Managing MAC Address Table 133
switch records the association between the MAC address of User B and the
corresponding port to the MAC address table of the switch.
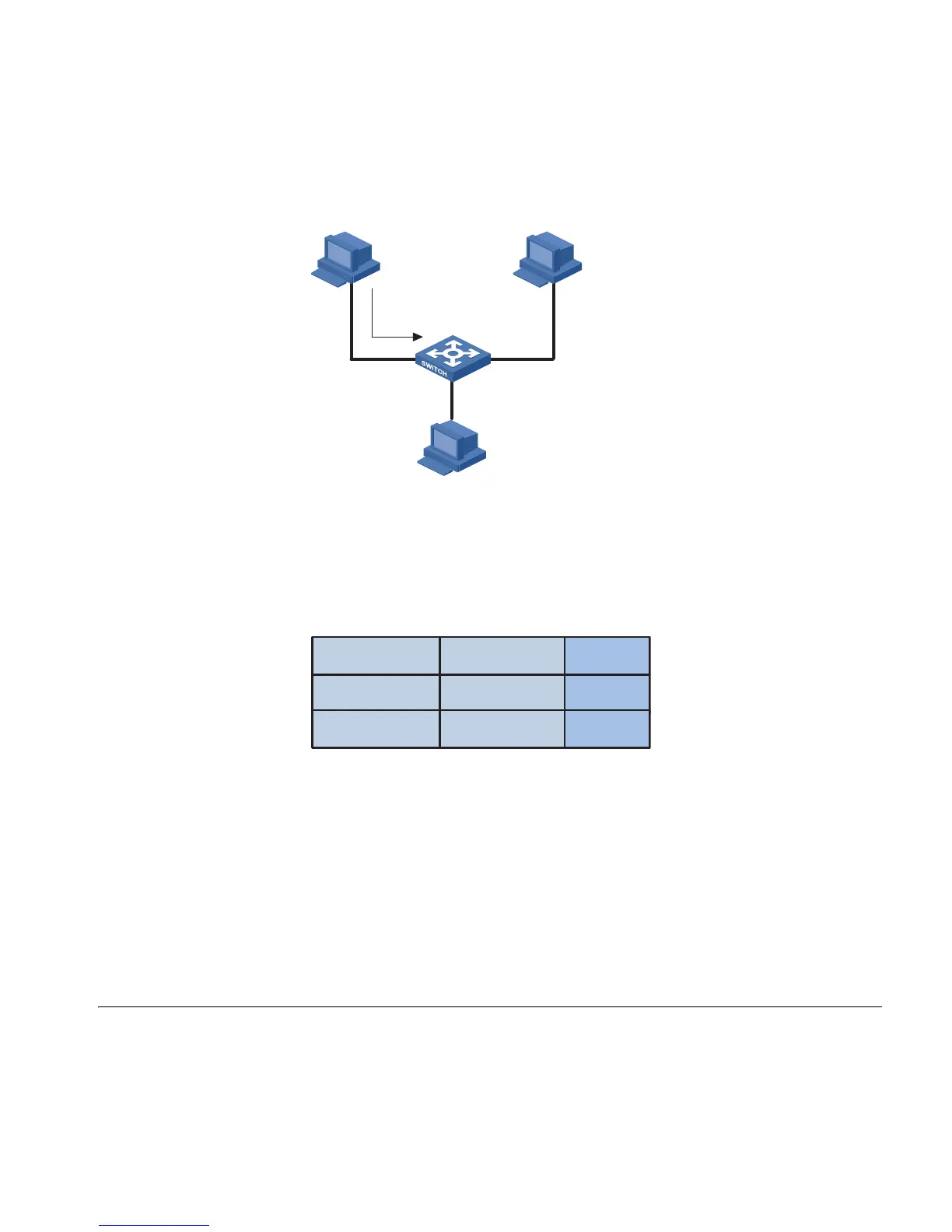
Figure 44 MAC address learning diagram (3)
4 At this time, the MAC address table of the switch includes two forwarding entries
shown in
Figure 45. When forwarding the response packet, the switch unicasts
the packet instead of broadcasting it to User A through Ethernet 1/0/1, because
MAC-A is already in the MAC address table.
Figure 45 MAC address table entries of the switch (2)
5 After this interaction, the switch directly unicasts the communication packets
between User A and User B based on the corresponding MAC address table
entries.
n
■ Under some special circumstances, for example, User B is unreachable or User B
receives the packet but does not respond to it, the switch cannot learn the
MAC address of User B. Hence, the switch still broadcasts the packets destined
for User B.
■ The switch learns only unicast addresses by using the MAC address learning
mechanism but directly drops any packet with a broadcast source MAC
address.
Managing MAC
Address Table
Aging of MAC address table
To fully utilize a MAC address table, which has a limited capacity, the switch uses
an aging mechanism for updating the table. That is, the switch starts an aging
timer for an entry when dynamically creating the entry. The switch removes the
MAC address entry if no more packets with the MAC address recorded in the
entry are received within the aging time.
Eth1/0/1
Eth1/0/3Eth1/0/4
User A
User B User C
Port VLAN IDMAC-address
Ethernet1/0/1 1MAC-A
Ethernet1/0/4 1MAC-B
 Loading...
Loading...











