© 2019 Thorlabs GmbH63
PAX1000
8.1.6 Polarization in Fibers
Different types of optical fiber affect the polarization state of the propagating light differently.
The most common types of optical fibers are multimode, single mode, and polarization main-
taining.
There are many different types of multimode fibers (MMFs), but all support more than one
guided optical mode. In most cases, MMFs support hundreds or thousands of optical modes.
The exact modes excited by the input light, and the power distribution among them, depend on
input coupling conditions. Each mode travels at a different velocity, and mode mixing occurs at
bends and other points of inhomogeneity within the fiber. The SOP of light that has propagated
through a MMF is totally arbitrary, which makes MMFs incompatible for use with applications
that require preserving polarization states.
Single mode fibers (SMFs) support only one guided mode, but this mode consists of two com-
ponents with orthogonal polarizations. An ideal fiber has a perfectly cylindrical geometry, as
well as an index of refraction profile that is radially symmetric and unchanging down the length
of the fiber. The orthogonal polarization components in an ideal SMF propagate at the same
velocity, as well as independently of one another without mixing. Under these perfect condi-
tions, the input and output SOPs are identical.
In actuality, an optical fiber cannot be fabricated with a perfectly cylindrical geometry. The small
geometrical deviations combined with mechanical stresses, such as those occurring at fiber
bends, cause the effective refractive index of the two orthogonal components to differ by a
small amount (i.e. SMF exhibits low levels of birefringence). Under these conditions, the two or-
thogonal polarization mode components travel at slightly different velocities as they propagate
down the fiber. As this delays one polarization component with respect to the other, propaga-
ting through the SMF transforms the input SOP to an arbitrary output SOP. The effect on polari-
zation is more pronounced for longer transmission distances.
In addition, microscopic inhomogeneities in the refractive index that occur naturally during fiber
fabrication, as well as microbends, can scatter (couple) light from one polarization component
into the other polarization component. The similarity of the effective refractive indices of the two
polarization components facilitates this scatter-induced mixing, which acts to further randomize
the output SOP.
If it is of interest to preserve the polarization state of light as it propagates through an optical
fiber, one approach is to design a single mode fiber that decouples the two orthogonal polariza-
tion components and keeps them from mixing with one another. Such a fiber would be de-
signed so that the effective refractive index for light polarized in one direction differs signific-
antly from that for light polarized in the orthogonal direction. These types of fibers, which are
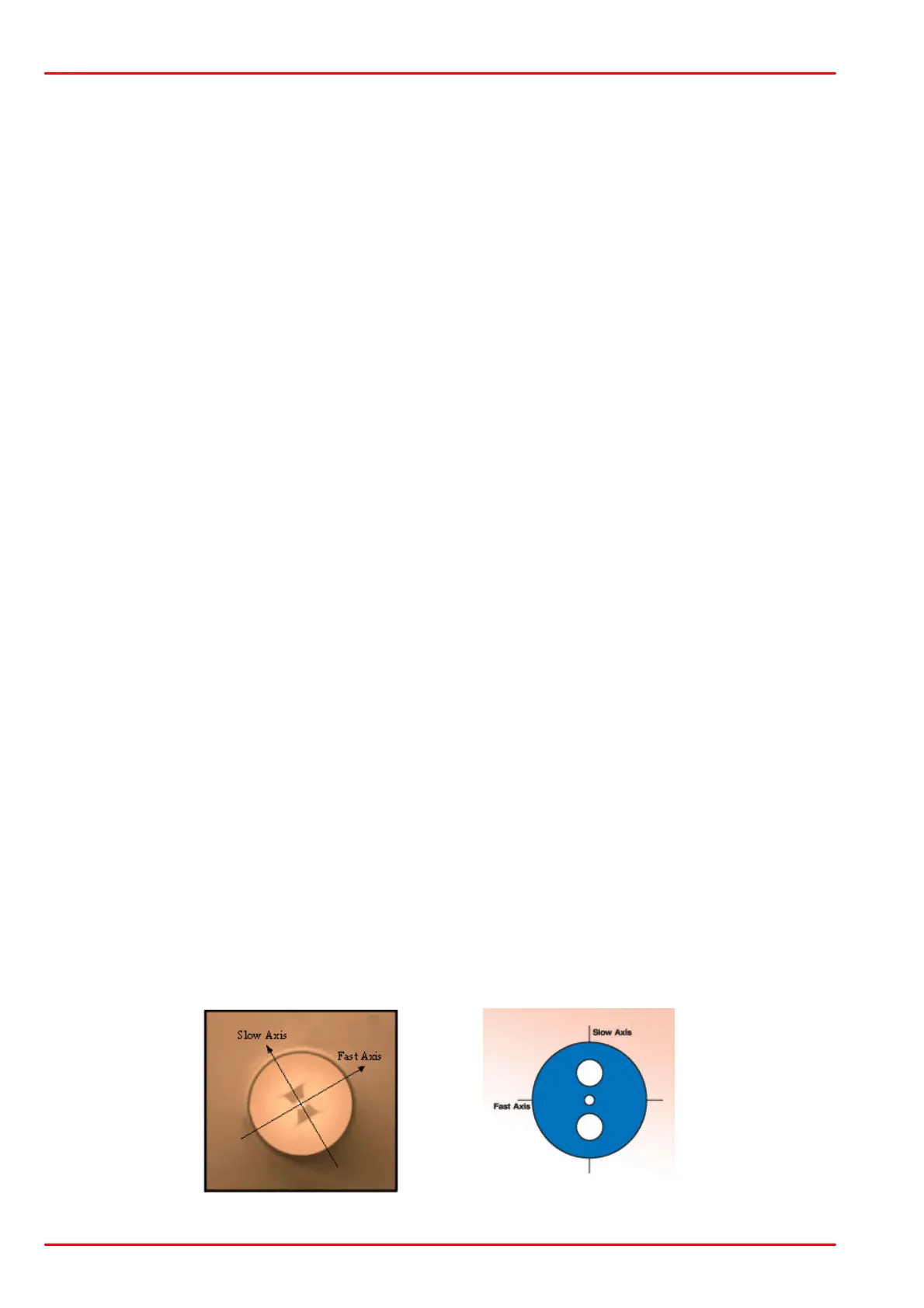
designed to have significant levels of birefringence, are called polarization maintaining fibers
(PMF). They typically use mechanical stress or anisotropic geometries to create the difference
in refractive index. In any PMF fiber, light polarized along one axis of the fiber, the “slow” axis,
travels at a lower velocity than light polarized along the orthogonal, “fast” axis. An example of a
PMF is one with elliptically shaped core, instead of the circularly shaped cores in SMF.
Examples of stress-birefringent PMF fibers are PANDA and Bow-Tie.
 Loading...
Loading...