MSTP Overview 151
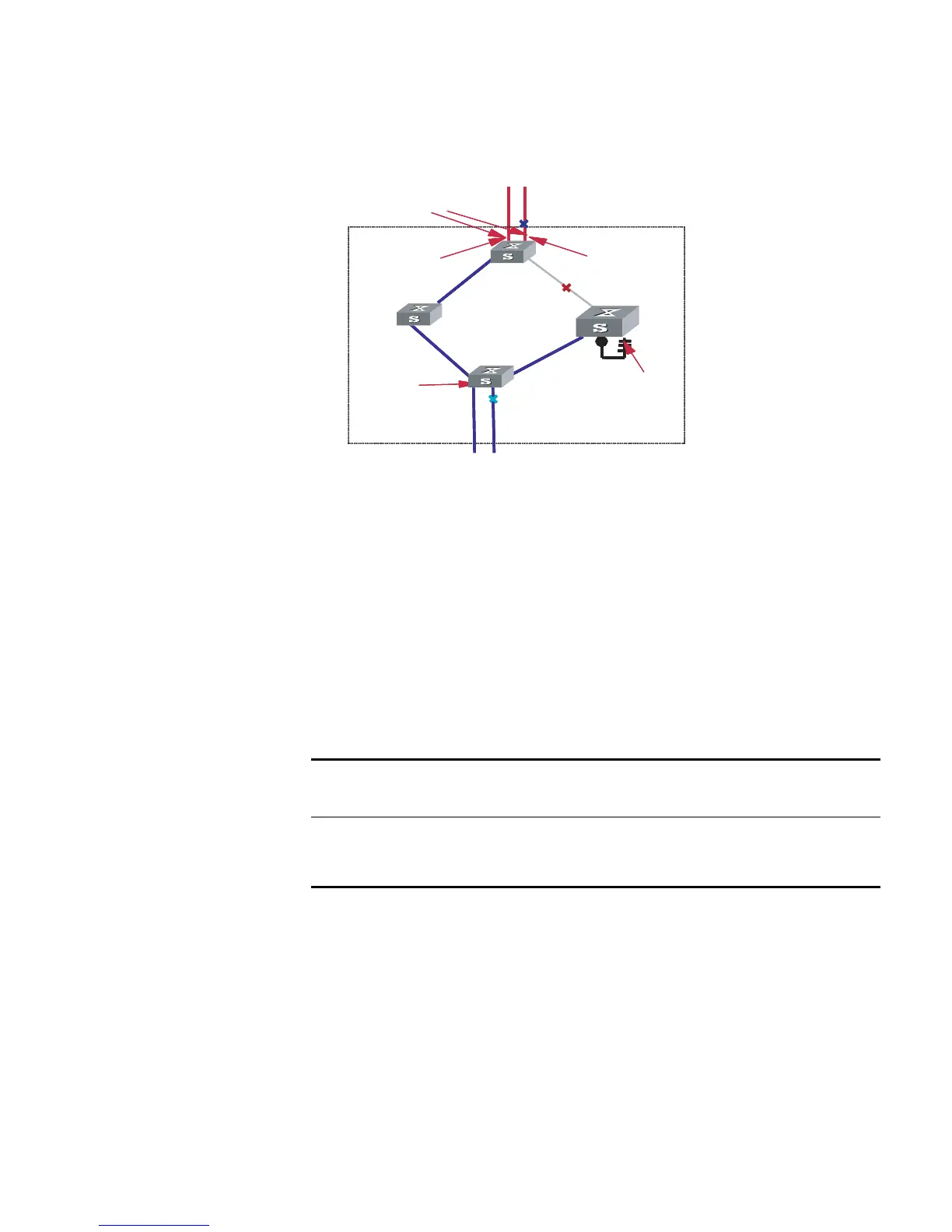
Figure 50 Port roles
Port state
In MSTP, a port can be in one of the following three states:
■ Forwarding state. Ports in this state can forward user packets and receive/send
BPDU packets.
■ Learning state. Ports in this state can receive/send BPDU packets.
■ Discarding state. Ports in this state can only receive BPDU packets.
Port roles and port states are not mutually dependent. Table 100 lists possible
combinations of port states and port roles.
Principle of MSTP MSTP divides a Layer 2 network into multiple MST regions. The CSTs are generated
between these MST regions, and multiple spanning trees (also called MSTIs) can
be generated in each MST region. As well as RSTP, MSTP uses configuration BPDUs
for spanning tree calculation. The only difference is that the configuration BPDUs
for MSTP carry the MSTP configuration information on the switches.
Calculate the CIST
Through comparing configuration BPDUs, the switch of the highest priority in the
network is selected as the root of the CIST. In each MST region, an IST is calculated
by MSTP. At the same time, MSTP regards each MST region as a switch to calculate
the CSTs of the network. The CSTs, together with the ISTs, form the CIST of the
network.
Tab le 100 Combinations of port states and port roles
Port role/
Port state
Root/
port/Master
port
Designated
port
Region edge
port
Alternate
port
Backup port
Forwarding ‚X ‚X ‚X - -
Learning ‚X ‚X ‚X - -
Discarding ‚X ‚X ‚X ‚X ‚X
MST region
C
A
B
D
Port 4
Port 1
Port 2
Connected to the
common root
Edge port
Master
port
Alternate port
Designated
port
Backup
port
Port 3
Port 5
Port 6
MST region
C
A
B
D
Port 4
Port 1
Port 2
Connected to the
common root
Edge port
Master
port
Alternate port
Designated
port
Backup
port
Port 3
Port 5
Port 6
MST region
C
A
B
D
Port 4
Port 1
Port 2
Connected to the
common root
Edge port
Master
port
Alternate port
Designated
port
Backup
port
Port 3
Port 5
Port 6
MST region
C
MST region
C
A
B
D
Port 4
Port 1
Port 2
Connected to the
common root
Edge port
Master
port
Alternate port
Designated
port
Backup
port
Port 3
Port 5
Port 6
 Loading...
Loading...











