4-6 IRIS OWNER’S GUIDE
SERIES 3000 Version 1.0
Workstation Administration
sys:*:0:
system:*:0:
daemon:*:1:
bin:*:2:
adm:*:3:
sgi_use:
*
:4:
uucp:*:5:uucp
sgi_use:*:6:
sgi_use:*:7:
uucpadm:*:8:uucp
lp:*:9:
user:*:20:
vlsi:*:21:steve
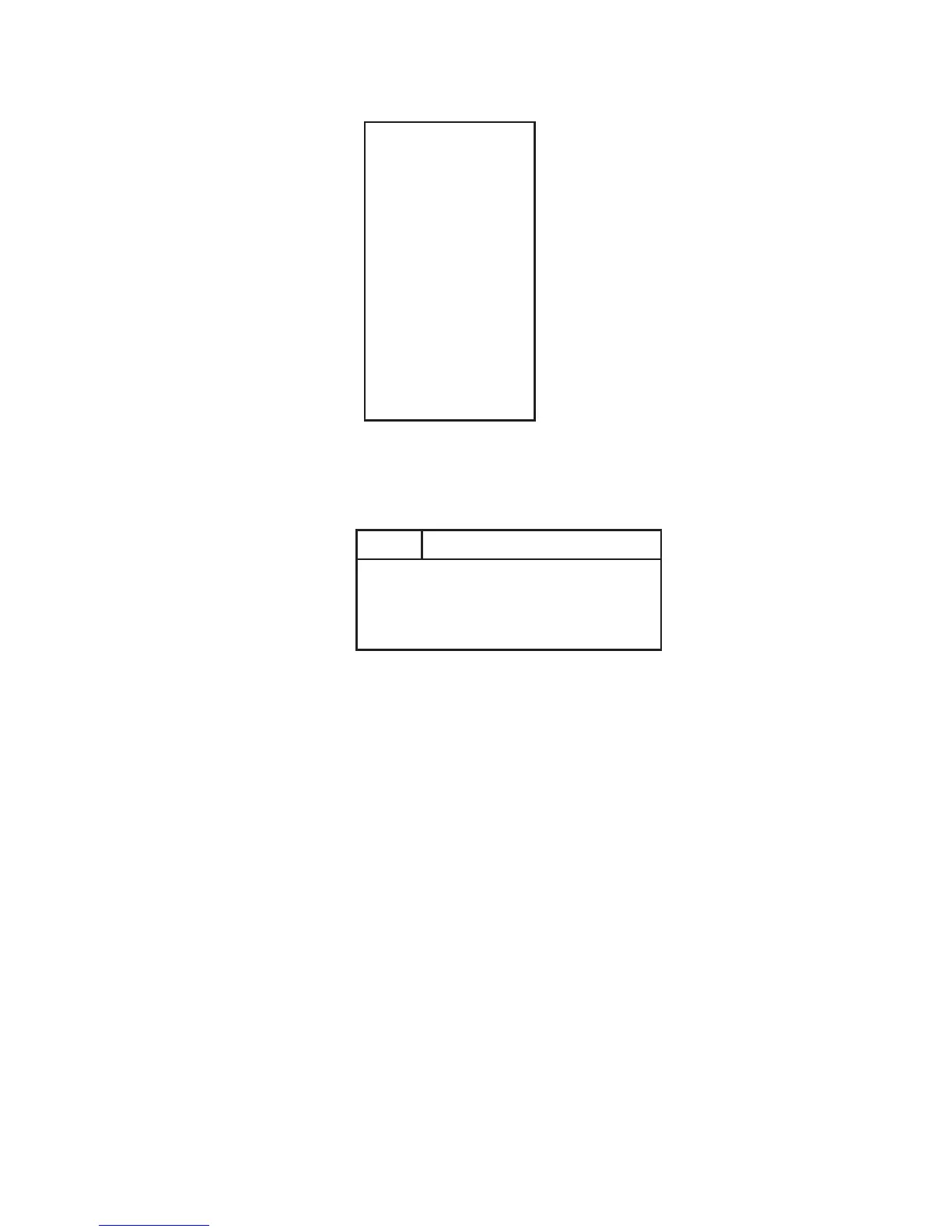
Figure 4-2: Sample /etc/group File
Figure 4-2 contains an example /etc/group file. The file contains a
line for each group on the system. Each line consists of four fields
separated by colons (:).
Field Contents
1
2
3
4
Group Name
Encrypted Group Password
Group Number
Group Members
To add a user to a group, append the user’s name to the list of group
members. Separate group members with commas. For example, to
add jose to the group vlsi, append the name jose to the line for the
group vlsi:
vlsi:*:21:steve,jose
4. The new user should log in and use the passwd command to establish
a password for the account. Issue the exit command to return to a
login shell if you are now the super-user.
passwd
New password: password
Re-enter new password: password
The password is encrypted and added to the file /etc/passwd.
If the user forgets his or her password, the encrypted password can
be removed from the user’s entry in /etc/passwd.
 Loading...
Loading...