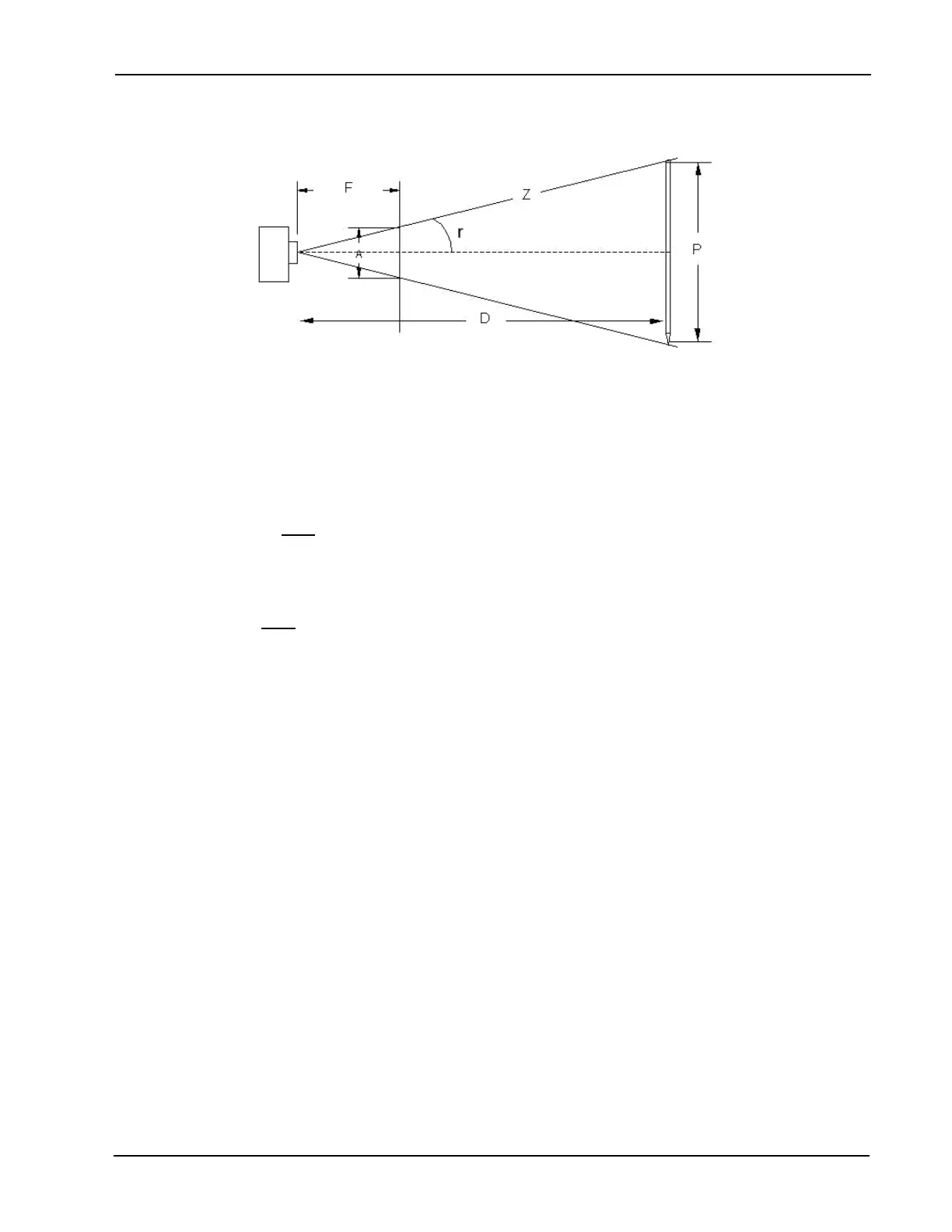
First, we must nd the angle r by applying formulas from basic trigonometry:
tan r = (A/2) and Z
2
= (P/2)
2
+ D
2
F
Since we know A,F,P and Z can be calculated and the angle can be found using trigonometric tables. Once
the angle is known, we can use it in another trigonometry formula to nd D:
D = (P/2)
tan r
Since we know P and r we can calculate D – we now know the distance the pen is from the camera.
Applying this to the 3D Aligner, the image analysis software takes each image and precisely measures the
size of each dot on the photograph – this is the perceived size (A). We already discussed the known values of
focal length (F) and size of the dots (P). Thus, using the above math the 3D Aligner can measure the distance
from the cameras to any dot on the targets and can do so with a high degree of accuracy – it can measure a
target 20 feet away to less than 1 mm accuracy.

 Loading...
Loading...