194 CHAPTER 15: MULTICAST OVERVIEW
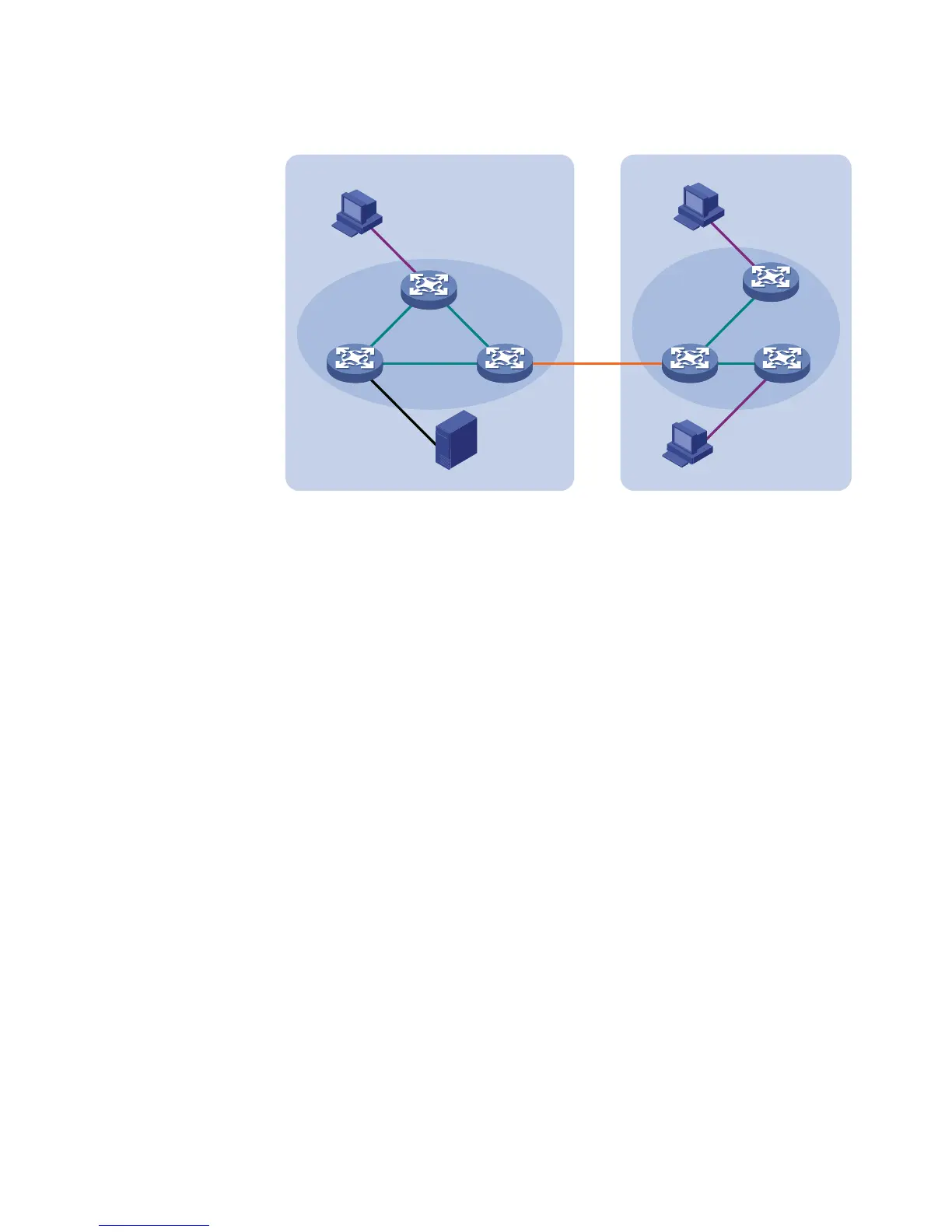
Figure 60 Positions of Layer 3 multicast protocol
■ Multicast management protocols
Typically, the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used between
hosts and Layer 3 multicast devices directly connected with the hosts. These
protocols define the mechanism of establishing and maintaining group
memberships between hosts and Layer 3 multicast devices.
■ Multicast routing protocols
A multicast routing protocol runs on Layer 3 multicast devices to establish and
maintain multicast routes and forward multicast packets correctly and
efficiently. Multicast routes constitute a loop-free data transmission path from a
data source to multiple receivers, namely a multicast distribution tree.
In the ASM model, multicast routes come in intra-domain routes and
inter-domain routes.
■ An intra-domain multicast routing protocol is used to discover multicast
sources and build multicast distribution trees within an autonomous system
(AS) so as to deliver multicast data to receivers. Among a variety of mature
intra-domain multicast routing protocols, protocol independent multicast
(PIM) is a popular one. Based on the forwarding mechanism, PIM comes in
two modes - dense mode (often referred to as PIM-DM) and sparse mode
(often referred to as PIM-SM).
■ An inter-domain multicast routing protocol is used for delivery of multicast
information between two ASs. So far, mature solutions include multicast
source discovery protocol (MSDP).
For the SSM model, multicast routes are not divided into inter-domain routes
and intra-domain routes. Since receivers know the position of the multicast
source, channels established through PIM-SM are sufficient for multicast
information transport.
AS 1 AS 2
Source
Receiver
Receiver
Receiver
PIM
PIM
MSDP
IGMP
IGMP
IGMP
 Loading...
Loading...











