AH500 Programming Manual
6-392
6.19.2 Explanation of Communication Instructions
API
Instruction code
Operand Function
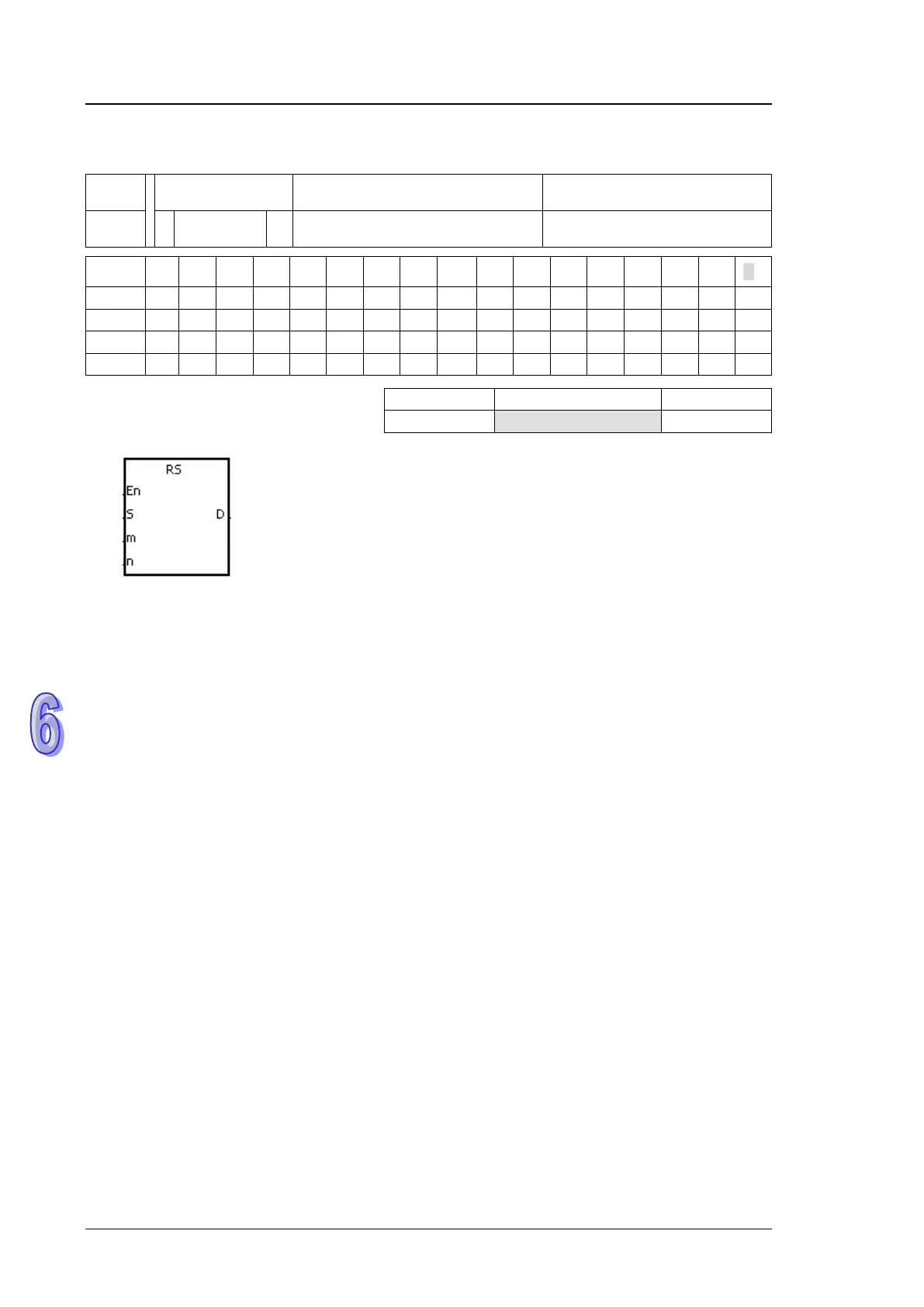
1800 RS
S, m, D, n
Transmitting the user-defined
communication command
Device
X Y M S T C HC D L SM SR E PR K 16#
“$” DF
Pulse instruction
16-bit instruction (9 steps)
32-bit instruction
- AH500 -
Symbol:
S
:
Initial transmission device Word
m
:
Number of data which is sent Word
D
:
Initial reception device Word
n
:
Number of data which is received Word
Explanation:
1. The instruction is for the CPU module equipped with RS-232/422/485. Once the setups are
done in the S, m, D, and n, the instruction can be executed. When using the E (modifying
device) in the beginning position, do not change the values in E during operation to avoid
errors in data reading or writing.
2. The m and n can be 0, when the instruction is used for sending or receiving data.
3. The instruction can be used several times in the program, but one instruction is executed at a
time.
4. During the execution of the instruction RS, the data alteration is invalid.
5. The maximum transmission length (m, n) is 500 words.
6. Modes of 8-bit or 16-bit (SM106/SM107) for this instruciton can be selected by setting up the
special register.
7. If the communication protocol used with the device is consistent with MODBUS, users can use
the instruction MODRW. Please refer to the related instruction explanations for more details.
Communication setup
Before executing the serial communication instruction, users need to set up the communication
methods (RS232/485, transmission speed). Users can set up the PLC communication port in
HWCONFIG or set values in the relative spcial auxiliary relays to set up the communication.
1. Please refer to ISPSoft manual for more information on communication setups in HWCONFIG.
2. For setting values, communications, register formats in the relative special auxiliary relays,
plese refer to the additional remarks in this section.
Data transmission format
There are 2 modes for data transmission, 8-bit mode and 16-bit mode. For the 16-bit mode, data is
divided into the high 8-bit data and the low 8-bit data. As for the 8-bit mode, the high 8-bit data is
ignored, and the low 8-bit data can be sent or received.

 Loading...
Loading...











