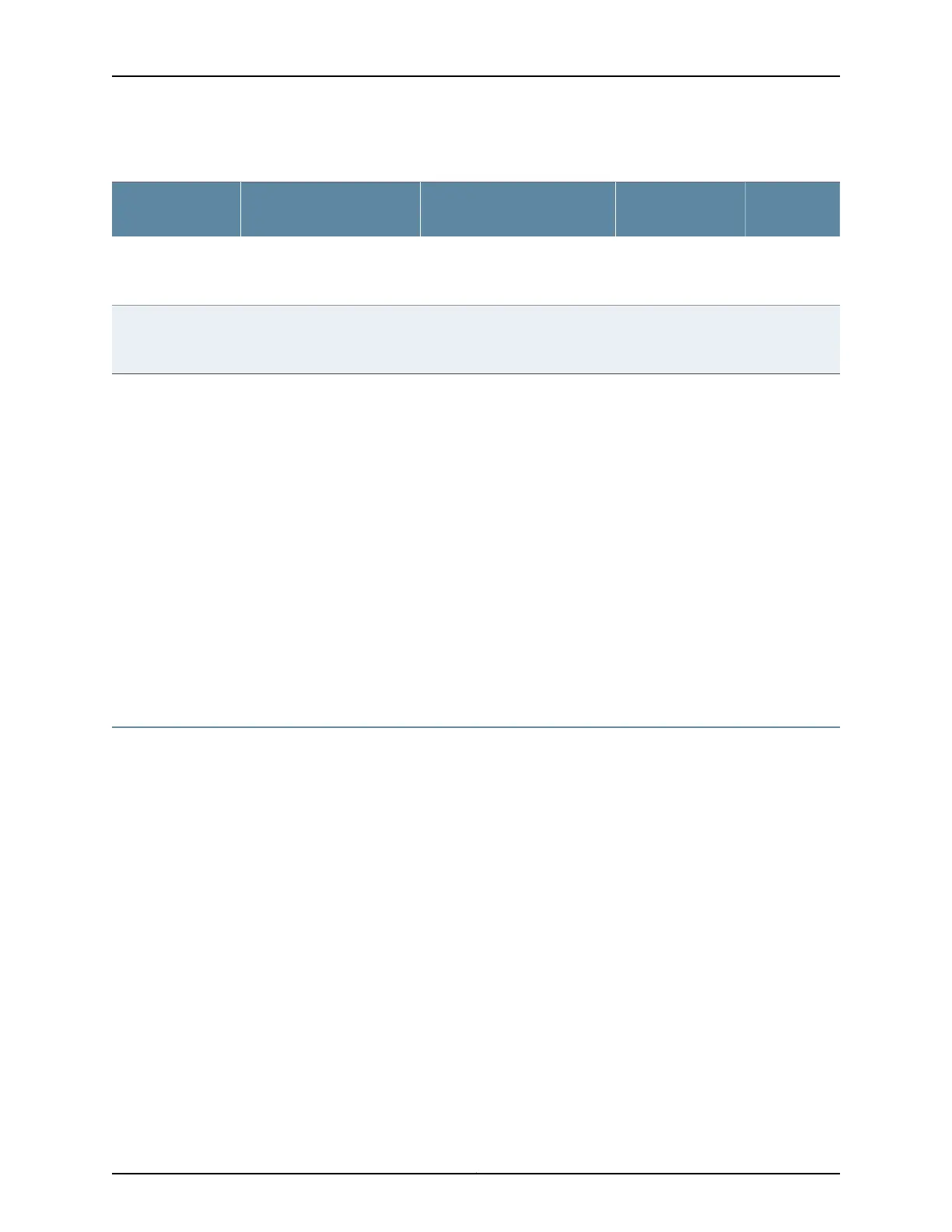
Table 28: Cable Specifications for Console and Management Connections for the QFX Series
Device
ReceptacleMaximum LengthCable SuppliedCable Specification
Porton QFX Series
Device
RJ-457 feet (2.13 meters)One 7-foot (2.13-meter) long
RJ-45 patch cable and RJ-45 to
DB-9 adapter
RS-232(EIA-232) serial cableConsole port
RJ-45328 feet
(100 meters)
One 7-foot (2.13-meter) long
RJ-45 patch cable
Category 5 cable or
equivalent suitable for
1000BASE-T operation
Management port
Related
Documentation
Console Port Connector Pinouts for the QFX Series•
• Management Port Connector Pinouts for the QFX Series
• Connecting a QFX Series Device to a Management Console
• Connecting a QFX3600 Device to a Network for Out-of-Band Management
• Connecting a QFX3500 Device to a Network for Out-of-Band Management
• Connecting a QFX3100 Director Device to a Network for Out-of-Band Management
• Connecting a QFX5100 Device to a Network for Out-of-Band Management
• Connecting a QFX5110 to a Network for Out-of-Band Management
• Connecting a QFX5200 to a Network for Out-of-Band Management
• Connecting a QFX5300 to a Network for Out-of-Band Management
Understanding QFX Series Fiber-Optic Cable Signal Loss, Attenuation, and Dispersion
To determine the power budget and power margin needed for fiber-optic connections,
you need to understand how signal loss, attenuation, and dispersion affect transmission.
The QFX Series uses various types of network cables, including multimode and
single-mode fiber-optic cables.
•
Signal Loss in Multimode and Single-Mode Fiber-Optic Cables on page 63
•
Attenuation and Dispersion in Fiber-Optic Cable on page 64
Signal Loss in Multimode and Single-Mode Fiber-Optic Cables
Multimode fiber is large enough in diameter to allow rays of light to reflect internally
(bounce off the walls of the fiber). Interfaces with multimode optics typically use LEDs
as light sources. However, LEDs are not coherent light sources. They spray varying
wavelengths of light into the multimode fiber, which reflect the light at different angles.
Light rays travel in jagged lines through a multimode fiber, causing signal dispersion.
When light traveling in the fiber core radiates into the fiber cladding (layers of lower
refractive index material in close contact with a core material of higher refractive index),
higher-order mode loss occurs. Together, these factors reduce the transmission distance
of multimode fiber compared to that of single-mode fiber.
63Copyright © 2017, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 7: Transceiver and Cable Specifications
 Loading...
Loading...











