Ion optics 1-9
Ion optics
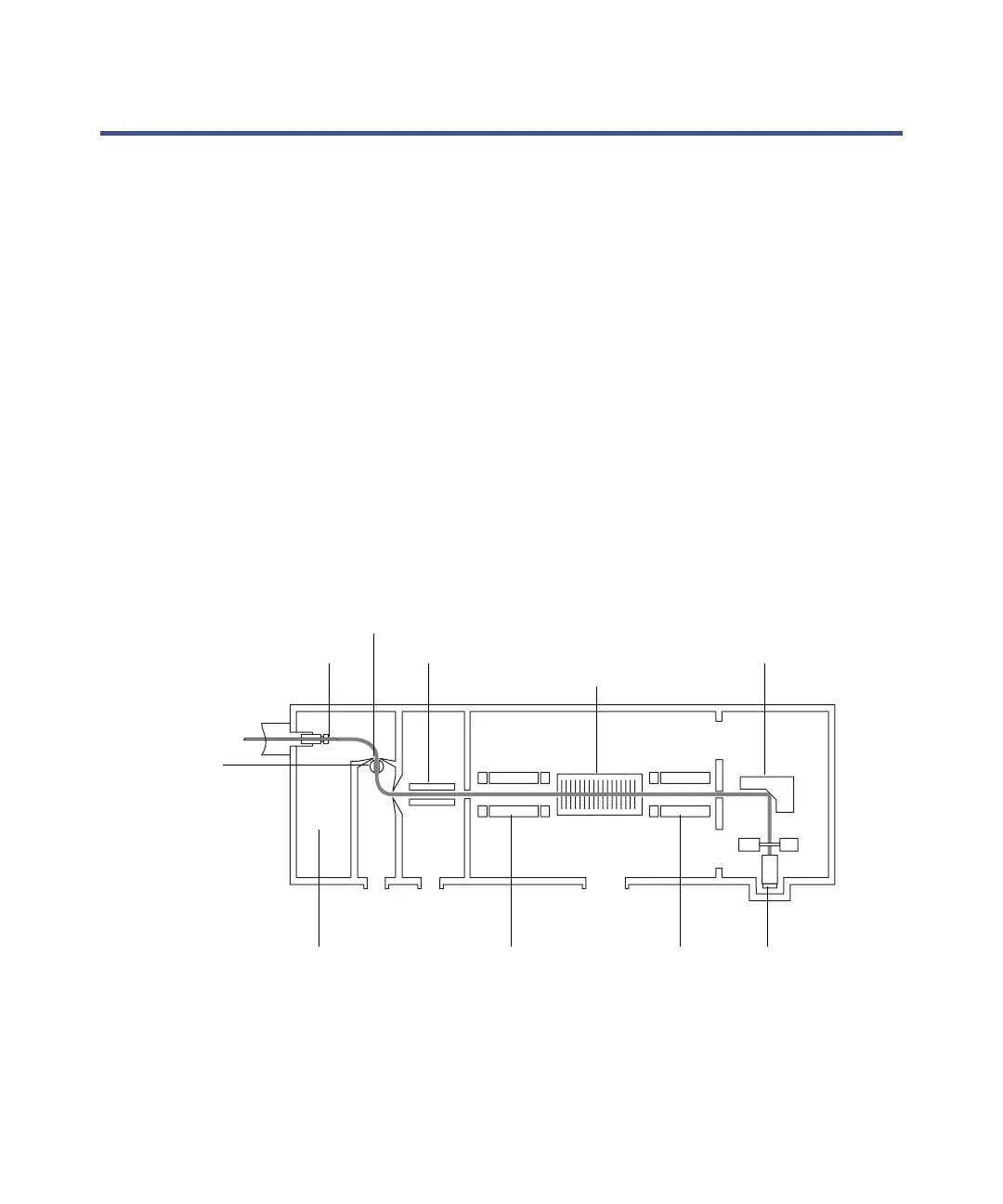
The TQ Detector’s ion optics operate as follows:
• Samples from the LC or Intellistart fluidics system are introduced at
atmospheric pressure into the ionization source.
• The ions pass through the sample cone into the vacuum system.
• The ions pass through the transfer optics to the first quadrupole where
they are filtered according to their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z).
• The mass-separated ions pass into the T-Wave™ collision cell where
they either undergo collision-induced dissociation (CID) or pass to the
second quadrupole. Any fragment ions are then mass-analyzed by the
second quadrupole.
• The transmitted ions are detected by the photomultiplier detection
system.
• The signal is amplified, digitized, and sent to the MassLynx mass
spectrometry software.
Ion optics overview:
Sample cone
Isolation valve
T-Wave collision
cell
Z-Spray ion source Quadrupole 1
(MS1)
Quadrupole 2
(MS2)
Detector
Conversion dynode
Sample inlet Transfer optics
 Loading...
Loading...