SecoGear Medium-voltage Switchgear Application and Technical Guide DET-882
System and Equipment Protection
34 ©2017 General Electric All Rights Reserved
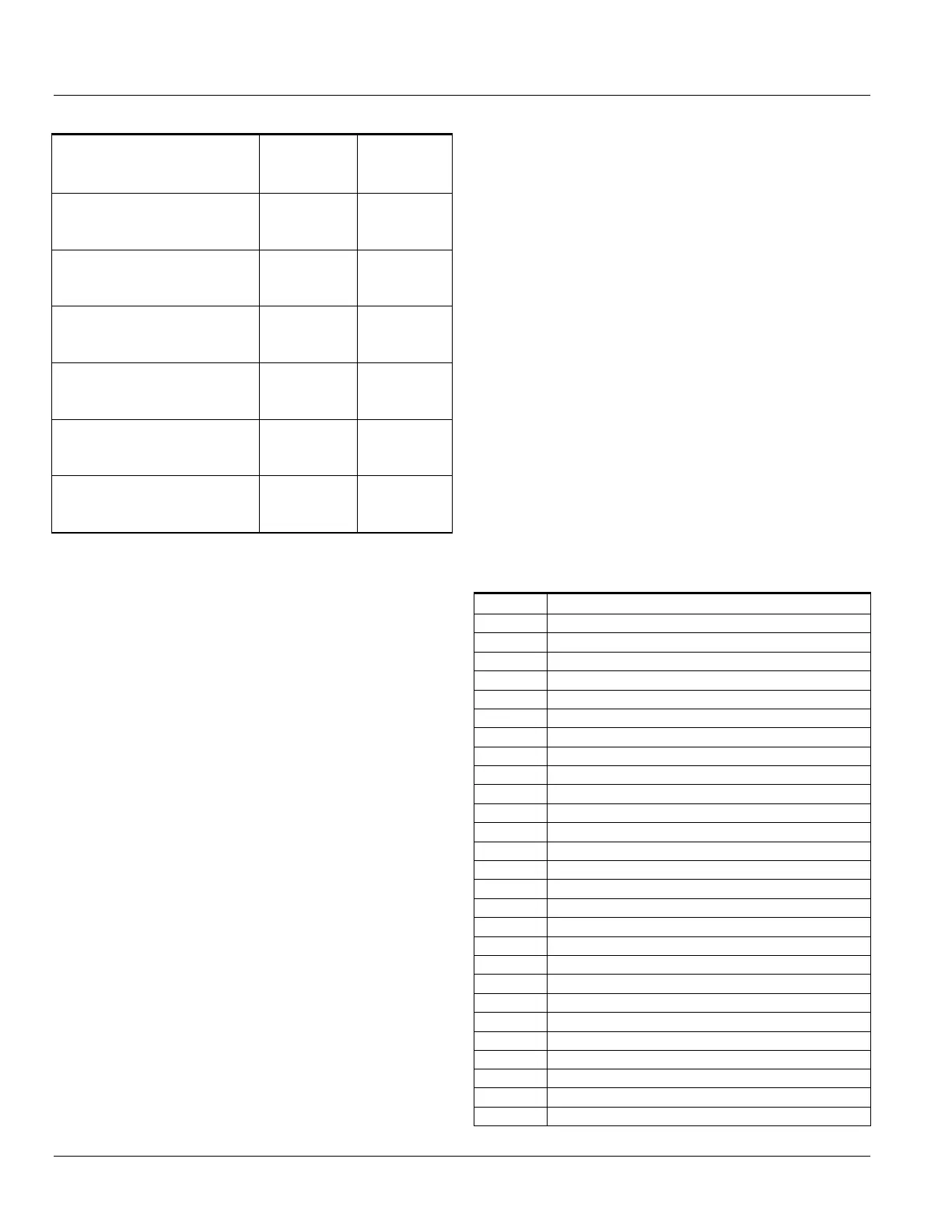
Table 4-3: Multiple Ratio CTs
Accuracy
Accuracy
50/100/150/200/250
C100 C200
100/200/300/400/500
C200 C400
300/400/500/800/1100
C200 C400
300/400/500/800/1100/
C200 C400
300/500/800/1000/1100/
C200 C400
500/1000/1500/2000/2500
C200 C400
Metering and Test Block
Current transformer relaying accuracy and excitation
characteristics are particularly important when considering
lower-rated current transformers on systems with high
available short-circuit currents and for all differential relay
applications. Excitation characteristics and accuracy
classes are available upon request.
Standard voltage transformers are mounted in rollout
trays, with primary and secondary fusing. Models are
available rated for line-to-line, or line-to-neutral
applications with system voltages from 2400 V to 14400 V.
Control and Transfer Switches
GE Series 95 control and transfer switches are furnished, or
as specified. Test blocks and plugs can be furnished to
facilitate circuit testing, using portable instruments and
meters. The current test block is arranged so that the
current circuit is maintained when the plug is removed
from the block.
Surge Protection
Every medium-voltage AC power system is subject to
transient voltages in excess of normal operating voltages.
There are many sources of transient voltages. The most
prominent ones are
• Lightning
• Physical contact with a higher voltage system
• Resonant effects in series inductive-capacitive circuits
• Repetitive restrikes (intermittent grounds)
• Switching surges
To mitigate the effects of these transient voltages, both
surge arresters and, where appropriate, surge capacitors
should be used. Surge arresters limit the crest voltage of a
voltage surge.
Surge capacitors reduce the steepness of the voltage wave
which reaches the protected equipment. Surge capacitors,
to be most effective, should be located as close to the
protected equipment (usually motors) as possible with
minimum inductance connections
ANSI DEVICE FUNCTIONS AND ACRONYMS
Table 4-4: ANSI Device Codes
Time delay starting or closing relay
Checking or interlocking relay
Control power disconnecting device
Speed or frequency, matching device
Data communications device
Shunting or discharge switch
Accelerating or decelerating device
Starting to running transition contractor
Electrically operated valve
Equalizer circuit breaker
Temperature control device
Synchronizing or synchronize-check device
 Loading...
Loading...