5-21 MINI-LINK BAS
EN/LZB 111 0542 P2B Technical Description
4. Ranging permit: the specified NU is requested to sign on.
5. Blanking permit: this corresponds to nothing being sent upstream.
When allowed by the above types of permits, a NU will send a slot
back to the node. This slot can be of 3 types:
• ATM slot: includes one ATM cell from the NU. If no ATM
traffic cell is available, an idle cell will be sent.
• Control minislot includes queues status in the NU.
• Ranging slot: the modem will use this slot to measure distance
and power of the NU.
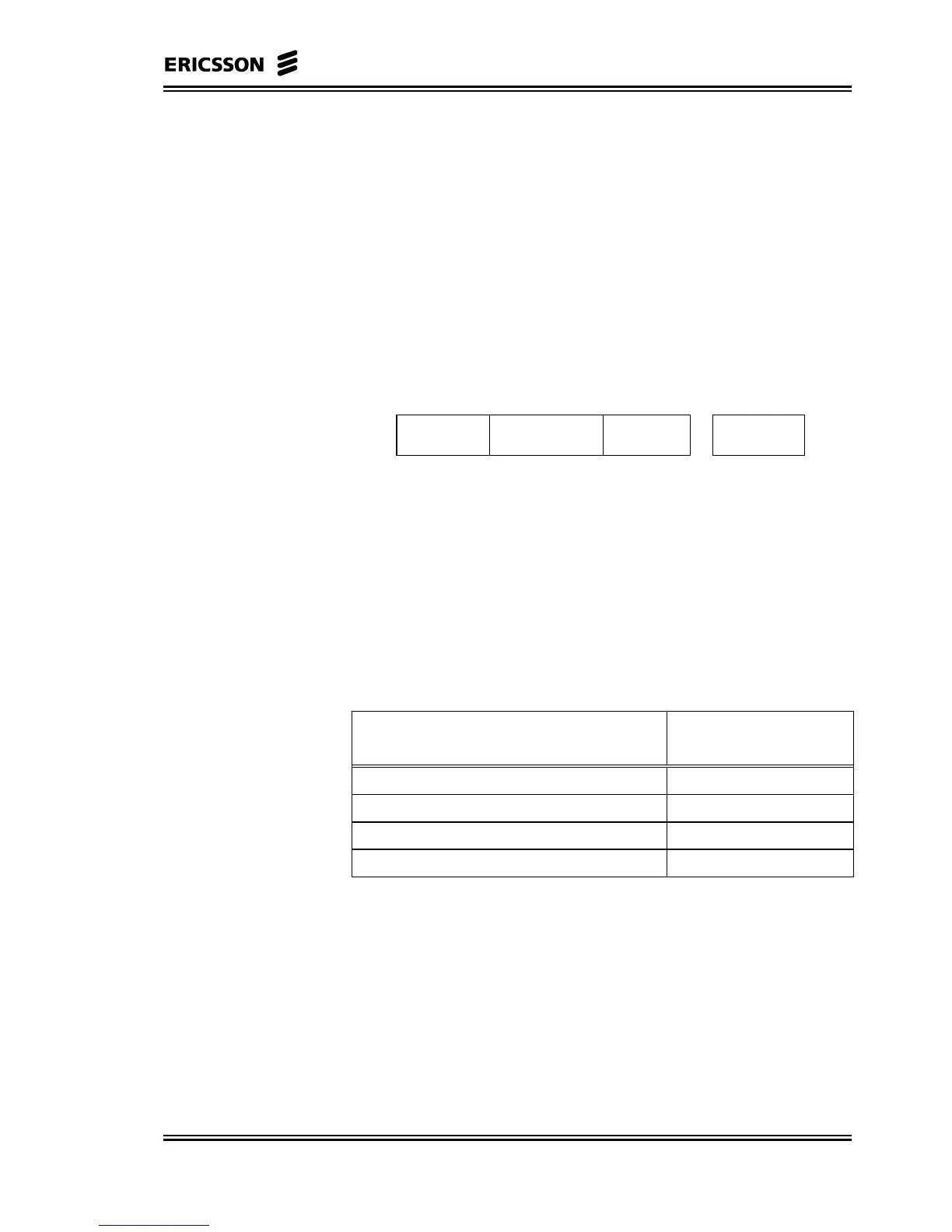
The structure of the permit field is depicted in Figure 5-9.
Permit type Terminal/Group Address#
+
CRC-8
(CRC-P)
4 bits 6 bits 6 bits 8 bits
Not Used
Figure 5-9 Downlink Permit Field Plus CRC-8
The permit field allows different permit types and has a capability to
address up to 64 NUs and for each NU can specify 64 lines, VC
connections.
In the permit field is also foreseen a CRC-8 aimed to check for error
and validate the information. In case of errors detection the permit is
deemed invalid and discarded.
In the following table the different types of permit are reported
together with a description of the usage and the addressing capability.
Permit Description
Terminal/Group Address
field (6 bits in hex)
CBR Polled Terminal Address
UBR Terminal Address
Ranging Terminal Address
Request Polling Group Address
Terminal identification is done through the terminal address for which
6 bits are provided. Therefore up to 64 terminals can be addressed.
Terminals are grouped in pools of 8 in order to minimise the
bandwidth usage in the polling procedure. A terminal group is
identified through the 3 most significant bits of the Terminal address.
In the following figure the structure of the request field (minislot) is
reported. The request fields are sent from terminals to the node in
answer to node polling.
 Loading...
Loading...