13. Electrical System
13-7
Charging voltage / current inspection
Caution
z Make sure the battery being charged
already before carry out inspection.
z While starting the engine, the starter
motor draws large amount of current from
the battery.
z Use a fully charged battery having a
voltage larger than 13.0 V
After the engine is warmed up, replace the
original battery with a fully charged battery.
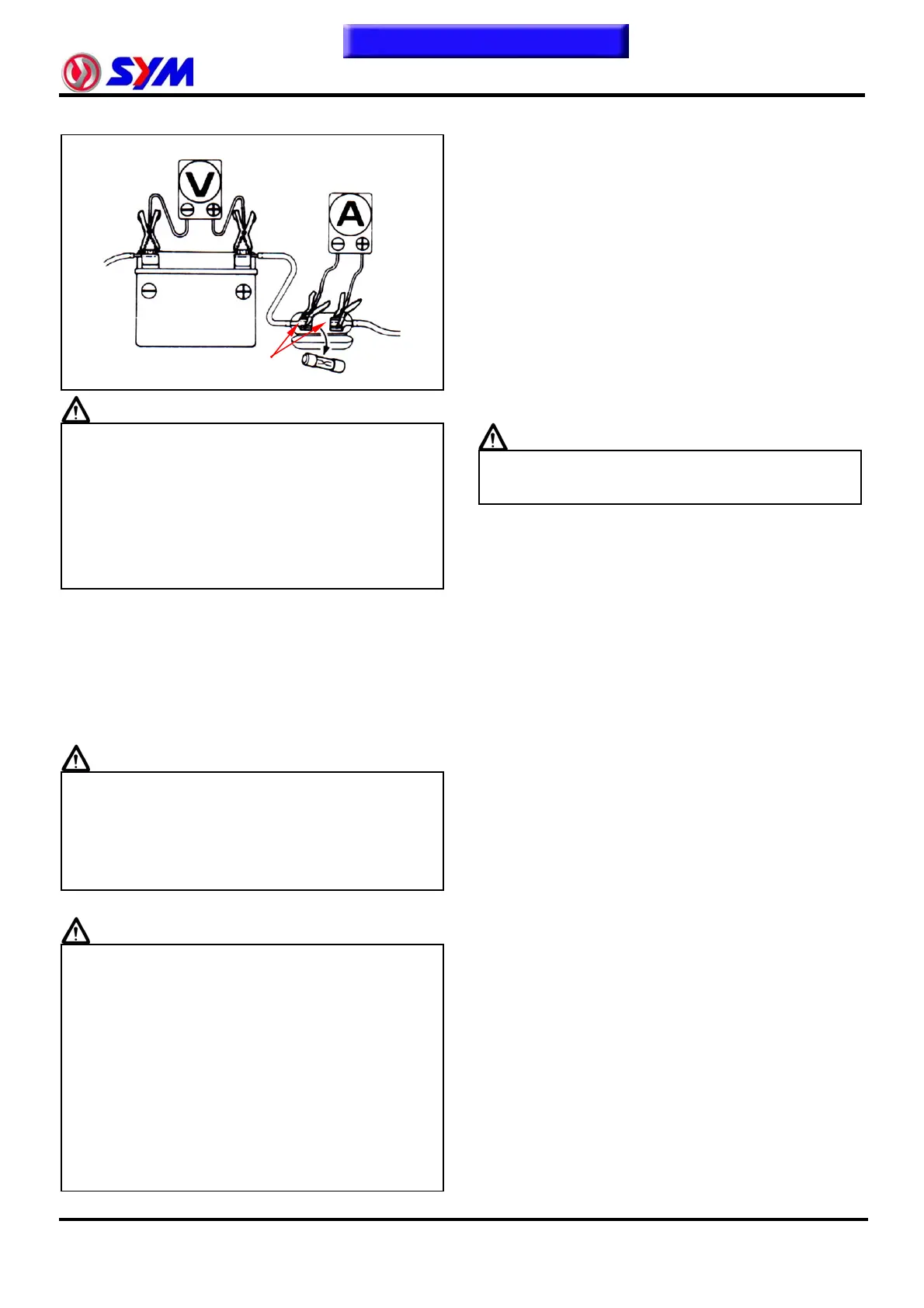
Connect a digital voltmeter to the battery
terminals.
Connect an ampere meter between both
ends of the main fuse.
Caution
z Use a ampere meter having an indication
that the current flows from the positive or
the negative direction. The measurement
should be at zero if the ampere meter is
one direction only.
Caution
y Do not use a short-circuit cable.
y While the starter motor is activated, the
surge current the motor may damage the
ammeter. Use the kick starter to start the
engine.
z The main switch shall be turned to OFF
position during the process of inspection.
Never tamper with the ampere meter and
the cable while there is current flowing
through. It may damage the ampere
meter.
Connect a tachometer.
Turn on the headlight to high beam and start
the engine.
Accelerate the engine to the specified
revolution per minute and measure the
charging voltage.
Charging current:
(headlight off) >0.7A / 2500rpm
>1.2A / 6000rpm
(headlight on) >0.4A / 2500rpm
>1.0A / 6000rpm
Charging controlled voltage
14.5±0.5V / 2100rpm
Caution
z Check if the charging current / voltage is
normal or not after replacing new battery.
The following problems are related to the
charging system; follow the instructions
provided in the checking list to correct it if any
one of the problems takes place.
1. The charging voltage can not exceed the
voltage between two battery terminals and
the charging current is in the discharging
direction.
2. The charging voltage and current are too
much higher than the standard values.
The following problems are not related to the
charging system; correct it if any by following
steps indicate in the checking list.
(1) The standard charging voltage and
current can only reach when the
revolution of the engine exceeds the
specified rpm.
- Bulbs used exceed their rate and
consume too much power.
- The replacement battery is aged and
does not have enough capacity.
(2) The charging voltage is normal, but the
current is not.
- The replacement battery is aged and
does not have enough capacity.
- Battery used do not have enough
electricity or is over charged.
- The fuse of the ammeter is blown.
- The ammeter is improperly connected.
(3) The charging current is normal, but the
voltage is not.
-The fuse of the voltmeter is blown.
Digital meter
Ampere meter
Fuse connector
To this chapter contents

 Loading...
Loading...