Specifications and Site Preparation Polycold Cryochiller
Cooling Water Installation and Operation Manual
Brooks Automation
3-8
214072 Revision B
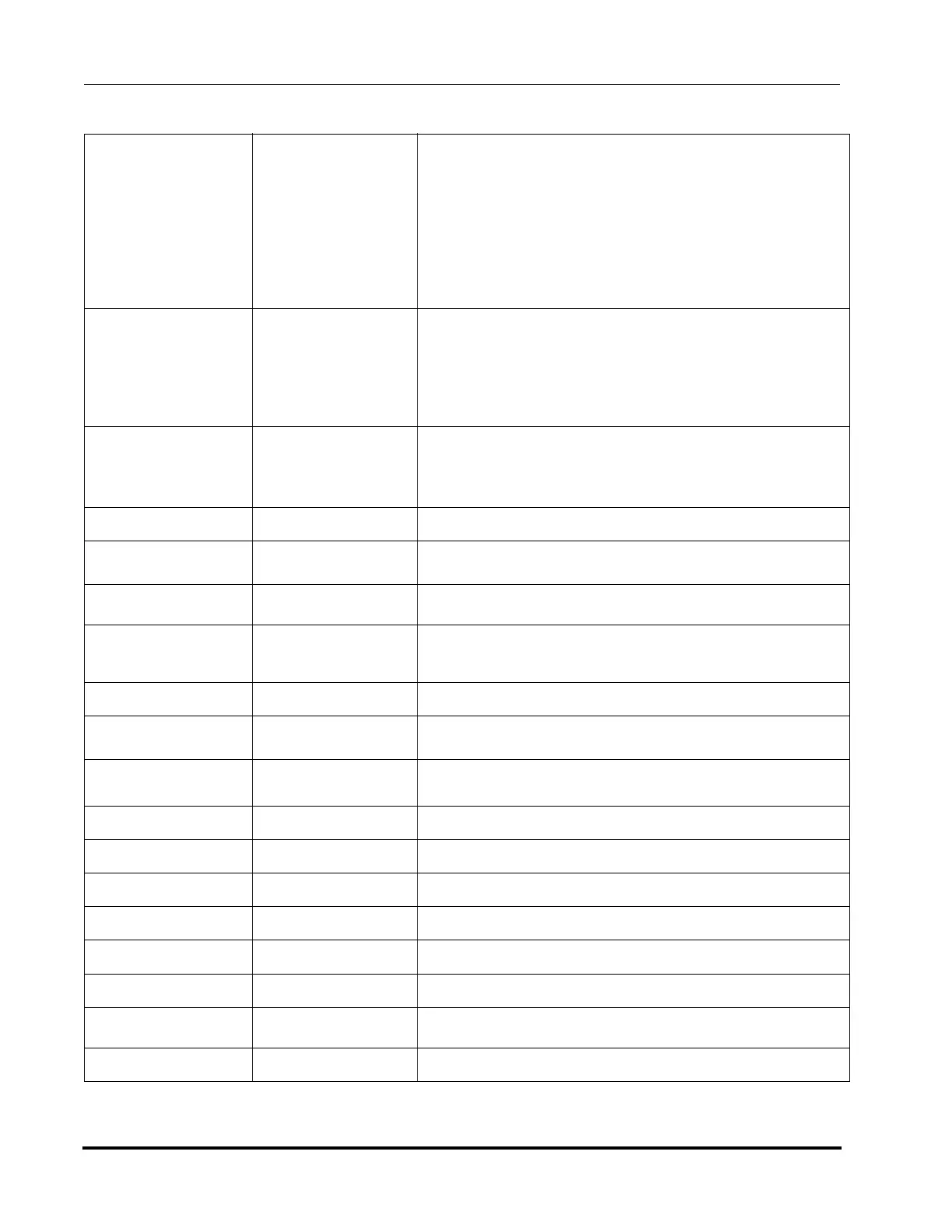
Total hardness
(°dH)
3.9 – 8.4 °dH
(70 - 150 ppm)
Maintain recommended levels to reduce scaling
Scaling affects heat transfer and can lead to crevice
corrosion.
Values below 100 ppm are strongly recommended as
there is a higher risk for scale above 5.6 °dH (100 ppm).
(Note: This assumes the majority of hardness is due to
calcium carbonate, CaCO
3
)
Alkalinity (HCO
3
)
70 - 250 ppm
Low levels cause copper corrosion, dissolution and
release into water.
High levels can cause increased chance of scaling.
Note: The alkalinity of interest is “methyl orange”
alkalinity or “m alkalinity”
Electrical
Conductivity
10 - 600 μS/cm
Conductivity above the recommended level indicates a
high concentration of ionic substances which results in
high dissolved solids and potential for particles and
scale.
Chlorides (Cl
-
)
< 100 ppm Higher levels can cause pitting corrosion.
Free Chlorine (Cl
2
)
< 0.5 ppm
Higher levels accelerates copper leaching by oxidation
and dissolution of the metal surface.
Sulphate (SO
4
2-
)
< 100 ppm
Levels higher than 100 ppm increase the risk of copper pitting
corrosion.
Electrical Resistivity 2,000 - 100,000 Ω-cm
Resistivity is the inverse of Conductivity.
Higher resistivity above 100,000 Ω-cm can result in copper
corrosion.
Hydrogen Sulfide (H
2
S)
< 0.05 ppm Higher levels can lead to corrosion, pitting, and copper fatigue.
Free (aggressive)
Carbon Dioxide (CO
2
)
< 5 ppm Higher levels can indicate oxidation of metals.
Nitrate (NO
3
-
)
< 100 ppm
Nitrate ions help to inhibit corrosion, similar to Sulphate (SO
4
2-
)
Higher levels increase the risk of copper pitting corrosion.
Iron (Fe) < 0.3 ppm Higher levels can increase the risk of galvanic corrosion.
Aluminum (Al) < 0.2 ppm Higher levels can increase the risk of galvanic corrosion.
Manganese < 0.5 ppm Higher levels can increase the risk of galvanic corrosion.
Silica < 50 ppm
Total Copper (Cu) < 0.3 ppm Higher levels can increase the risk of galvanic corrosion.
HCO
3
-
/ SO
4
2-
> 1 ppm Lower levels below 1 ppm add risk of copper pitting
Turbidity < 5 FTU
Higher turbidity levels are signs of high levels of microorganisms.
Clean water is less likely to form deposits.
Ammonium (NH
4
+
)
< 2 ppm Higher levels increase the risk of copper corrosion.
Table 3-7: Water Purity Properties
 Loading...
Loading...