Modes of Operation
Depending on the application, the power supply can be used as a constant
current source or as a constant voltage source.
In order to understand constant current and constant voltage operation, a
numeric example will be used.
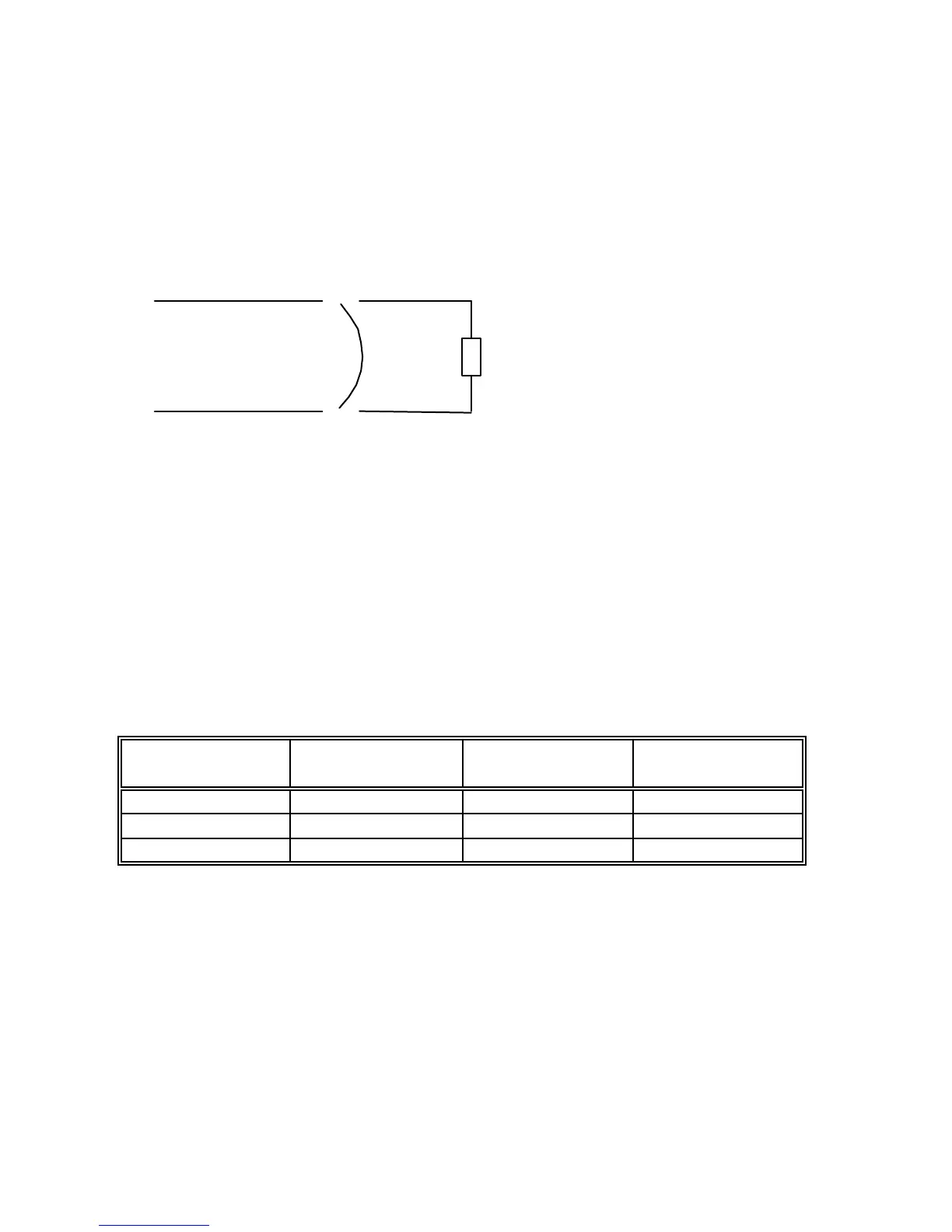
U
out
R
Let’s consider a resistor connected to the output terminals of the power supply
(R resistor).
Limit (programmed) values are:
U
lim
=5V
I
lim
=2A
U
out
and I
out
are the voltage and current values measured at the output
terminals of the power supply.
Depending on the resistor value, the power supply will pass from one mode of
operation to another
R (Ù) U
out
(V) I
out
(A) Mode of
operation
10 5 0.5 CV
5 5 1 CV
1 2 2 CC
In constant voltage mode, programmed voltage value is equal with the voltage
value measured at the output terminals of the power supply. (U
out
= U
lim
).
Using Ohm’s law, depending on the resistor’s value, output current value can
be calculated and it is smaller than current limit value (see first and second
rows of the table).
The power supply will remain in CV operation as long as the limit current
value is greater than output current value.
 Loading...
Loading...











