– 49 –
AR-1 Economy of Materials (Cross-sectional Area)
Explanation
When the distance from the edge of the sheet metal to the bend is x (cm) and the cross-
sectional area is y (cm
2
), y can be expressed by the following expression.
y = x (20 – 2x) = 20x – 2x
2
(0 x 10)
Differentiating y by x gives us:
y = 20 – 4x = 4 (5 – x)
Determining the value of x when y= 0 produces the following:
4 (5 – x) = 0 x = 5
This means that when x = 5, the value of y is at its maximum, so the sheet metal should be bent
at the two points that are 5 cm from either of its sides.
The following graph shows the relationship between the bend points and cross-sectional area.
The following is the operation required on a graphic scientific calculator, which also makes
the calculation easier to understand.
Operation
•
Expression Input
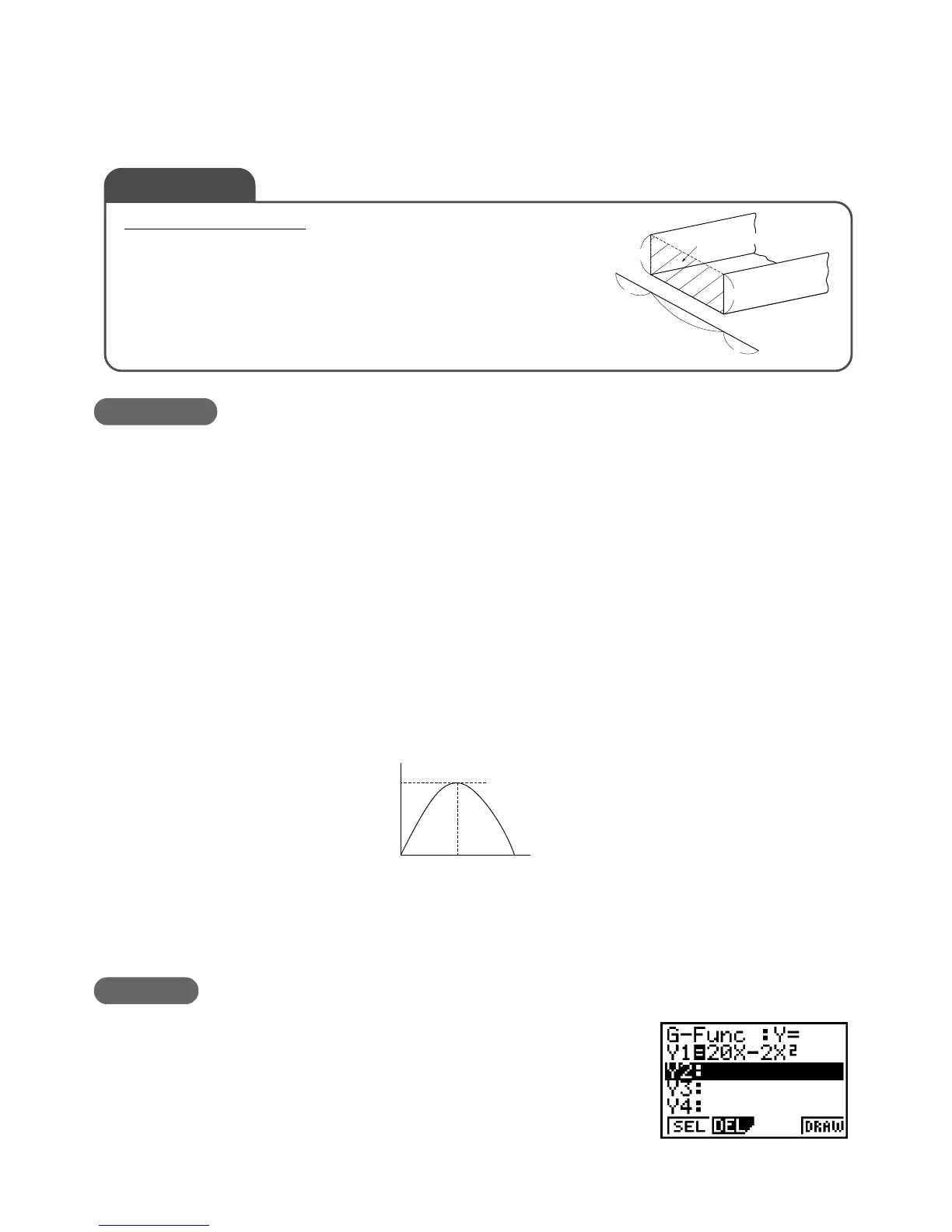
From the Main Menu, enter the GRAPH Mode.
After making sure the cursor is located at Y1:, perform
the following key operation.
20T-2Txw
Economy of Materials
You want to form a piece of sheet metal to make a shape like
the one shown in the illustration nearby, in order to create the
largest possible cross-sectional area. Draw a graph to deter-
mine the distance from the edge of the sheet metal where it
should be bent in order to produce the largest possible area
using a piece of sheet metal that is 20 cm wide.
Exercise 1
Cross-sectional area
x
x
Unit: cm
20–2
x
x
x
0510
50
y
x
(0<x<10)
y = 20x
–
2
x
2
JIKKYO SHUPPAN CO., LTD.: SHIN KOGYO SURI
(NEW EDITION)

 Loading...
Loading...