MINI-LINK BAS 5-22
Technical Description EN/LZB 111 0542 P2B
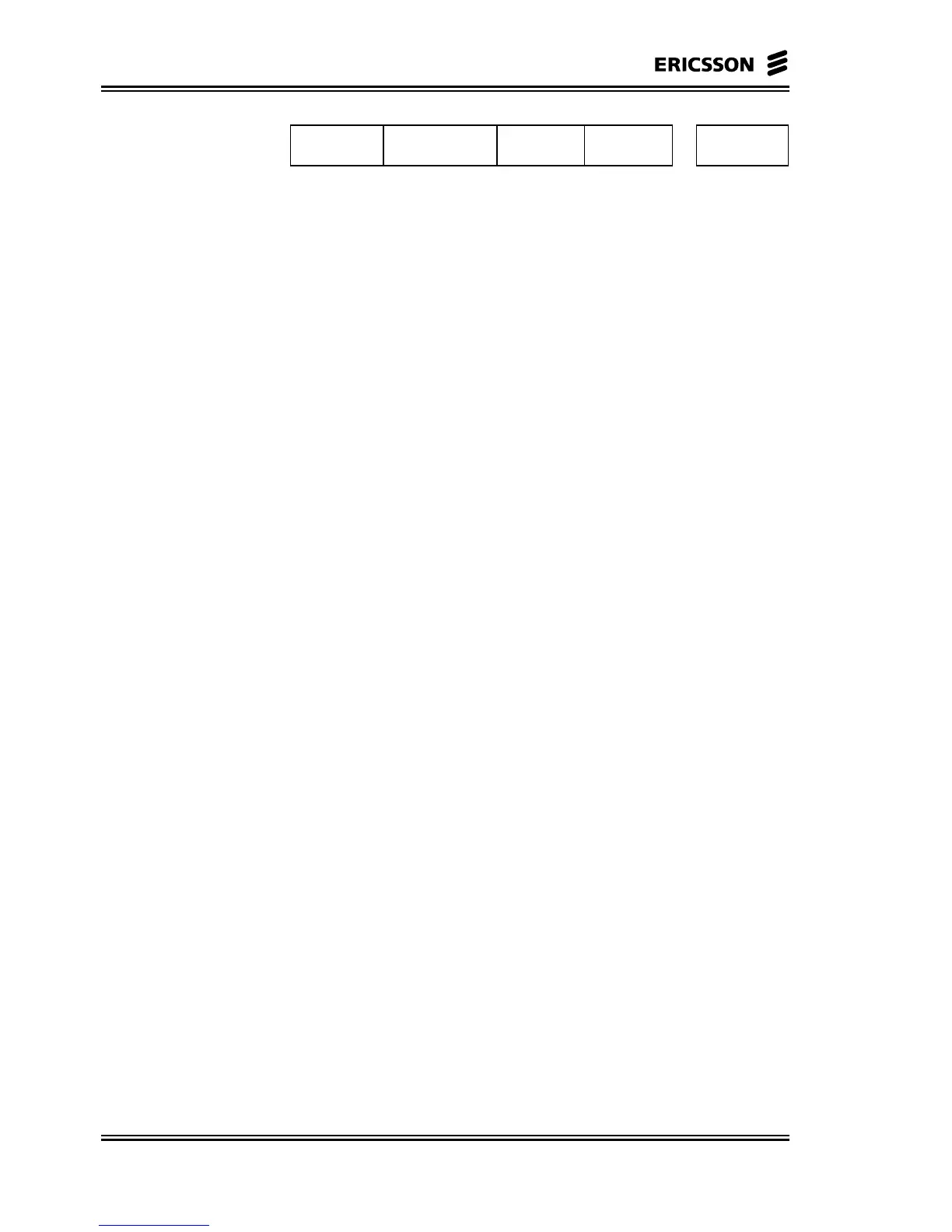
CBR
request
Not Used
+
CRC-4
4 bits 6 bits 6 bits 8 bits
Not Used
6 bits
UBR
request
Figure 5-10 Request Field, Minislot
The request field contains the present buffer status of the addressed
NU in terms of the number of ATM cells that are in each buffer at the
polling instant. The maximum request value for each queue is 63,
together with the polling rate, that limits the maximum achievable
data rate for a terminal.
Three values of the polling cycle are possible. For each of these cycles
the possible maximum bit rate is calculated for an AT which is always
authorised to transmit its cells, capability which is not an effective
band, for more information see table at paragraph 5.4.1.1.
5.5.1 Sign-On
The sign-on procedure is aimed to bring a terminal into service.
Sign-on could be required either for a new terminal to be brought into
service, initial sign-on, or for a terminal that lost contact with node
because of a failure occurrence. Initial sign-on is always initiated by
command from the CP.
A unique number or string, called terminal identity, is associated to
each terminal. The terminal identity is set by an ACT during
installation and is stored in non-volatile memory.
The terminal identity must also be set in the CP from EM in order to
make the sign on successful.
The sign-on procedure foresees two sub procedures to be
accomplished, namely the distance ranging and the power ranging.
After the completion of the distance and power ranging a little time is
required to allow control loops to get lock condition before the
sign-on procedure is assumed to be completed.
5.5.2 Distance Ranging
Distance ranging is made when a NU has to be signed on. The purpose
of this procedure is to measure the distance to the new NU, and then
to adjust the delay to a desired value.
In fact all NUs are to be located virtually at the same distance,
measured in delay time, from the RN. This delay is fixed to a
reference value, the maximum Round Trip Delay (RTD), and is
calculated between the moment at which a data permits are emitted
from the node to the moment at which the corresponding slot is
received. This adjustment is done setting a programmable delay in the
modem at the considered NU.
 Loading...
Loading...