Chapter 1. Assembly Language and Processors
8080
8085
IACCUMULATORl
FLAGS
I
I
B
I
C
I
HIGH
LOW
INSTRUCTION I
I
STACK
!
POINTER
I
DECODER
I
D
I
E
I
I
PROGRAM
!
COUNTER
I
DATA
BUS
LATCH
J.-
I
H
I
L ADDRESS
I
BUS
LATCH
J
+
•
ROM
RAM
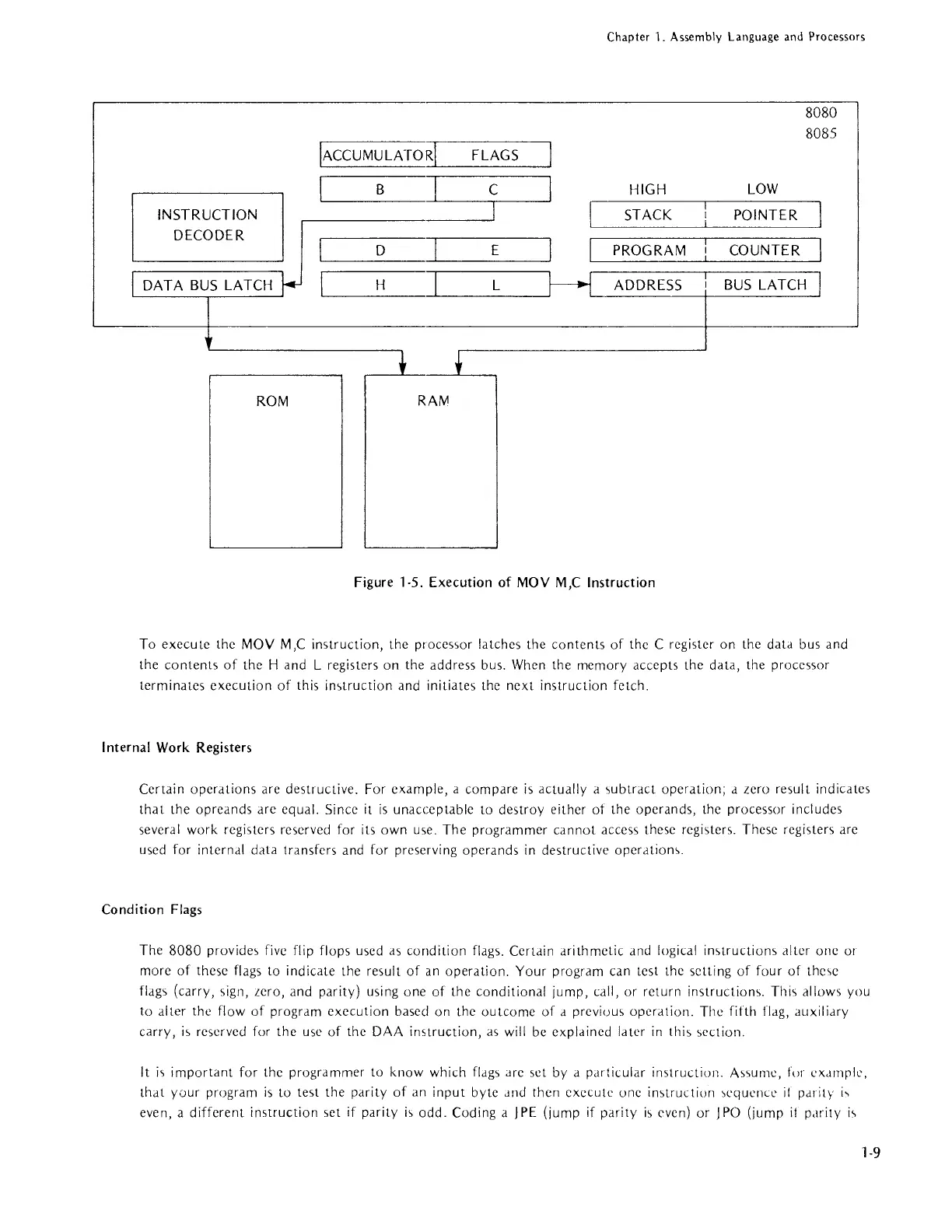
Figure 1-5. Execution
of
MOV
M,C
Instruction
To execute the
MOV
M,C
instruction, the processor latches the
contents
of
the C register on the data bus and
the
contents
of
the
Hand
L registers on the address bus. When the memory accepts the data, the processor
terminates execution
of
this in5truction and initiates the next instruction fetch.
Internal Work Registers
Certain operations are destructive. For example, a compare
is
actually a subtract operation; a zero result indicates
that
the opreands are equal. Since
it
is
unacceptable to destroy either of the operands, the processor includes
several work registers reserved for its own use. The programmer
cannot
access these registers. These registers are
used for internal
data transfers and for preserving operands
in
destructive operation5.
Condition
Flags
The
8080 provide5 five flip flops used as condition flags. Certain arithmetic and logical instructions alter
one
or
more
of
these flags to indicate the result
of
an
operation. Your program can test the setting
of
four
of
these
flags
(carry, sign, Lero, and parity) using one
of
the conditional jump, call, or return instruction5. This allows you
to alter the flow
of
program execution based on the
outcome
of
a previou5 operation. The fifth flag, auxiliJrY
carry,
i5
reserved for
the
usc
of
the DAA instruction,
as
will
be explained later
in
thi5 5ection.
It
i'i
important
for the programmer to know which
fldgs
Jre set by a pdrticular instruction.
A5'>urlle,
fur ex,lmpic,
that
your program
is
to test the parity
of
In
input byte Jnd then execute one instructiun 'ol'qUl'ncl'
il
pdrity i,
even, a different instruction set if parity
i5
odd. Coding a jPE (jump
if
parity
i5
even)
or
jPO (jump
il
parity
IS
1-9
 Loading...
Loading...