23
ARP CONFIGURATION
Introduction to ARP
ARP Function Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used to resolve an IP address into a data link
layer address.
An IP address is the address of a host at the network layer. To send a network layer
packet to a destination host, the device must know the data link layer address
(MAC address, for example) of the destination host or the next hop. To this end,
the IP address must be resolved into the corresponding data link layer address.
n
Unless otherwise stated, a data link layer address in this chapter refers to a 48-bit
Ethernet MAC address.
ARP Message Format ARP messages are classified as ARP request messages and ARP reply messages.
Figure 84 illustrates the format of these two types of ARP messages.
■ As for an ARP request, all the fields except the hardware address of the receiver
field are set. The hardware address of the receiver is what the sender requests
for.
■ As for an ARP reply, all the fields are set.
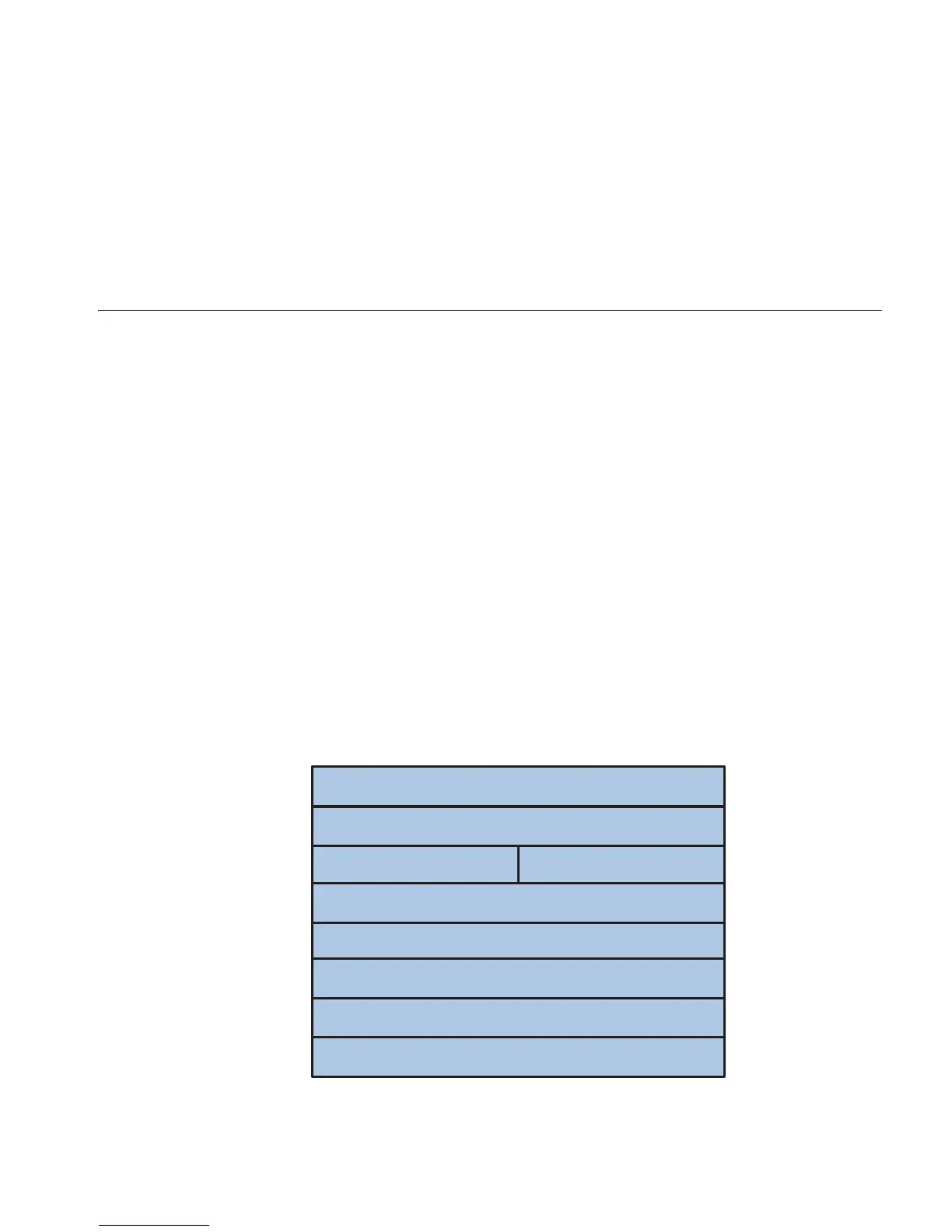
Figure 84 ARP message format
Table 210 describes the fields of an ARP packet.
Hardware type (16 bits)
Protocol type (16 bits)
Length of hardware address
Length of protocol address
Operator (16 bits)
Hardware address of the sender
IP address of the sender
Hardware address of the receiver
IP address of the receiver
Hardware type (16 bits)Hardware type (16 bits)
Protocol type (16 bits)
Length of hardware address
Length of protocol address
Operator (16 bits)
Hardware address of the sender
IP address of the sender
Hardware address of the receiver
IP address of the receiver
 Loading...
Loading...











