Chapter 6 Applied Instructions
6-6
6.1.2 Explanation of Comparison Instructions
API
Instruction code Operand
Function
0000~
0005
D
LD※
S
1
, S
2
Comparing the values
Device
X Y M S T C HC D L SM SR E PR K 16# “$” DF
Pulse instruction 16-bit instruction (5 steps)
32-bit instruction (5 steps)
AH500 AH500
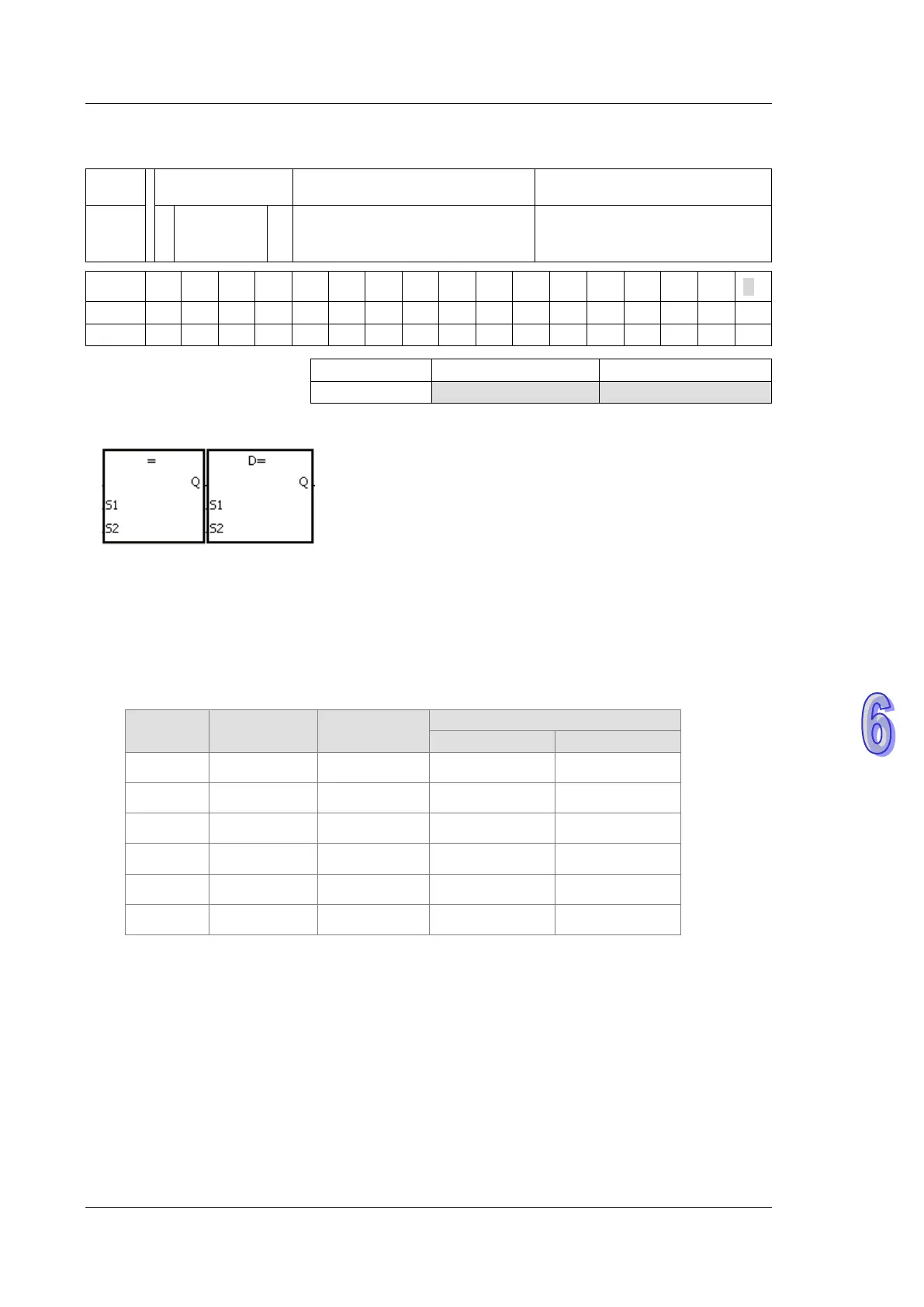
Symbol:
Taking LD= and DLD= for example
S
1
:
Data source 1
Word/Double word
S
2
:
Data source 2
Word/Double word
Explanation:
1. The instructions are used to compare the value in S
1
with that in S
2
. Take the instruction LD=
for example. When the comparison result is that the value in S
1
is equal to that in S
2
, the
condition of the instruction is met. When the comparison result is that the value in S
1
is not
equal to that in S
2
, the condition of the instruction is not met.
2. Only the 32-bit instruction can use the 32-bit counter.
number
instruction
instruction
Comparison operation result
0000
LD= DLD= S
1
=S
2
S
1
≠S
2
0001
LD<> DLD<>
S
1
≠S
2
S
1
=S
2
0002
LD> DLD> S
1
>S
2
S
1
≦S
2
0003
LD>= DLD>= S
1
≧S
2
S
1
<S
2
0004
LD< DLD< S
1
<S
2
S
1
≧S
2
0005
LD<= DLD<= S
1
≦S
2
S
1
>S
2
Example:
1. When the value in C10 is equal to 200, Y0.10 is ON.
2. When the value in D200 is greater than -30, Y0.11 keeps ON.
3. When the value in (C201, C200) is less than 678,493, or when M3 is ON, M50 is ON.

 Loading...
Loading...











