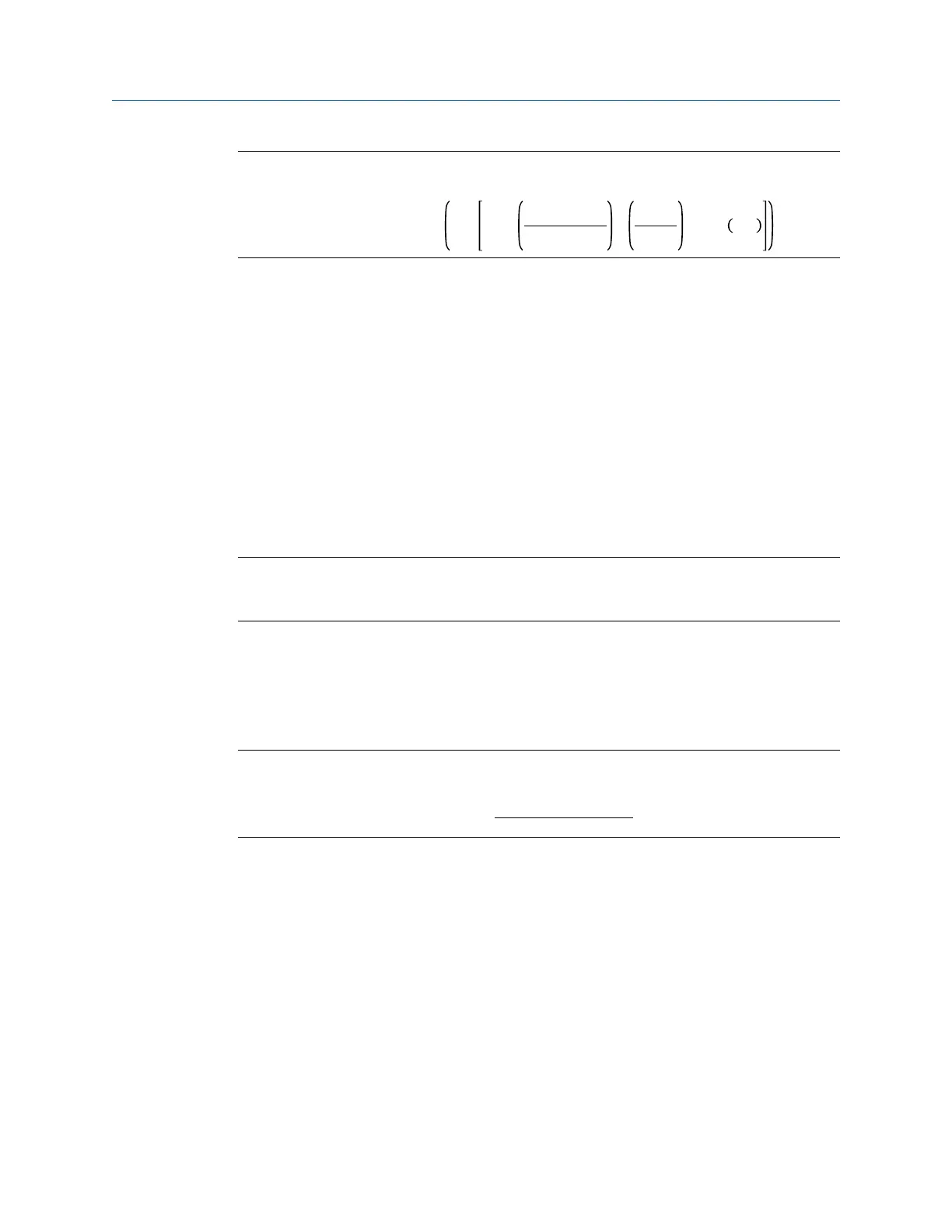
Equation 4-4
= 1 + 0.5 •
ℎ
2
ℎ,
2
•
ℎ
2
ℎ
2
• tan
2
75°
For all other port angles,
PortAngleFactor=1
where
V
chord
=
chord average gas velocity (m/s) (FlowVelA ... FlowVelD)
C
chord
=
chord average sound velocity (m/s) (SndVelA ... SndVelD)
L
chord
=
chord "L" dimension (m) (LA ... LD)
X
chord
chord average transit time in the upstream direction (s) (MeanTmA1 ... MeanTmD1)
t
1
=
chord average transit time in the upstream direction (s) (MeanTmA1 ... MeanTmD1)
t
2
=
chord average transit time in the downstream direction (s) (MeanTmA2 ... MeanTmD2)
Note
that a positive chord gas velocity indicates flow in the forward direction whereas a negative chord
gas velocity indicates flow in the reverse direction.
4.4.1
Average sound velocity
The Average Sound Velocity is calculated as the average of the active chord sound velocity
measurements as shown in the equation below:
Equation 4-5
=
ℎ
•
ℎ
ℎ
where
C
Avg
=
average sound velocity (m/s) (AvgSndVel)
C
chord
=
chord average sound velocity (m/s) (SndVelA... SndVelD)
NumActiveChords =
number of active chords
4.4.2 Optional AGA10 sound velocity calculation and
comparison
The Daniel 3410 Series Gas Ultrasonic Flow Meter offers an option to calculate the sound
velocity (using AGA10 equations and gas property data) and compare the result to the
meter- measured sound velocity on an hourly basis.
Measurement
22 3410 Series Gas Ultrasonic Flow meters

 Loading...
Loading...